Abstract
Purpose
Content-based image retrieval (CBIR) bears great potential for computer-aided diagnosis (CAD). However, current CBIR systems are not able to integrate with clinical workflow and PACS generally. One essential factor in this setting is scheduling. Applied and proved with modalities and the acquisition of images for a long time, we now establish scheduling with CBIR.
Methods
Our workflow is based on the IHE integration profile ‘Post-Processing Workflow’ (PPW) and the use of a DICOM work list.
Results
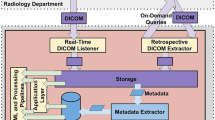
We configured dcm4chee PACS and its including IHE actors for the application of CBIR. In order to achieve a convenient interface for integrating arbitrary CBIR systems, we realized an adapter between the CBIR system and PACS. Our system architecture constitutes modular components communicating over standard protocols.
Conclusion
The proposed workflow management system offers the possibility to embed CBIR conveniently into PACS environments. We achieve a chain of references that fills the information gap between acquisition and post-processing. Our approach takes into account the tight and solid organization of scheduled and performed tasks in clinical settings.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AET:
-
Application entity title
- CAD:
-
Computer-aided diagnosis
- CBIR:
-
Content-based image retrieval
- CR:
-
Computed radiography
- DICOM:
-
Digital imaging and communications in medicine
- EC:
-
Evidence creator actor (IHE)
- GP-PPS:
-
General purpose performed procedure step
- GP-SPS:
-
General purpose scheduled procedure step
- GPWL:
-
General purpose worklist
- HIS:
-
Hospital information system
- HL7:
-
Health level 7
- HTML:
-
Hypertext Markup Language
- ID:
-
Image display actor (IHE)
- IHE:
-
Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise
- IM/IA:
-
Image manager/image archive actor (IHE)
- IOD:
-
Information object definition
- PACS:
-
Picture archiving and communication system
- PPM:
-
Post-processing manager actor (IHE)
- PWF:
-
Post-processing workflow integration profile
- RIS:
-
Radiology information system
- SOAP:
-
Simple object access protocol
- SOP:
-
Service object pair
- XML:
-
Extended markup language
- XSL:
-
Extensible stylesheet language
References
Eakins JP, Graham ME (1999) Content-based image retrieval—a report to the JISC technology applications programme. Technical Report, Institute for Image Data Research, University of Northumbria at Newcastle. http://www.jisc.ac.uk/uploaded_documents/jtap-039.doc. Accessed 17 March 2010
Müller H, Michoux N, Bandon D, Geissbuhler A (2004) A review of content-based image retrieval systems in medical applications—clinical benefits and future directions. Int J Med Inform 73(1): 1–23
Traina C Jr, Traina AJ, Araujo MR et al (2005) Using an image-extended relational database to support content-based image retrieval in a PACS. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 80(1): 71–83
Fischer B, Deserno TM, Ott B, Günther RW (2008) Integration of a research CBIR system with RIS and PACS for radiological routine. Proc SPIE Med Imaging 6919: 691914.1–691914.10
Le A, Mai L, Liu B, Huang HK (2008) The workflow and procedures for automatic integration of a computer-aided diagnosis workstation with a clinical PACS with real world examples. Proc SPIE Med Imaging 6919, doi:10.1117/12.772990
Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise (2010) http://www.ihe.net. Accessed 17 March 2010
IHE (2008) IHE technical framework, vol I: Integration profile. http://www.ihe.net/Technical_Framework/upload/ihe_tf_rev9-0ft_vol1_2008-06-27.pdf. Accessed 17 March 2010
dcm4che.org (2010) Open source clinical image and object management. http://www.dcm4che.org. Accessed 17 March 2010
National Electrical Manufacturers Association (2001) DICOM supplement 52: general purpose worklist. ftp://medical.nema.org/medical/dicom/final/sup52_ft.pdf. Accessed 17 March 2010
Lehmann TM, Güld MO, Thies C, Fischer B, Spitzer K, Keysers D, Ney H, Kohnen M, Schubert H, Wein BB (2004) Content-based image retrieval in medical applications. Methods Inf Med 43(4): 354–361
National Electrical Manufacturers Association (2000) DICOM supplement 23: structured reporting storage SOP classes. ftp://medical.nema.org/medical/dicom/final/sup23_ft.pdf. Accessed 17 March 2010
Fischer B, Brosig A, Welter P, Grouls C, Günther RW, Deserno TM (2010) Content-based image retrieval applied to bone age assessment. Proc SPIE Med Imaging 7624
Welter P, Deserno TM, Gülpers R, Wein BB, Grouls C, Günther RW (2010) Exemplary design of a DICOM structured report template for CBIR integration into radiological routine. Proc SPIE Med Imaging 7628
OFFIS (2010) DICOMscope DICOM viewer. http://dicom.offis.de. Accessed 17 March 2010
National Electrical Manufacturers Association (2007) DICOM supplement 96: unified worklist and procedure step. ftp://medical.nema.org/medical/dicom/supps/sup96_lb.pdf. Accessed 17 March 2010
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Welter, P., Hocken, C., Deserno, T.M. et al. Workflow management of content-based image retrieval for CAD support in PACS environments based on IHE. Int J CARS 5, 393–400 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-010-0416-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-010-0416-9