Abstract
Purpose
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE) is a common pediatric orthopedic disorder that requires surgical correction. Preoperative planning of a proximal femoral osteotomy is essential in cases of SCFE. This planning is usually done using 2D radiographs, but 3D data can be acquired with CT and analyzed with 3D visualization software.
Materials and methods
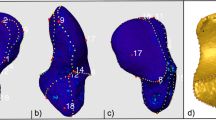
SCFEanalyzer is a computer program developed for preoperative planning of proximal femoral osteotomy to correct SCFE. Computed tomography scans were performed on human bone specimens: one pelvis and two femoral bones (right and left) and volume data of a patient. The CT data were used to test the abilities of the SCFEanalyzer software, which utilizes 3D virtual models of anatomic structures constructed from CT image data. Separation of anatomical bone structures is done by means of “cutting” 3D surface model of the pelvis. The software enables qualitative and quantitative spatial analysis of chosen parameters analogous to those done on the basis of plain radiographs. SCFEanalyzer makes it possible to evaluate the function of the hip joint by calculating the range of motion depending on the shape of bone structures based on oriented bounding box object representation.
Results
Pelvic and hip CT scans from a patient with SCFE were subjected to femoral geometry analysis and hip joint function assessment. These were done to plan and simulate osteotomy of the proximal femur. Analogous qualitative and quantitative evaluation after performing the virtual surgery were evaluated to determine the potential treatment effects.
Conclusion
The use of computer assistance in preoperative planning enable us to increase objectivity and repeatability, and to compare the results of different types of osteotomy on the proximal femur, and thus to choose the optimal operation in each individual case.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rippstein J (1955) Zur Bestimmung der Antetorsion des Schenkelhalses mittels zweier Roentgenaufnahmen. Z Orthop 86: 345–360
Dunlap K, Shands AR, Hollister LC, Gaul SJ, Streit HA (1953) A new method for determination of torsion of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg A-35: 289–311
Lauenstein C (1901) Nachweis der Kocherschen Verbiegungs des Shenkelhalses bei der Coxa vara durch Roentgen-Strahlen. Fortschr Geb Roentgenstrahlen 4: 61–64
Richard G (1950) Methodik der Torsionsbestimmung mit Hilfe des Roentgenbildes. Z Orthop 79: 636–644
Kordelle J, Millis M, Jolesz FA, Kikinis R, Richolt JA (2001) Three-dimensional analysis of the proximal femur in patients with slipped capital femoral epiphysis based on the computed tomography. J Pediatr Orthop 21: 179–182 doi:10.1097/00004694-200103000-00009
Richolt JA, Everett E, Teschner M, Kikinis R, Millis MB (2000) Computerassistierte Plannung von Umstellungsosteoto-mien in Faellen von Epiphysiolysis capitis femoris. Orthopaede 29: 599–604
Richolt JA, Teschner M, Everett P, Girod B, Millis M, Kikinis R (1998) Planning and evaluation of reorienting osteotomies of the proximal femur in cases of SCFE using virtual three-dimensional models. LNCS 1496: 1–8
DiGioia A, Jaramaz B, Colgan BD (1998) Computer assisted orthopaedic surgery: image guided and robotic assistive technologies. Clin Orthop Relat Res 354: 8–16
DiGioia A, Jaramaz B (1999) Computer-assisted tools and interventional technologies. Lancet 354: 46 doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(99)90389-6
Sikorski JM, Chauhan S (2003) Computer-assisted orthopaedic surgery: Do we need caos? J Bone Joint Surg Br 85: 319–323 doi:10.1302/0301-620X.85B3.14212
Terzopoulos D, Fleisher K (1988) Deformable models. Vis Comput 4: 306–331 doi:10.1007/BF01908877
Southwick WO (1967) Osteotomy through the lesser trochanter for slipped capital femoral epiphysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 49: 807–835
Imhäuser G (1957) Zur Pathogenese und Therapie der jugendlichen Hûftkopflösung. Z Orthop 88: 3–41
Kramer WG, Craig WA, Noel S (1976) Compensating osteotomy at the base of the femoral neck for slipped capital femoral epiphysis. J Bone Joint Surg 58-A: 796–800
Fish JB (1984) Cuneiform osteotomy of the femoral neck in the treatment of slipped capital femoral epiphysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 66-A: 1153–1168
Schroeder W, Martin K, Lorensen M (1997) The Visualization Toolkit, an object-oriented approach to 3D graphics. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Strzelecki M (2003) Surface modeling in medical applications, Master thesis, Poznan University of Technology
Czwojdziñski A, Czubak J, Drapikowski P, Pietrzak S (2004) The attempt of using of computer assisted orthopedic surgery in the pre-operative evaluation and the treatment of diseases of the hip. Conference book of XXIII meeting of the European Paediatric Orthopaedic Society (EPOS), Geneva 31 March–3 April 2004, p 67
Gottschalk S, Lin MC, Manocha D (1996) OBB-tree: A hierarchical structure for rapid interference detection. SIGGRAPH, pp 171–180
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The application of computer assistance in planning osteotomy of the proximal femur in cases of SCFE.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Drapikowski, P., Tyrakowski, M., Czubak, J. et al. Computer assisted SCFE osteotomy planning. Int J CARS 3, 421–426 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-008-0248-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-008-0248-z