Abstract
As a basic osteotomy technique, U osteotomy can be applied for certain complex foot and ankle deformities. Gradual correction cases using Ilizarov apparatus and Taylor Spatial Frame have been reported. This paper proposes a novel parallel distraction apparatus for U osteotomy (PDA-Uos) to supplement the correction equipment for surgeon. Designed with an adjustable structure, the PDA-Uos can adopt different assembly shapes (joint connection points). However, the influence of the change in assembly shape on interference-free workspace and self-structural performance of the external fixator have received little attention. To address this issue and enhance the selection of the most suitable assembly shape for patient, an algorithm to obtain the interference-free workspace of different assembly shapes is proposed based on the inverse position solution of the PDA-Uos. Additionally, correction ability indices are defined according to the requirements of accurately controlled motion and high structural stiffness of the external fixator along the correction path. The results of simulation cases indicate that the interference-free workspace and the correction ability vary according to the assembly shape and thus the proposed method can be used to select an assembly shape with sufficient workspace and the best correction ability before performing correction for a given patient.

Graphical abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
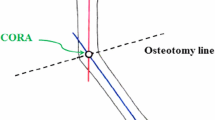
- CORA:
-
center of rotation of angulation
- CPMA:
-
correction path motion ability
- CPSA:
-
correction path stiffness ability
- DDMA:
-
directional distraction motion ability
- DDSA:
-
directional distraction stiffness ability
- DOF:
-
degrees of freedom
- EFRA:
-
external force resistance ability
- OSF:
-
Ortho-SUV frame
- PDA-Uos:
-
parallel distraction apparatus for U osteotomy
- ROM:
-
range of motion
- TSF:
-
Taylor Spatial Frame™
- U-P-S:
-
universal–prismatic–spherical
References
Ramlee MH, Derus A (2016) The use of external fixator for ankle and foot injuries management-a review on biomechanical perspective. Med Dev Diagn Eng 1:5–10
Takata M, Vilensky VA, Tsuchiya H, Solomin LN (2013) Foot deformity correction with hexapod external fixator, the Ortho-SUV frame. J Foot Ankle Surg 52:324–330
Grant AD, Atar D, Lehman WB (1992) The Ilizarov technique in correction of complex foot deformities. Clin Orthop Relat Res:94–103
Kocaoglu M, Eralp L, Atalar AC, Bilen FE (2002) Correction of complex foot deformities using the Ilizarov external fixator. J Foot Ankle Surg 41:30–39
Kucukkaya M, Kuzgun U (2009) Neuromuscular deformity: treatment with external fixation. Foot Ankle Clin N Am 14:447–470
Conway JD (2008) Charcot salvage of the foot and ankle using external fixation. Foot Ankle Clin N Am 13:157–173
Lamn BM, Standard SC, Galley IJ, Herzenberg JE, Paley D (2006) External fixation for the foot and ankle in children. Clin Podiatr Med Surg 23:137–166
Beaman DN, Gellman R (2008) The basics of ring external fixator application and care. Foot Ankle Clin N Am 13:15–27
Hosny GA (2002) Correction of foot deformities by the Ilizarov method without corrective osteotomies or soft tissue release. J Pediatr Orthoped 11:121–128
Shalaby H, Hefny H (2007) Correction of complex foot deformities using the V-osteotomy and the Ilizarov technique. Strat Traum Limb Recon 2:21–30
Tecimel O, Ocguder DA, Dogan M, Ugurlu M, Bozkurt M, Atesalp S (2013) Ilizarov external fixator for correction of complex foot deformities. Eklem Hast Cerrahisi 24:72–76
Elmowafi H (2004) Assessment of percutaneous V osteotomy of the calcaneus with Ilizarov application for correction of complex foot deformities. Acta Orthop Belg 70:586
Paley D (1993) The correction of complex foot deformities using Ilizarov’s distraction osteotomies. Clin Orthop Relat Res:97–111
Gourdine-Shaw MC, Lamm BM, Paley D, Herzenberg JE (2012) Distraction osteogenesis for complex foot deformities: U-osteotomy with external fixation. J Bone Joint Surg 94:1420
