Abstract
Objective
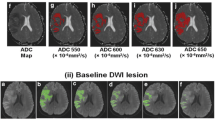
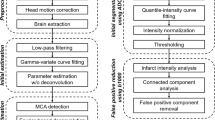
Fast, accurate and automatic segmentation of acute ischemic stroke lesions is important for clinical trials and has potential for efficient stroke management. To identify stroke slices, stroke hemisphere, and segment stroke regions in diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DWI), divergence based algorithms are proposed.
Materials and methods
The study used 57 DWI volumes with inter 0.94–2.42 mm and intra 5–14 mm plane resolutions. We used ratio of intensity probability density functions (pdf) as a divergence measure. For slice identification, this measure is the ratio of pdfs of slice and the volume; for hemisphere and infarct segmentation, it is the ratio of the difference of the pdfs of the left and right hemispheres to the sum of their pdfs. The median and cross over points are thresholds for slice and region segmentation while hemisphere identification is threshold free. Descriptive statistics were determined and ROC analysis was performed.
Results
The median sensitivity, specificity, and Dice statistical index for segmentation are 86.34%, 99.83%, 0.72, respectively. For slice and hemisphere identification sensitivity and specificity are (90.05%; 68.78%) and (94.74%; 94.74%), respectively. The algorithm implemented in VC++ takes 3–5 s per volume.
Conclusion
This automatic, accurate and fast method is potentially useful in clinical setting and clinical trials to localize and quantify the stroke regions, eliminate inter- and intra-variability, and laborious and time consuming, operator-dependent manual segmentation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sasaki M, Kudo K, Oikawa H (2006) CT perfusion for acute stroke: current concepts on technical aspects and clinical applications. International Congress Series. 1290: 30–36
Murphy BD, Fox AJ, Lee DH, Sahlas DJ, Black SE, Hogan MJ et al (2006) Identification of penumbra and infarct in acute ischemic stroke using computed tomography perfusion-derived blood flow and blood volume measurements. Stroke 37: 1771–1777. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000227243.96808.53
Hoeffner EG, Case I, Jain R, Gujar SK, Shah GV, Deveikis JP, Carlos RC, Thompson BG, Harrigan MR, Mukherji SK (2004) Cerebral perfusion CT: techniques and clinical applications. Radiology 231: 632–644. doi:10.1148/radiol.2313021488
Chalela JA, Kidwell CS, Nentwich LM, Luby M, Butman JA, Demchuk AM et al (2007) Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography in emergency assessment of patients with suspected acute stroke: a prospective comparison. Lancet 369: 293–298. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60151-2
Mitsias PD, Ewing JR, Lu M, Khalighi MM, Pasnoor M, Ebadian HB et al (2004) Multiparametric iterative self-organizing MR imaging data analysis techniques for assessment of tissue viability in acute cerebral ischemia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25: 1499–1508
Kabir Y, Dojat M, Scherrer B, Forbes F, Garbay C (2007) Multimodal MRI segmentation of ischemic stroke lesions. In: Proceedings of the 29th annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society (EMBS), pp 1595–1598
Neumann-Haefelin T, Wittsack HJ, Wenerski F, Siebler M, Seitz RJ, Modder U et al (1999) Diffusion- and Perfusion-weighted MRI, the DWI/PWI mismatch region in acute stroke. Stroke 30: 1591–1597
Sobesky J, Weber OZ, Lehnhardt FG, Hesselmann V, Neveling M, Jacobs A et al (2005) Does the mismatch match the penumbra? Magnetic resonance imaging and positron emission tomography in the early ischemic stroke. Stroke 36: 980–985. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000160751.79241.a3
Martel AL, Allder SJ, Delay GS, Morgan PS, Moody AR (1999) Measurement of infarct volume in stroke patients using adaptive segmentation of diffusion weighted MR images. In: Second international conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, MICCAI’99, held in Cambridge, UK, in September, pp 22–25
Li W, Tian J (2003) Automatic segmentation of brain infarction in diffusion-weighted MR images. In: Sonka M, Fitzpatrick MJ (eds) Medical imaging 2003: image processing. Proc SPIE 5032:1531–1542
