Abstract
Purpose
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is often used to detect and treat neonatal cerebral disorders. However, neonatal MR image interpretation is limited by intra- and inter-observer variability. To reduce such variability, a template-based computer-aided diagnosis system is being developed, and several methods for creating templates were evaluated.
Method
Spatial normalization for each individual’s MR images is used to accommodate the individual variation in brain shape. Because the conventional normalization uses as adult brain template, it can be difficult to analyze the neonatal brain, as there are large difference between the adult brain and the neonatal brain. This article investigates three approaches for defining a neonatal template for 1-week-old newborns for diagnosing neonatal cerebral disorders. The first approach uses an individual neonatal head as the template. The second approach applies skull stripping to the first approach, and the third approach produces a template by averaging brain MR images of 7 neonates. To validate the approaches, the normalization accuracy was evaluated using mutual information and anatomical landmarks.
Results
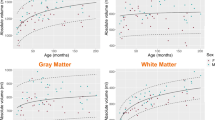
The experimental results of 7 neonates (revised age 5.6 ± 17.6 days) showed that normalization accuracy was significantly higher with the third approach than with the conventional adult template and the other two approaches (P < 0.01).
Conclusion
Three approaches to neonatal brain template matching for spinal normalization of MRI scans were applied, demonstrating that a population average gave the best results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braak H, Braak E (1991) Neuropathologic stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol 82(4): 239–259
Kitagaki H, Mori E, Yamaji S, Ishii K, Hirono N, Kobashi S, Hata Y (1998) Frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer disease: evaluation of cortical atrophy with automated hemispheric surface display generated with MR images. Radiology 208(2): 431–439
Evans AC, Collins DL, Milner B (1992) An MRI-based stereotactic atlas from 250 young normal subjects. Soc Neurosci Abstr 18: 408
Evans AC, Collins DL, Mills SR, Brown ED, Kelly RL, Peters TM (1993) 3D statistical neuroanatomical models from 305 MRI volumes In: Proceedings of the IEEE-nuclear science symposium and medical imaging conference, vol 3, pp 1813–1817
Good CD, Johnsrude IS, Ashburner J, Henson RN, Friston KJ, Frackowiak RS (2001) A voxel-based morphometric study of ageing in 465 normal adult human brains. NeuroImage 14(1): 21–36
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2001) Why voxel-based morphometry should be used. NeuroImage 14(6): 1238–1243
Barkovich AJ (2000) Concepts of myelin and myelination in neuroradiology. Am J Neuroradiol 21(6): 1099–1109
Kazemi K, Moghaddam HA, Grebe R, Gondry-Jouet C, Wallois F (2007) A neonatal atlas template for spatial normalization of whole-brain magnetic resonance images of newborns: preliminary results. NeuroImage 37(2): 463–473
Muragasova M, Doria V, Srinivasan L, Aljabar P, Edwards AD, Rueckert D (2009) A spatio-temporal atlas of the growing brain for fMRI studies, MICCAI 2009 workshop: image analysis of developing brain
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (1999) Nonlinear spatial normalization using basis functions. Hum Brain Mapp 7(4): 254–266
Jenkinson M, Pechaud M, Smith S (2005) BET2: MR-based estimation of brain, skull and scalp surfaces, In: Eleventh annual meeting of the organization for human brain mapping
Hashioka A, Yamaguchi K, Kobashi S, Kuramoto K, Wakata Y, Ando K, Ishikura R, Ishikawa T, Hirota S, Hata Y (2011) Neonatal brain MR image segmentation based on system-of-systems in engineering technology In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on system of systems engineering, pp 107–112
Guimond A, Meunier J, Thirion J (2000) Average brain models: a convergence study. Comput Vis Image Unders 77(2): 192–210
Mases F, Collignon A, Vandermeulen D (1997) Multimodality image registration by maximization of mutual information. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 16(2): 187–198
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hashioka, A., Kobashi, S., Kuramoto, K. et al. A neonatal brain MR image template of 1 week newborn. Int J CARS 7, 273–280 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-011-0646-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-011-0646-5