Lamm BM, Paley D, Testani M, Herzenberg JE (2007) Tarsal tunnel decompression in leg lengthening and deformity correction of the foot and ankle. J Foot Ankle Surg 46:201–206
Dhar S (2010) Ilizarov external fixation in the correction of severe pediatric foot and ankle deformities. Foot Ankle Clin 15:265–285
Ilizarov GA, Shevtsov VI, Shestakov VA, Kuzmin NV (1987) Treatment of foot deformities in adults using transosseous osteosynthesis with the Ilizarov frame. KNIIEKOT Institute, Kurgan
Mendicino RW, Murphy LJ, Maskill MP, Catanzariti AR, Penny H (2008) Application of a constrained external fixator frame for treatment of a fixed equinus contracture. J Foot Ankle Surg 47:468–475
Floerkemeier T, Stukenborg-Colsman C, Windhagen H, Waizy H (2011) Correction of severe foot deformities using the Taylor spatial frame. Foot Ankle Int 32:176–182
Burns JK, Sullivan R (2004) Correction of severe residual clubfoot deformity in adolescents with the Ilizarov technique. Foot Ankle Clin N Am 9:571–582
Eidelman M, Katzman A (2011) Treatment of arthrogrypotic foot deformities with the Taylor spatial frame. J Pediatr Orthoped 31:429–434
Horn DM, Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR (2011) Supramalleolar osteotomy using circular external fixation with six-axis deformity correction of the distal tibia. Foot Ankle Int 32:986–993
Nomura I, Watanabe K, Matsubara H, Nishida H, Shirai T, Tsuchiya H (2014) Correction of a severe poliomyelitic equinocavovarus foot using an adjustable external fixation frame. J Foot Ankle Surg 53:235–238
Wukich DK, Belczyk RJ (2006) An introduction to the Taylor spatial frame for foot and ankle applications. Oper Tech Orthop 16:2–9
Shenoy R, Kubicek G, Pearse M (2011) The Taylor spatial frame for correction of neglected fracture dislocation of the ankle. J Foot Ankle Surg 50:736–739
Paley D (2005) Principles of deformity correction. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 177–193
Kurtz R, Hayward V (1992) Multiple-goal kinematic optimization of a parallel spherical mechanism with actuator redundancy. IEEE Trans Robot Autom 8:644–651
Wu J, Wang J, Li T, Wang L (2007) Analysis and application of a 2-DOF planar parallel mechanism. J Mech Des 129:434–437
Ng C, Ong S, Nee A (2006) Design and development of 3-DOF modular micro parallel kinematic manipulator. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 31:188–200
Enferadi J, Nikrooz R (2017) The performance indices optimization of a symmetrical fully spherical parallel mechanism for dimensional synthesis. J Intell Robot Syst pp:1–17
Turner CH (1998) Three rules for bone adaptation to mechanical stimuli. Bone 23:399–407
Ilizarov GA (1987) The principles of the Ilizarov method. Bull Hosp Jt Dis Orthop Inst 48:1–11
Ilizarov GA (1989) The tension-stress effect on the genesis and growth of tissues, part I: the influence of stability of fixation and soft tissue preservation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 238:249–281
Ilizarov GA (1989) The tension-stress effect on the genesis and growth of tissues, part II: the influence of the rate and frequency of distraction. Clin Orthop Relat Res 239:263–285
Chao EY, Kasman RA, An KN (1982) Rigidity and stress analyses of external fracture fixation devices-a theoretical approach. J Biomech 15:971–983
Nielsen JK, Saltzman CL, Brown TD (2005) Determination of ankle external fixation stiffness by expedited interactive finite element analysis. J Orthop Res 23:1321–1328
Henderson DJ, Rushbrook JL, Stewart TD, Harwood PJ (2016) What are the biomechanical effects of half-pin and fine-wire configurations on fracture site movement in circular frames? Clin Orthop Relat Res 474:1041–1049
Yang L, Saleh M, Nayagam S (2000) The effects of different wire and screw combinations on the stiffness of a hybrid external fixator. In Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine 214:669–676
Baran O, Havitcioglu H, Tatari H, Cecen B (2008) The stiffness characteristics of hybrid Ilizarov fixators. J Biomech 41:2960–2963