Li W, Tian J, Li E, Dai J (2004) Robust unsupervised segmentation of infarct lesion from diffusion tensor MR images using multiscale statistical classification and partial volume voxel reclassification. Neuroimage 23(4): 1507–1518. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.08.009
Bhanu Prakash KN, Gupta V, Bilello M, Beauchamp N, Nowinski WL (2006) Identification, segmentation, and image property study of acute infarcts in diffusion-weighted images by using a probabilistic neural network and adaptive gaussian mixture model. Acad Radiol 13(12): 1474–1484. doi:10.1016/j.acra.2006.09.045
Nowinski WL, Qian GY, Bhanu Prakash KN, Volkau I, Thirunavuukarasuu A, Beauchamp NJ et al (2005) Atlas-assisted MR stroke image interpretation by using anatomical and blood supply territories atlases. Program 91st Radiological Society of North America Scientific Assembly and Annual Meeting RSNA, Chicago, Illinois, USA, 27 November–2 December, p 857
Nowinski WL, Qian G, Bhanu Prakash KN, Volkau I, Thirunavuukarasuu A, Hu Q et al (2007) A CAD system for acute ischemic stroke image processing. Int J CARS 2(Suppl 1): 220–222. doi:10.1007/s11548-007-0132-2
Gupta V, Bhanu Prakash KN, Nowinski WL (2008) Automatic and rapid identification of infarct slices and hemisphere in DWI scans. Acad Radiol 15(1): 24–39
Mahalanobis PC (1936) On the generalized distance in statistics. Proc Natl Inst Sci India 12: 49–55
Llorente LP (2005) Statistical inference based on divergence measures, Chaps. 1, 2. CRC press, Boca Raton
Chan HM, Chung ACS, Yu SCH, Norbash A, Wells WM (2003) Multi-modal image registration by minimizing Kullback–Leibler distance between expected and observed joint class histograms. Proc IEEE Comput Soc Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit 2: 570–576
Pluim JPW, Maintz JBA, Viergever MA (2003) Mutual-information-based registration of medical images: a survey. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 22: 986–1004. doi:10.1109/TMI.2003.815867
Hibbard LS (2004) Region segmentation using information divergence measures. Med Image Anal 8: 233–244. doi:10.1016/j.media.2004.06.003
Volkau I, Bhanu Prakash KN, Anand A, Aziz A, Nowinski WL (2006) Extraction of the midsagittal plane from morphological neuroimages using the Kullback–Leibler’s measure. Med Image Anal 10(6): 863–874. doi:10.1016/j.media.2006.07.005
Kummer RV, Back T, Ay H (2003) Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Ischemic Stroke, vol 121. Springer, Heidelberg ISBN 3540008616
Liu Y, Collins R, Rothfus WE (2001) Robust midsagittal plane extraction from normal and pathological 3-D neuroradiology images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 20: 175–192. doi:10.1109/42.918469
Hu Q, Nowinski WL (2003) A rapid algorithm for robust and automatic extraction of the midsagittal plane of the human cerebrum from neuroimages based on local symmetry and outlier removal. Neuroimage 20: 2153–2165. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2003.08.009
Bevington PR, Keith Robinson D (2003) Data reduction and error analysis for physical sciences, 3rd edn. Mc-Graw Hill, New York, p 13
Mandel J (1984) The Statistical analysis of experimental data. Courier Dover Publications, New York, p 72
Hanley JA, McNeil BJ (1982) The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 143: 29–36
MedCalc Software Broekstraat 52, 9030 Mariakerke, Belgium. http://www.medcalc.be/
Zou KH, Warfield SK, Bharatha A, Clare MC, Kaus MR, Kaus MR, Haker SJ, Wells WM, Jolesz FA, Kikinis R (2004) Statistical validation of image segmentation quality based on spatial overlap index. Acad Radiol 11: 178–189. doi:10.1016/S1076-6332(03)00671-8
Anbeek P, Vincken KL, Osch MJP, Bisschops RHC, Grond J (2004) Automatic segmentation of different sized white matter lesions by voxel probability estimation. Med Image Anal 8: 205–215. doi:10.1016/j.media.2004.06.019
Zijdenbos AP, Dawant BM, Margolin RA, Palmer AC (1994) Morphometric analysis of white matter lesions in MR images: method and validation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 13: 716–724. doi:10.1109/42.363096
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhanu Prakash, K.N., Gupta, V., Jianbo, H. et al. Automatic processing of diffusion-weighted ischemic stroke images based on divergence measures: slice and hemisphere identification, and stroke region segmentation. Int J CARS 3, 559–570 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-008-0260-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-008-0260-3