Abstract
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) refers to a group of various abnormal inflammations of lung tissues and early diagnosis of these disease patterns is crucial for the treatment. Yet it is difficult to make an accurate diagnosis due to the similarity among the clinical manifestations of these diseases. In order to assist the radiologists, computer-aided diagnosis systems have been developed. Besides, the potential of deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) is also expected to exert on the medical image analysis in recent years. In this paper, we design a new deep convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture to achieve the classification task of ILD patterns. Furthermore, we also propose a novel two-stage transfer learning (TSTL) method to deal with the problem of the lack of training data, which leverages the knowledge learned from sufficient textural source data and auxiliary unlabeled lung CT data to the target domain. We adopt the unsupervised manner to learn the unlabeled data, by which the objective function composed of the prediction confidence and mutual information are optimized. The experimental results show that our proposed CNN architecture achieves desirable performance and outperforms most of the state-of-the-art ones. The comparative analysis demonstrates the promising feasibility and advantages of the proposed two-stage transfer learning strategy as well as the potential of the knowledge learning from lung CT data.

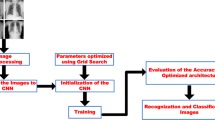
The framework of the proposed two-stage transfer learning method.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altaf F, Islam S, Akhtar N, Janjua NK (2019) Going deep in medical image analysis: Concepts, methods, challenges and future directions. arXiv:1902.05655
Anthimopoulos M, Christodoulidis S, Ebner L, Christe A, Mougiakakou S (2016) Lung pattern classification for interstitial lung diseases using a deep convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans Med Imag 35 (5):1207–1216
Aziz ZA, Wells AU, Hansell DM, Bain G, Copley SJ, Desai SR, Ellis SM, Gleeson FV, Grubnic S, Nicholson AG, et al. (2004) Hrct diagnosis of diffuse parenchymal lung disease: inter-observer variation. Thorax 59(6):506–511
Azizpour H, Razavian AS, Sullivan J, Maki A, Carlsson S (2016) Factors of transferability for a generic ConvNet representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 38(9):1790–1802
Chen G, Zhang J, Zhuo D, Pan Y, Pang C (2019) Identification of pulmonary nodules via CT images with hierarchical fully convolutional networks. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing:1–14
Cheplygina V, Pena IP, Pedersen JH, Lynch DA, Sørensen L., de Bruijne M (2018) Transfer learning for multicenter classification of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. IEEE J Biomed Health Informat 22 (5):1486–1496
Christodoulidis S, Anthimopoulos M, Ebner L, Christe A, Mougiakakou S (2017) Multisource transfer learning with convolutional neural networks for lung pattern analysis. IEEE J Biomed Health Informat 21(1):76–84
Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li LJ, Li K, Fei-Fei L (2009) Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit
Depeursinge A, Vargas A, Platon A, Geissbuhler A, Poletti PA, Müller H. (2012) Building a reference multimedia database for interstitial lung diseases. Comput Med Imag Graph 36(3):227–238
Gao M, Bagci U, Lu L, Wu A, Buty M, Shin HC, Roth H, Papadakis GZ, Depeursinge A, Summers RM (2015) Holistic classification of ct attenuation patterns for interstitial lung diseases via deep convolutional neural networks. 1st Workshop Deep Learn. Med. Image Anal:41–48
Guo W, Xu Z, Zhang H (2018) Interstitial lung disease classification using improved densenet. Multimed Tools Appl:1–12
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit, pp 770–778
Hinton GE, Salakhutdinov RR (2006) Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science 313(5786):504–507
Hjelm RD, Fedorov A, Lavoie-Marchildon S, Grewal K, Trischler A, Bengio Y (2018) Learning deep representations by mutual information estimation and maximization. arXiv:1808.06670
Huang G, Liu Z, Van Der Maaten L, Weinberger KQ (2017) Densely connected convolutional networks. In: Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit, pp 4700–4708
Kingma DP, Ba J (2014) Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. arXiv:1412.6980
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proc Adv Neural Inf Process Syst, pp 1097–1105
Kylberg G (2011) The Kylberg texture dataset v. 1.0, centre for image analysis, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences and Uppsala University, external report (blue series) no 35
