Abstract
An atlas-based multimodal registration method for 2-dimension images with discrepancy structures was proposed in this paper. Atlas was utilized for complementing the discrepancy structure information in multimodal medical images. The scheme includes three steps: floating image to atlas registration, atlas to reference image registration, and field-based deformation. To evaluate the performance, a frame model, a brain model, and clinical images were employed in registration experiments. We measured the registration performance by the squared sum of intensity differences. Results indicate that this method is robust and performs better than the direct registration for multimodal images with discrepancy structures. We conclude that the proposed method is suitable for multimodal images with discrepancy structures.

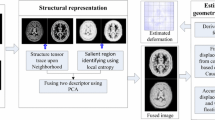
An Atlas-based multimodal registration method schematic diagram







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brainweb: Simulated brain database. http://brainweb.bic.mni.mcgill.ca/brainweb/
Mirt: Medical image registration toolbox. https://sites.google.com/site/myronenko/research/mirt
Alvén J, Norlén A, Enqvist O, Kahl F (2015) ÜBeratlas: robust speed-up of feature-based registration and multi-atlas segmentation. In: Scandinavian conference on image analysis. Springer, Berlin, pp 92–102
Arabi H, Zaidi H (2016) One registration multi-atlas-based pseudo-CT generation for attenuation correction in PET/MRI. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 43(11):2021–2035
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2005) Unified segmentation. Neuroimage 26(3):839–851
Avants BB, Tustison NJ, Stauffer M, Song G, Wu B, Gee JC (2014) The insight toolkit image registration framework. Front Neuroinform 8:44
Bai J, Trinh TLH, Chuang KH, Qiu A (2012) Atlas-based automatic mouse brain image segmentation revisited: model complexity vs. image registration. Magn Reson Imaging 30(6):789–798
Bai W, Shi W, O’Regan DP, Tong T, Wang H, Jamil-Copley S, Peters NS, Rueckert D (2013) A probabilistic patch-based label fusion model for multi-atlas segmentation with registration refinement: application to cardiac mr images. IEEE Trans sMed Imaging 32(7):1302–1315
Heinrich MP, Jenkinson M, Bhushan M, Matin T, Gleeson FV, Brady M, Schnabel JA (2012) Mind: modality independent neighbourhood descriptor for multi-modal deformable registration. Med Image Anal 16 (7):1423–1435
Kahl F, Alvén J, Enqvist O, Fejne F, Ulén J, Fredriksson J, Landgren M, Larsson V (2015) Good features for reliable registration in multi-atlas segmentation. Proceedings of the VISCERAL Challenge at ISBI 1390:12–17
Kallenberg M, Karssemeijer N (2012) Segmentation of the pectoral muscle in breast mri using atlas-based approaches. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, pp 371–8
Legg PA, Rosin PL, Marshall D, Morgan JE (2015) Feature neighbourhood mutual information for multi-modal image registration: an application to eye fundus imaging. Pattern Recogn 48(6):1937–1946
Lorenzo-Valdés M, Sanchez-Ortiz GI, Mohiaddin R, Rueckert D (2002) Atlas-based segmentation and tracking of 3d cardiac MR images using non-rigid registration. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention. Springer, Berlin, pp 642–650
Luan H, Qi F, Xue Z, Chen L, Shen D (2008) Multimodality image registration by maximization of quantitative–qualitative measure of mutual information. Pattern Recogn 41(1):285–298
Mattes D, Haynor DR, Vesselle H, Lewellen TK, Eubank W (2003) PET-CT image registration in the chest using free-form deformations. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 22(1):120–128
Oktay O, Gomez A, Keraudren K, Schuh A, Bai W, Shi W, Penney G, Rueckert D (2015) Probabilistic edge map (PEM) for 3D ultrasound image registration and multi-atlas left ventricle segmentation. In: International conference on functional imaging and modeling of the heart. Springer, Berlin, pp 223–230
Rivaz H, Collins DL (2012) Self-similarity weighted mutual information: a new nonrigid image registration metric. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, pp 91–8
Rubeaux M, Nunes JC, Albera L, Garreau M (2014) Medical image registration using Edgeworth-based approximation of mutual information. Irbm 35(3):139–148
Rueckert D, Sonoda LI, Hayes C, Hill DL, Leach MO, Hawkes DJ (1999) Nonrigid registration using free-form deformations: application to breast mr images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 18(8):712–721
Studholme C, Hill DL, Hawkes DJ (1999) An overlap invariant entropy measure of 3D medical image alignment. Pattern Recogn 32(1):71–86
Viola P, Wells III WM (1997) Alignment by maximization of mutual information. Int J Comput Vis 24(2):137–154
Wang F, Vemuri BC (2007) Non-rigid multi-modal image registration using cross-cumulative residual entropy. Int J Comput Vis 74(2):201–215
Wang F, Vemuri BC, Rao M, Chen Y (2003) Cumulative residual entropy, a new measure of information & its application to image alignment. In: Proceedings. Ninth IEEE international conference on Computer vision, 2003, IEEE, pp 548–553
Yang X, Wu N, Cheng G, Zhou Z, David SY, Beitler JJ, Curran WJ, Liu T (2014) Automated segmentation of the parotid gland based on atlas registration and machine learning: a longitudinal mri study in head-and-neck radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 90(5):1225–1233
Zhuang X, Shen J (2016) Multi-scale patch and multi-modality atlases for whole heart segmentation of MRI. Med Image Anal 31:77
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank L. Cao, J. Jv, and C. Xin for assisting in sorting data, and the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments.
Funding
This study was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant nos. 61571036, 61502025, 61771039) and Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission Major Program (SX2016-04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, W., Chen, H., Peng, Y. et al. An atlas-based multimodal registration method for 2D images with discrepancy structures. Med Biol Eng Comput 56, 2151–2161 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-018-1808-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-018-1808-1