Abstract
Purpose
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second leading neurodegenerative disease after Alzheimer’s disease. In PD research and its surgical treatment, such as deep brain stimulation (DBS), anatomical structural identification and references for spatial normalization are essential, and human brain atlases/templates are proven highly instrumental. However, two shortcomings affect current templates used for PD. First, many templates are derived from a single healthy subject that is not sufficiently representative of the PD-population anatomy. This may result in suboptimal surgical plans for DBS surgery and biased analysis for morphological studies. Second, commonly used mono-contrast templates lack sufficient image contrast for some subcortical structures (i.e., subthalamic nucleus) and biochemical information (i.e., iron content), a valuable feature in current PD research.
Methods
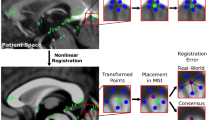
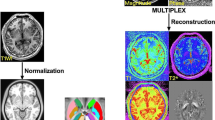
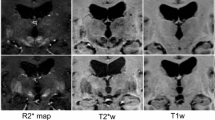
We employed a novel T1–T2* fusion MRI that visualizes both cortical and subcortical structures to drive groupwise registration to create co-registered multi-contrast (T1w, T2*w, T1–T2* fusion, phase, and an R2* map) unbiased templates from 15 PD patients, and a high-resolution histology-derived 3D atlas is co-registered. For validation, these templates are compared against the Colin27 template for landmark registration and midbrain nuclei segmentation.
Results
While the T1w, T2*w, and T1–T2* fusion templates provide excellent anatomical details for both cortical and subcortical structures, the phase and R2* map contain the biochemical features. By one-way ANOVA tests, our templates significantly (\(p<0.05\)) outperform the Colin27 template in the registration-based tasks.
Conclusion
The proposed unbiased templates are more representative of the population of interest and can benefit both the surgical planning and research of PD.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rajput AH, Offord KP, Beard CM, Kurland LT (1984) Epidemiology of parkinsonism: incidence, classification, and mortality. Ann Neurol 16(3):278–282
Kleiner-Fisman G, Fisman DN, Sime E, Saint-Cyr JA, Lozano AM, Lang AE (2003) Long-term follow up of bilateral deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in patients with advanced Parkinson disease. J Neurosurg 99(3):489–495
Vingerhoets FJ, Villemure JG, Temperli P, Pollo C, Pralong E, Ghika J (2002) Subthalamic DBS replaces levodopa in Parkinson’s disease: two-year follow-up. Neurology 58(3):396–401
Schaltenbrand G, Wahren W (1977) Atlas for stereotaxy of the human brain. 2nd, rev. and enl. edn. Year Book Medical Publishers, Chicago
Talairach J, Tournoux P (1988) Co-planar stereotaxic atlas of the human brain : 3-dimensional proportional system : an approach to cerebral imaging. G. Thieme; New York
Lalys F, Haegelen C, Ferre JC, El-Ganaoui O, Jannin P (2010) Construction and assessment of a 3-T MRI brain template. Neuroimage 49(1):345–354
Bardinet E, Bhattacharjee M, Dormont D, Pidoux B, Malandain G, Schupbach M, Ayache N, Cornu P, Agid Y, Yelnik J (2009) A three-dimensional histological atlas of the human basal ganglia. II. Atlas deformation strategy and evaluation in deep brain stimulation for Parkinson disease. J Neurosurg 110(2):208–219
Chakravarty MM, Sadikot AF, Germann J, Bertrand G, Collins DL (2008) Towards a validation of atlas warping techniques. Med Image Anal 12(6):713–726
Haegelen C, Coupe P, Fonov V, Guizard N, Jannin P, Morandi X, Collins DL (2013) Automated segmentation of basal ganglia and deep brain structures in MRI of Parkinson’s disease. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 8(1):99–110
Murphy DGM, Decarli C, Schapiro MB, Rapoport SI, Horwitz B (1992) Age-related differences in volumes of subcortical nuclei, brain matter, and cerebrospinal-fluid in healthy-men as measured with magnetic-resonance-imaging. Arch Neurol Chicago 49(8):839–845
Scahill RI, Frost C, Jenkins R, Whitwell JL, Rossor MN, Fox NC (2003) A longitudinal study of brain volume changes in normal aging using serial registered magnetic resonance imaging. Arch Neurol Chicago 60(7):989–994
Hutchinson M, Raff U (2000) Structural changes of the substantia nigra in Parkinson’s disease as revealed by MR imaging. Am J Neuroradiol 21(4):697–701
Nagano-Saito A, Washimi Y, Arahata Y, Kachi T, Lerch JP, Evans AC, Dagher A, Ito K (2005) Cerebral atrophy and its relation to cognitive impairment in Parkinson disease. Neurology 64(2):224–229