LeCun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, Haffner P, et al. (1998) Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc IEEE 86(11):2278–2324
Li Q, Cai W, Wang X, Zhou Y, Feng DD, Chen M (2014) Medical image classification with convolutional neural network. In: Proc 13th Int Conf Control Automat Robot Vis. IEEE, pp 844–848
Litjens G, Kooi T, Bejnordi BE, Setio AAA, Ciompi F, Ghafoorian M, Van Der Laak JA, Van Ginneken B, Sánchez CI (2017) A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med Imag Anal 42:60–88
Lu Y, Chen L, Saidi A (2017) Optimal transport for deep joint transfer learning. arXiv:1709.02995
O’Neil A, Shepherd M, Beveridge E, Goatman K (2017) A comparison of texture features versus deep learning for image classification in interstitial lung disease. In: Proc Ann Conf Med Imag Und Anal. Springer, pp 743–753
Pan SJ, Yang Q (2010) A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 22(10):1345–1359
Pang S, Du A, Orgun MA, Yu Z (2019) A novel fused convolutional neural network for biomedical image classification. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing 57(1):107–121
Paszke A, Gross S, Chintala S, Chanan G, Yang E, DeVito Z, Lin Z, Desmaison A, Antiga L, Lerer A (2017) Automatic differentiation in pytorch
Samala RK, Chan HP, Hadjiiski L, Helvie MA, Richter CD, Cha KH (2018) Breast cancer diagnosis in digital breast tomosynthesis: effects of training sample size on multi-stage transfer learning using deep neural nets. IEEE Trans Med Imag
Sharif Razavian A, Azizpour H, Sullivan J, Carlsson S (2014) Cnn features off-the-shelf: an astounding baseline for recognition. In: Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit, pp. 806–813
Shin HC, Roth HR, Gao M, Lu L, Xu Z, Nogues I, Yao J, Mollura D, Summers RM (2016) Deep convolutional neural networks for computer-aided detection: CNN architectures, dataset characteristics and transfer learning. IEEE Trans Med Imag 35(5):1285–1298
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv:1409.1556
Sluimer I, Schilham A, Prokop M, Van Ginneken B (2006) Computer analysis of computed tomography scans of the lung: a survey. IEEE Trans Med Imag 25(4):385–405
Society B, Committee S (1999) The diagnosis, assessment and treatment of diffuse parenchymal lung disease in adults. Thorax 54(Suppl 1):S1–S28
Suzuki A, Sakanashi H, Kido S, Shouno H (2018) Feature representation analysis of deep convolutional neural network using two-stage feature transfer-an application for diffuse lung disease classification. arXiv:1810.06282
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Vanhoucke V, Rabinovich A (2015) Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit, pp 1–9
Tajbakhsh N, Shin JY, Gurudu SR, Hurst RT, Kendall CB, Gotway MB, Liang J (2016) Convolutional neural networks for medical image analysis: full training or fine tuning. IEEE Trans Med Imag 35 (5):1299–1312
Tan B, Zhang Y, Pan SJ, Yang Q (2017) Distant domain transfer learning. In: Proc. 31th AAAI Conf Artif Intell
Tarando SR, Fetita C, Faccinetto A, Brillet PY (2016) Increasing cad system efficacy for lung texture analysis using a convolutional network. In: Medical imaging 2016: Computer-aided diagnosis, vol 9785, p 97850Q
Van Ginneken B, Armato S.G III, de Hoop B, van Amelsvoortvan de Vorst S, Duindam T, Niemeijer M, Murphy K, Schilham A, Retico A, Fantacci ME, et al. (2010) Comparing and combining algorithms for computer-aided detection of pulmonary nodules in computed tomography scans: the ANODE09 study. Med Imag Anal 14(6):707–722
Wei X, Chen J, Cai C (2017) Using deep convolutional neural networks and transfer learning for mammography mass lesion classification. J Comput Theor Nanos 14(8):3802–3806
Yap MH, Pons G, Martí J, Ganau S, Sentís M, Zwiggelaar R, Davison AK, Martí R (2018) Automated breast ultrasound lesions detection using convolutional neural networks. IEEE J Biomed Health Informat 22(4):1218–1226
Yosinski J, Clune J, Bengio Y, Lipson H (2014) How transferable are features in deep neural networks?. In: Proc Adv Neural Inf Process Syst, pp 3320–3328
Zheng L, Zhao Y, Wang S, Wang J, Tian Q (2016) Good practice in CNN feature transfer. arXiv:1604.00133
Zhuang F, Cheng X, Luo P, Pan SJ, He Q (2015) Supervised representation learning: transfer learning with deep autoencoders. In: Proc 24th Int Conf Artif Intell
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Sheng Huang and Feifei Lee contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, S., Lee, F., Miao, R. et al. A deep convolutional neural network architecture for interstitial lung disease pattern classification. Med Biol Eng Comput 58, 725–737 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-019-02111-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-019-02111-w