Abstract
Purpose
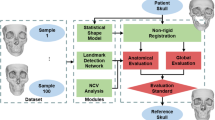
Virtual reconstruction of large cranial defects is still a challenging task. The current reconstruction procedures depend on the surgeon’s experience and skills in planning the reconstruction based on mirroring and manual adaptation. The aim of this study is to propose and evaluate a computer-based approach employing a statistical shape model (SSM) of the cranial vault.
Methods
An SSM was created based on 131 CT scans of pathologically unaffected adult crania. After segmentation, the resulting surface mesh of one patient was established as template and subsequently registered to the entire sample. Using the registered surface meshes, an SSM was generated capturing the shape variability of the cranial vault. The knowledge about this shape variation in healthy patients was used to estimate the missing parts. The accuracy of the reconstruction was evaluated by using 31 CT scans not included in the SSM. Both unilateral and bilateral bony defects were created on each skull. The reconstruction was performed using the current gold standard of mirroring the intact to the affected side, and the result was compared to the outcome of our proposed SSM-driven method. The accuracy of the reconstruction was determined by calculating the distances to the corresponding parts on the intact skull.
Results
While unilateral defects could be reconstructed with both methods, the reconstruction of bilateral defects was, for obvious reasons, only possible employing the SSM-based method. Comparing all groups, the analysis shows a significantly higher precision of the SSM group, with a mean error of 0.47 mm compared to the mirroring group which exhibited a mean error of 1.13 mm. Reconstructions of bilateral defects yielded only slightly higher estimation errors than those of unilateral defects.
Conclusion
The presented computer-based approach using SSM is a precise and simple tool in the field of computer-assisted surgery. It helps to reconstruct large-size defects of the skull considering the natural asymmetry of the cranium and is not limited to unilateral defects.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marsell R, Einhorn TA (2011) The biology of fracture healing. Injury 42(6):551–555
Ehrenfeld M, Manson PN, Prein J (2012) Principles of internal fixation of the craniomaxillofacial skeleton. AO Foundation, Thieme, Stuttgart
Unterhofer C, Wipplinger C, Verius M, Recheis W, Thome C, Ortler M (2017) Reconstruction of large cranial defects with poly-methyl-methacrylate (PMMA) using a rapid prototyping model and a new technique for intraoperative implant modeling. Neurologia i neurochirurgia polska 51(3):214–220
Toro C, Robiony M, Costa F, Zerman N, Politi M (2007) Feasibility of preoperative planning using anatomical facsimile models for mandibular reconstruction. Head Face Med 3(1):5
Wagner MEH, Lichtenstein JT, Winkelmann M, H-o Shin, Gellrich N-C, Essig H (2015) Development and first clinical application of automated virtual reconstruction of unilateral midface defects. J Cranio-Maxillofac Surg 43(8):1340–1347
Wilde F, Hanken H, Probst F, Schramm A, Heiland M, Cornelius CP (2015) Multicenter study on the use of patient-specific CAD/CAM reconstruction plates for mandibular reconstruction. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 10(12):2035–2051
Schramm A, Suarez-Cunqueiro MM, Rücker M, Kokemueller H, Bormann KH, Metzger MC, Gellrich NC (2009) Computer-assisted therapy in orbital and mid-facial reconstructions. Int J Med Robot Comput Assist Surg: MRCAS 5(2):111–124
Schramm A, Wilde F (2011) Computer-assisted reconstruction of the facial skeleton. HNO 59(8):800–806
Gui H, Yang H, Zhang S, Shen SG, Ye M, Schmelzeisen R (2015) Mirroring tool: The simplest computer-aided simulation technology? J Craniofac Surg 26(7):2115–2119
Egger J, Gall M, Tax A, Ucal M, Zefferer U, Li X, von Campe G, Schafer U, Schmalstieg D, Chen X (2017) Interactive reconstructions of cranial 3D implants under MeVisLab as an alternative to commercial planning software. PLoS One 12(3):e0172694