Montgomery EB (2010) Deep brain stimulation programming: principles and practice. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Chakravarty MM, Sadikot AF, Germann J, Hellier P, Bertrand G, Collins DL (2009) Comparison of piece-wise linear, linear, and nonlinear atlas-to-patient warping techniques: analysis of the labeling of subcortical nuclei for functional neurosurgical applications. Hum Brain Mapp 30(11):3574–3595
Richter EO, Hoque T, Halliday W, Lozano AM, Saint-Cyr JA (2004) Determining the position and size of the subthalamic nucleus based on magnetic resonance imaging results in patients with advanced Parkinson disease. J Neurosurg 100(3):541–546
Duval C, Panisset M, Strafella AP, Sadikot AF (2006) The impact of ventrolateral thalamotomy on tremor and voluntary motor behavior in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Exp Brain Res 170(2):160–171
Lehericy S, Bardinet E, Tremblay L, Van de Moortele PF, Pochon JB, Dormont D, Kim DS, Yelnik J, Ugurbil K (2006) Motor control in basal ganglia circuits using fMRI and brain atlas approaches. Cereb Cortex 16(2):149–161
Burton EJ, McKeith IG, Burn DJ, Williams ED, O’Brien JT (2004) Cerebral atrophy in Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia: a comparison with Alzheimer’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies and controls. Brain 127(Pt 4):791–800
Summerfield C, Junque C, Tolosa E, Salgado-Pineda P, Gomez-Anson B, Marti MJ, Pastor P, Ramirez-Ruiz B, Mercader J (2005) Structural brain changes in Parkinson disease with dementia: a voxel-based morphometry study. Arch Neurol Chicago 62(2):281–285
Sudhyadhom A, Haq IU, Foote KD, Okun MS, Bova FJ (2009) A high resolution and high contrast MRI for differentiation of subcortical structures for DBS targeting: the fast gray matter acquisition T1 inversion recovery (FGATIR). Neuroimage 47(Suppl 2):T44–T52
Xiao Y, Bailey L, Chakravarty MM, Beriault S, Sadikot AF, Pike GB, Collins DL (2012) Atlas-based segmentation of the subthalamic nucleus, red nucleus, and substantia nigra for deep brain stimulation by incorporating multiple MRI contrasts. In: Information processing in computer-assisted interventions (IPCAI), pp 135–145
Yelnik J, Bardinet E, Dormont D, Malandain G, Ourselin S, Tande D, Karachi C, Ayache N, Cornu P, Agid Y (2007) A three-dimensional, histological and deformable atlas of the human basal ganglia. I. Atlas construction based on immunohistochemical and MRI data. Neuroimage 34(2):618–638
Pallavaram S, Dawant BM, Koyama T, Yu H, Neimat J, Konrad PE, D’Haese PF (2009) Validation of a fully automatic method for the routine selection of the anterior and posterior commissures in magnetic resonance images. Stereot Funct Neuros 87(3):148–154
Chakravarty MM, Bertrand G, Hodge CP, Sadikot AF, Collins DL (2006) The creation of a brain atlas for image guided neurosurgery using serial histological data. Neuroimage 30(2):359–376
Guimond A, Meunier J, Thirion JP (1998) Automatic computation of average brain models. Lect Notes Comput Sc 1496:631–640
Guimond A, Meunier J, Thirion JP (2000) Average brain models: a convergence study. Comput Vis Image Und 77(2):192–210
Bhatia KK, Aljabar P, Boardman JP, Srinivasan L, Murgasova M, Counsell SJ, Rutherford MA, Hajnal J, Edwards AD, Rueckert D (2007) Groupwise combined segmentation and registration for atlas construction. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv 10(Pt 1):532–540
Fonov V, Evans AC, Botteron K, Almli CR, McKinstry RC, Collins DL (2011) Unbiased average age-appropriate atlases for pediatric studies. Neuroimage 54(1):313–327
Joshi S, Davis B, Jomier M, Gerig G (2004) Unbiased diffeomorphic atlas construction for computational anatomy. Neuroimage 23(Suppl 1):S151–S160
Lorenzen P, Prastawa M, Davis B, Gerig G, Bullitt E, Joshi S (2006) Multi-modal image set registration and atlas formation. Med Image Anal 10(3):440–451
Shattuck DW, Mirza M, Adisetiyo V, Hojatkashani C, Salamon G, Narr KL, Poldrack RA, Bilder RM, Toga AW (2008) Construction of a 3D probabilistic atlas of human cortical structures. Neuroimage 39(3):1064–1080
Wang Q, Seghers D, D’Agostino E, Maes F, Vandermeulen D, Suetens P, Hammers A (2005) Construction and validation of mean shape atlas templates for atlas-based brain image segmentation. Inf Process Med Imaging 19:689–700
O’Gorman RL, Shmueli K, Ashkan K, Samuel M, Lythgoe DJ, Shahidiani A, Wastling SJ, Footman M, Selway RP, Jarosz J (2011) Optimal MRI methods for direct stereotactic targeting of the subthalamic nucleus and globus pallidus. Eur Radiol 21(1):130–136
