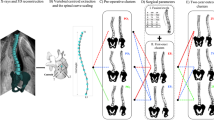
Abstract
While classification is important for assessing adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS), it however suffers from low interobserver and intraobserver reliability. Classification using ensemble methods may contribute to improving reliability using the proper 2D and 3D images of spine curvature features. In this study, we present two new techniques to describe the spine, namely, leave-one-out and fan leave-one-out. Using these techniques, three descriptors are computed from a stereoradiographic 3D reconstruction to describe the relationship between a vertebra and its neighbors. A dynamic ensemble selection method is introduced for automatic spine classification. The performance of the method is evaluated on a dataset containing 962 3D spine models categorized according to three curve types. With a log loss of 0.5623, the dynamic ensemble selection outperforms voting and stacking ensemble learning techniques. This method can improve intraobserver and interobserver reliability, identify the best combination of descriptors for characterizing spine curve types, and provide assistance to clinicians in the form of information to classify borderline curvature types.

ᅟ



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45:5–32. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010933404324
Britto AS, Sabourin R, Oliveira LES (2014) Dynamic selection of classifiers—a comprehensive review. Pattern Recogn 47:3665–3680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2014.05.003
Delorme S, Petit Y, De Guise JA, Labelle H, Aubin C-E, Dansereau J (2003) Assessment of the 3-d reconstruction and high-resolution geometrical modeling of the human skeletal trunk from 2-D radiographic images. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 50:989–998. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2003.814525
Dietterich TG (2000) Ensemble methods in machine learning. In: Multiple classifier systems. MCS 2000. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 1857. Springer, Berlin
Donzelli S, Poma S, Balzarini L, Borboni A, Respizzi S, Villafane JH, Zaina F, Negrini S (2015) State of the art of current 3-D scoliosis classifications: a systematic review from a clinical perspective. J Neuroeng Rehabil 12:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12984-015-0083-8
Duong L, Cheriet F, Labelle H (2006) Three-dimensional classification of spinal deformities using fuzzy clustering. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 31:923–930. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.brs.0000209312.62384.c1
Duong L, Mac-Thiong J-M, Cheriet F, Labelle H (2009) Three-dimensional subclassification of Lenke type 1 scoliotic curves. J Spinal Disord Tech 22:135–143. https://doi.org/10.1097/BSD.0b013e31816845bc
Duong L, Cheriet F, Labelle H (2010) Automatic classification of spinal deformities using support vector machines. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 57:1143–1151
Fernández-Delgado M, Cernadas E, Barro S, Amorim D (2014) Do we need hundreds of classifiers to solve real world classification problems? J Mach Learn Res 15:3133–3181
Garcia-Cano E, Arambula-Cosio F, Duong L, Bellefleur C, Roy-Beaudry M, Joncas J, Parent S, Labelle H (2016) Dynamic ensemble selection of learner-descriptor classifiers to assess curve types in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis : a preliminary study. Communication lors de la conférence : 46e Réunion Annuelle de la Société de la Scoliose du Québec, Estérel, QC, Canada, 20–22 Oct. 2016
Kadoury S, Labelle H (2012) Classification of three-dimensional thoracic deformities in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis from a multivariate analysis. Eur Spine J 21:40–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-011-2004-2
Kadoury S, Shen J, Parent S (2014) Global geometric torsion estimation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Med Biol Eng Comput 52:309–319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-013-1132-8
King HA, Moe JH, Bradford DS, Winter RB (1983) The selection of fusion levels in thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 65:1302–1313
Kittler J, Hatef M, Duin RPW, Matas J (1998) On combining classifiers. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 20:226–239. https://doi.org/10.1109/34.667881
Ko AHR, Sabourin R, Britto AS (2008) From dynamic classifier selection to dynamic ensemble selection. Pattern Recogn 41:1735–1748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2007.10.015
Lenke LG, Betz RR, Harms J, Bridwell KH, Clements DH, Lowe TG, Blanke KM (2001) Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. A new classification to determine extent of spinal arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 83–A:1169–1181
Pedregosa F, Varoquaux G, Gramfort A, Michel V, Thirion B, Grisel O, Blondel M, Prettenhofer P, Weiss R, Dubourg V, Vanderplas J, Passos A, Cournapeau D, Brucher M, Perrot M, Duchesnay E (2011) Scikit-learn: machine learning in Python. J Mach Learn Res 12:1825–2830
Phan P, Mezghani N, Wai EK, De Guise JA, Labelle H (2013) Artificial neural networks assessing adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: comparison with Lenke classification. Spine J 13:1527–1533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2013.07.449
Sangole AP, Aubin C-E, Labelle H, Stokes IAF, Lenke LG, Jackson R, Newton PO (2009) Three-dimensional classification of thoracic scoliotic curves. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 34:91–99. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181877bbb
Shen J, Parent S, Kadoury S (2014) Classification of spinal deformities using a parametric torsion estimator. In: Yao J, Klinder T, Li S (eds) Computational methods and clinical applications for spine imaging. Lecture Notes in Computational Vision and Biomechanics, vol 17. Springer, Cham
Stokes IAF (1994) Three-dimensional terminology of spinal deformity. A report presented to the Scoliosis Research Society by the Scoliosis Research Society Working Group on 3-D terminology of spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 19:236–248
Stokes IA, Bigalow LC, Moreland MS (1986) Measurement of axial rotation of vertebrae in scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 11:213–218. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007632-198604000-00006
Thong WE, Labelle H, Shen J, Parent S, Kadoury S (2015) Stacked auto-encoders for classification of 3D spine models in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. In: Yao J, Glocker B, Klinder T, Li S (eds) Recent advances in computational methods and clinical applications for spine imaging. Lecture Notes in Computational Vision and Biomechanics, vol 20. Springer, Cham
Thong W, Parent S, Wu J, Aubin C-E, Labelle H, Kadoury S (2016) Three-dimensional morphology study of surgical adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patient from encoded geometric models. Eur Spine J 25:3104–3113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4426-3
Woźniak M, Graña M, Corchado E (2014) A survey of multiple classifier systems as hybrid systems. Information Fusion 16:3–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2013.04.006
Acknowledgments
A preliminary short abstract of this work was presented in [10].
Funding
This research was funded by CONACYT CVU 323619 in Mexico, Fonds de recherche du Québec – Nature et technologies (FRQNT), file 194703, and the Ministère des Relations internationales et de la Francophonie.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García-Cano, E., Arámbula Cosío, F., Duong, L. et al. Dynamic ensemble selection of learner-descriptor classifiers to assess curve types in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Med Biol Eng Comput 56, 2221–2231 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-018-1853-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-018-1853-9