Abstract
Purpose
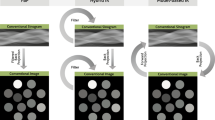
Temporal subtraction images constructed from image registration can facilitate the visualization of pathologic changes. In this study, we propose a deformable image registration (DIR) framework for creating temporal subtraction images of chest radiographs.
Methods
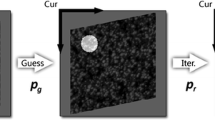
We developed a DIR methodology using two different image similarity metrics, varying flow (VF) and compressible flow (CF). The proposed registration method consists of block matching, filtering, and interpolation. Specifically, corresponding point pairs between reference and target images are initially determined by minimizing a nonlinear least squares formulation using grid-searching optimization. A two-step filtering process, including least median of squares filtering and backward matching filtering, is then applied to the estimated point matches in order to remove erroneous matches. Finally, moving least squares is used to generate a full displacement field from the filtered point pairs.
Results
We applied the proposed DIR method to 10 pairs of clinical chest radiographs and compared it with the demons and B-spline algorithms using the five-point rating score method. The average quality scores were 2.7 and 3 for the demons and B-spline methods, but 3.5 and 4.1 for the VF and CF methods. In addition, subtraction images improved the visual perception of abnormalities in the lungs by using the proposed method.
Conclusion
The VF and CF models achieved a higher accuracy than the demons and the B-spline methods. Furthermore, the proposed methodology demonstrated the ability to create clinically acceptable temporal subtraction chest radiographs that enhance interval changes and can be used to detect abnormalities such as non-small cell lung cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu Q, He L, Chao Y, Suzuki K, Nakamura T (2012) A mutual-information-based image registration method for chest-radiograph temporal subtraction. In: Proceedings of CSIP, pp 1098–1101
Ishida T, Katsuragawa S, Nakamura K, MacMahon H, Doi K (1999) Iterative image warping technique for temporal subtraction of sequential chest radiographs to detect interval change. Med Phys 26(7):1320–1329
Loeckx D, Maes F, Vandermeulen D, Suetens P (2003) Temporal subtraction of thorax CR images using a statistical deformation model. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 22:1490–1504
McAdams HP, Samei E, Dobbins J III, Tourassi GD, Ravin CE (2006) Recent advances in chest radiography. Radiology 241:663–683
Yang J, Wang Y, Tang S, Zhou S, Liu Y, Chen W (2007) Multiresolution elastic registration of X-ray angiography images using thin-plate spline. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 54(1):152–166
Yin Y, Hoffman EA, Lin CL (2009) Local tissue-weight-based nonrigid registration of lung images with application to regional ventilation. In: Proceedings of SPIE, vol 7262, p 72620C
Gorbunova V, Sporring J, Lo P, Loeve M, Tiddens HA, Nielsen M, Dirksen A, de Bruijne M (2012) Mass preserving image registration for lung CT. Med Image Anal 16(4):786–795
Castillo E, Castillo R, Zhang Y, Guerrero T (2009) Compressible image registration for thoracic computed tomography images. J Med Biol Eng 29(5):222–233
Kano A, Doi K, MacMahon H, Hassell DD, Giger ML (1994) Digital image subtraction of temporally sequential chest images for detection of interval change. Med Phys 21(3):453–461
Okazaki H, Nakamura K, Watanabe H, Matsuki Y, Uozumi T, Kakeda K, Oda N, Nakata H, Katsuragawa S, Doi K (2004) Improved detection of lung cancer arising in diffuse lung diseases on chest radiographs using temporal subtraction. Acad Radiol 11(5):498–505
Armato SG, Doshi DJ, Engelmann R, Caligiuri P, MacMahon H (2006) Temporal subtraction of dual-energy chest radiographs. Med Phys 3(6):1911–1919
Aoki T, Oda N, Yamashita Y, Yamamoto K, Korogi Y (2012) Usefulness of computerized method for lung nodule detection on digital chest radiographs using similar subtraction images from different patients. Eur J Radiol 81:1062–1067
Inaba T, He L, Suzuki K, Murakami K, Chao Y (2009) A genetic-algorithm-based temporal subtraction for chest radiographs. J Adv Comput Intell Intell Inf 13:289–296
Guo S, Wu X, Luo Z (2008) Automatic extraction of control points for chest X-ray images and elastic registration. In: Proceedings of ICBBE, pp 2651–2654
Christensen GE, Rabbitt RD, Miller MI (1994) 3D brain mapping using deformable neuroanatomy. Phys Med Biol 39:609–618
Castillo E, Castillo R, White B, Rojo J, Guerrero T (2012) Least median of squares filtering of locally optimal point matches for compressible flow image registration. Phys Med Biol 57:4827–4833
Castillo E, Castillo R, Martinez J, Shenoy M, Guerrero T (2010) Four-dimensional deformable image registration using trajectory modeling. Phys Med Biol 55(1):305–327
Corpetti T, Memin E, Perez P (2002) Dense estimation of fluid flow. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 24(3):365–380
Song SM, Leahy RM (1991) Computation of 3D velocity fields from 3D cine CT images of a human heart. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 10:295–306
Wildes RP, Amabile MJ, Lanzilloto A, Leu T (2000) Recovering estimates of fluid flow from image sequence data. Comput Vis Image Underst 80:246–266
Castillo R, Castillo E, Guerra R, Johnson VE, McPhail T, Garg AK, Guerrero T (2009) A framework for evaluation of deformable image registration spatial accuracy using large landmark point sets. Phys Med Biol 54(7):1849–1870
Olsen M, Johnstone E, Kuester F, Driscoll N, Ashford S (2011) New automated point-cloud alignment for ground-based light detection and ranging data of long coastal sections. J Surv Eng 137(1):14–25
Li Q, Katsuragawa S, Ishida T, Yoshida H, Tsukuda S, MacMahon H, Doi K (2000) Contralateral subtraction: a novel technique for detection of asymmetric abnormalities on digital chest radiographs. Med Phys 27(1):47–55
Armato SG, Doshi DJ, Engelmann R, Croteau CL, MacMahon H (2006) Temporal subtraction in chest radiography: automated assessment of registration accuracy. Med Phys 33(5):1239–1249
Li Q, Katsuragawa S, Doi K (2000) Improved contralateral subtraction images by use of elastic matching technique. Med Phys 27(8):1934–1942
MacMahon H, Armato SG III (2009) Temporal subtraction chest radiography. Eur J Radiol 72(2):238–243
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Samantha Aso and Justin Yu in the Department of Radiation Oncology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, for providing help in subtraction image observation. This work is partially funded by MD Anderson’s Cancer Center Support Grant (CA016672) and the National Institutes of Health through an NIH Director’s New Innovator Award (DP2OD007044), and by the grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC No. 60771025).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Castillo, E., Luo, HY. et al. Deformable image registration for temporal subtraction of chest radiographs. Int J CARS 9, 513–522 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-013-0947-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-013-0947-y