Schenck JF, Zimmerman EA (2004) High-field magnetic resonance imaging of brain iron: birth of a biomarker? NMR Biomed 17(7):433–445
Boelmans K, Holst B, Hackius M, Finsterbusch J, Gerloff C, Fiehler J, Munchau A (2012) Brain iron deposition fingerprints in Parkinson’s disease and progressive supranuclear palsy. Mov Disord 27(3):421–427
Gorell JM, Ordidge RJ, Brown GG, Deniau JC, Buderer NM, Helpern JA (1995) Increased iron-related MRI contrast in the substantia nigra in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 45(6):1138–1143
Ogg RJ, Langston JW, Haacke EM, Steen RG, Taylor JS (1999) The correlation between phase shifts in gradient-echo MR images and regional brain iron concentration. Magn Reson Imaging 17(8):1141–1148
Peran P, Hagberg G, Luccichenti G, Cherubini A, Brainovich V, Celsis P, Caltagirone C, Sabatini U (2007) Voxel-based analysis of R2* maps in the healthy human brain. J Magn Reson Imaging 26(6):1413–1420
Forkert ND, Schmidt-Richberg A, Treszl A, Hilgetag C, Fiehler J, Munchau A, Handels H, Boelmans K (2013) Automated volumes-of-interest identification for classical and atypical Parkinsonian syndrome differentiation using T2’ MR imaging. Methods Inf Med 52(2):128–136
Xiao Y, Beriault S, Pike GB, Collins DL (2012b) Multicontrast multiecho FLASH MRI for targeting the subthalamic nucleus. Magn Reson Imaging 30(5):627–640
Coupe P, Yger P, Prima S, Hellier P, Kervrann C, Barillot C (2008) An optimized blockwise nonlocal means denoising filter for 3-D magnetic resonance images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 27(4):425–441
Sled JG, Zijdenbos AP, Evans AC (1998) A nonparametric method for automatic correction of intensity nonuniformity in MRI data. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 17(1):87–97
Smith SM (2002) Fast robust automated brain extraction. Hum Brain Mapp 17(3):143–155
Collins DL, Neelin P, Peters TM, Evans AC (1994) Automatic 3D intersubject registration of MR volumetric data in standardized Talairach space. J Comput Assist Tomogr 18(2):192–205
Miller M, Banerjee A, Christensen G, Joshi S, Khaneja N, Grenander U, Matejic L (1997) Statistical methods in computational anatomy. Stat Methods Med Res 6(3):267–299
Nyul LG, Udupa JK (1999) On standardizing the MR image intensity scale. Magn Reson Med 42(6):1072–1081
Beriault S, Subaie FA, Collins DL, Sadikot AF, Pike GB (2012) A multi-modal approach to computer-assisted deep brain stimulation trajectory planning. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 7(5):687–704
Holmes CJ, Hoge R, Collins L, Woods R, Toga AW, Evans AC (1998) Enhancement of MR images using registration for signal averaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr 22(2):324–333
Ardekani BA, Guckemus S, Bachman A, Hoptman MJ, Wojtaszek M, Nierenberg J (2005) Quantitative comparison of algorithms for inter-subject registration of 3D volumetric brain MRI scans. J Neurosci Methods 142(1):67–76
Avants BB, Epstein CL, Grossman M, Gee JC (2008) Symmetric diffeomorphic image registration with cross-correlation: evaluating automated labeling of elderly and neurodegenerative brain. Med Image Anal 12(1):26–41
Guizzard N, Fonov V, Collins DL (2009) Symmetric optimization scheme versus constrained symmetrization for non-linear registrations. In: MICCAI workshop on “Medical Image Analysis on Multiple Sclerosis (validation and methodological issues)”
Volz S, Hattingen E, Preibisch C, Gasser T, Deichmann R (2009) Reduction of susceptibility-induced signal losses in multi-gradient-echo images: application to improved visualization of the subthalamic nucleus. Neuroimage 45(4):1135–1143
Guo T, Finnis KW, Parrent AG, Peters TM (2005) Development and application of functional databases for planning deep-brain neurosurgical procedures. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv 8(Pt 1):835–842
Conflict of interest
Yiming Xiao, Vladimir Fonov, Silvain Bériault, Fahd Al Subaie, M. Mallar Chakravarty, Abbas F. Sadikot, G. Bruce Pike, and D. Louis Collins declare that they have no conflict of interest.
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Declaration of Helsinki 1975, as revised in 2008 (5). Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Y., Fonov, V., Bériault, S. et al. Multi-contrast unbiased MRI atlas of a Parkinson’s disease population. Int J CARS 10, 329–341 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-014-1068-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-014-1068-y