Lee MG, Chung K, Lee CJ, Park JH, Kim J, Kang TJ, Youn JR (2001) The viscoelastic bending stiffness of fiber-reinforced composite Ilizarov C-rings. Compos Sci Technol 61:2491–2500
Bronson DG, Samchukov ML, Birch JG, Browne RH, Ashman RB (1998) Stability of external circular fixation: a multi-variable biomechanical analysis. Clin Biomech 13:441–448
Gessmann J, Baecker H, Jettkant B, Muhr G, Seybold D (2011) Direct and indirect loading of the Ilizarov external fixator: the effect on the interfragmentary movements and compressive loads. Strat Traum Limb Recon 6:27–31
Gessmann J, Citak M, Jettkant B, Schidhauer TA, Seybold D (2011) The influence of a weight-bearing platform on the mechanical behavior of two Ilizarov ring fixators: tensioned wires vs. half-pins. J Orthop Surg Res 6:61
Waizy H, Windhagen H, Stukenborg-Colsman C, Floerkemeier T (2011) Taylor spatial frame in severe foot deformities using double osteotomy: technical approach and primary results. Int Orthop 35:1489–1495
Kirienko A, Villa A, Calhoun JH (2003) Ilizarov technique for complex foot and ankle deformities. Marcel Decker, New York, Basel, pp 59–84
Zhang X, Sun H, Chen J, Guo Y, Zhang Y, Sun Z, Wang T, Wei M, Zhang Y, Chen L (2019) Optimization of electronic prescription for parallel external fixator based on genetic algorithm. Int J Comput Ass Rad 14:861–871
Li J, Li S, Zhang L, Tao C, Ji R (2018) Position solution and kinematic interference analysis of a novel parallel hip-assistive mechanism. Mech Mach Theory 120:265–287
Rajacich N, Bell DF, Armstrong PF (1992) Pediatric applications of the Ilizarov method. Clin Orthop Relat Res 280:72–80
Iyun O, Borschneck DP, Ellis RE (2002) Computer-assisted correction of bone deformities using a 6-DOF parallel spatial mechanism. International Conference on Medical Image Computing & Computer-assisted Intervention. Springer-Verlag
Simpson AL, Ma B, Slagel B, Borschneck DP, Ellis RE (2008) Computer-assisted distraction osteogenesis by Ilizarov’s method. Int J Med Robotics Comput Assist Surg 4:310–320
Corona PS, Vicente M, Tetsworth K, Glatt V (2018) Preliminary results using patient-specific 3d printed models to improve preoperative planning for correction of post-traumatic tibial deformities with circular frames. Injury 49:S51–S59
Lee DJ, Yoon T, Lee C (2016) A study on the posture based control of robotic fixation device. Int J Appl Eng Res 11:6655–6659
Du H, Hu L, Li C, Wang T, Zhao L, Li Y, Mao Z, Liu D, Zhang L, He C, Zhang L, Hou H, Zhang L, Tang P (2015) Advancing computer-assisted orthopaedic surgery using a hexapod device for closed diaphyseal fracture reduction. Int J Med Robot Comp 11:348–359
Skomoroshko PV, Vilensky VA, Hammouda AI, Fletcher MDA, Solomin LN (2014) Determination of the maximal corrective ability and optimal placement of the Ortho-SUV frame for femoral deformity with respect to the soft tissue envelope, a biomechanical modelling study. Adv Orthop 2014:268567–268567
Ramlee MH, Sulong MA, Garcia-Nieto E, Penaranda DA, Felip AR, Kadir MRA (2018) Biomechanical features of six design of the delta external fixator for treating Pilon fracture: a finite element study. Med Biol Eng Comput 56:1–14
Seide K, Faschingbauer M, Wenzl ME, Weinrich N, Juergens C (2004) A hexapod robot external fixator for computer assisted fracture reduction and deformity correction. Int J Med Robot Comp 1:64–69
Faschingbauer M, Heuer HJD, Seide K, Wendlandt R, Munch M, Jurgens C, Kirchner R (2014) Accuracy of a hexapod parallel robot kinematics based external fixator. Int J Med Robot Comp 11:424–435
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants No. 51675008 and No. 51705007 and the Beijing Natural Science Foundation under Grants No. 3171001 and No. 17 L20019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zuo, S., Dong, M., Li, J. et al. Configuration design and correction ability evaluation of a novel external fixator for foot and ankle deformity treated by U osteotomy. Med Biol Eng Comput 58, 541–558 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-019-02103-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-019-02103-w