Guevara-Rojas G, Figl M, Schicho K, Seemann R, Traxler H, Vacariu A, Carbon C-C, Ewers R, Watzinger F (2014) Patient-specific polyetheretherketone facial implants in a computer-aided planning workflow. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 72(9):1801–1812
Lamecker H (2008) Variational and statistical shape modeling for 3D geometry reconstruction. Freie Universität Berlin, Berlin
Tarsitano A, Ciocca L, Cipriani R, Scotti R, Marchetti C (2015) Mandibular reconstruction using fibula free flap harvested using a customised cutting guide: how we do it. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Italica 35(3):198
Wilde F, Schramm A (2016) Computer-aided reconstruction of the facial skeleton: planning and implementation in clinical routine. HNO 64(9):641–649
Scolozzi P, Terzic A (2011) Mirroring computational planning, navigation guidance system, and intraoperative mobile C-arm cone-beam computed tomography with flat-panel detector: A new rationale in primary and secondary treatment of midfacial fractures? J Oral Maxillofac Surg 69(6):1697–1707
Wien W (2012) A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Heiland M, Habermann CR, Schmelzle R (2004) Indications and limitations of intraoperative navigation in maxillofacial surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 62(9):1059–1063
Zachow S (2015) Computational planning in facial surgery. Fac Plast Surg 31(05):446–462
Marreiros FM, Heuzé Y, Verius M, Unterhofer C, Freysinger W, Recheis W (2016) Custom implant design for large cranial defects. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 11(12):2217–2230
Fisher M, Medina M, Bojovic B, Ahn E, Dorafshar AH (2016) Indications for computer-aided design and manufacturing in congenital craniofacial reconstruction. Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr 9(03):235–241
Carr JC, Fright WR, Beatson RK (1997) Surface interpolation with radial basis functions for medical imaging. IEEE Trans Med Imag 16(1):96–107
Zhao L, Patel PK, Cohen M (2012) Application of virtual surgical planning with computer assisted design and manufacturing technology to cranio-maxillofacial surgery. Arch Plast Surg 39(4):309–316
Wu T, Engelhardt M, Fieten L, Popovic A, Radermacher K (2006) Anatomically constrained deformation for design of cranial implant: methodology and validation. In: Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention–MICCAI 2006, pp 9–16
Liao Y-L, Lu C-F, Wu C-T, Lee J-D, Lee S-T, Sun Y-N, Wu Y-T (2013) Using three-dimensional multigrid-based snake and multiresolution image registration for reconstruction of cranial defect. Med Biol Eng Comput 51(1):89–101
Zachow S, Kubiack K, Malinowski J, Lamecker H, Essig H, Gellrich N (2010) Modellgestützte chirurgische Rekonstruktion komplexer Mittelgesichtsfrakturen. In: Proceedings of the BMT biomed tech, Rostock, 2010. vol (Suppl. 01), pp 107–108
Rybak J, Kuss A, Lamecker H, Zachow S, Hege HC, Lienhard M, Singer J, Neubert K, Menzel R (2010) The digital bee brain: integrating and managing neurons in a common 3D reference system. Front Syst Neurosci 4:30
Fedorov A, Beichel R, Kalpathy-Cramer J, Finet J, Fillion-Robin J-C, Pujol S, Bauer C, Jennings D, Fennessy F, Sonka M, Buatti J, Aylward S, Miller JV, Pieper S, Kikinis R (2012) 3D Slicer as an image computing platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network. Magn Reson Imag 30(9):1323–1341
Avants BB, Tustison N, Song G (2009) Advanced normalization tools (ANTS). Insight J 2:1–35
Luthi M, Albrecht T, Vetter T (2009) Building shape models from lousy data. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv 12(Pt 2):1–8
Goodall C (1991) Procrustes methods in the statistical analysis of shape. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Methodological) 5(2):285–339
Schlager S (2015) RvtkStatismo: Integrating statismo and R using the vtkStandardMeshRepresenter. https://github.com/zarquon42b/RvtkStatismo. Accessed 2015
Lüthi M, Blanc R, Albrecht T, Gass T, Goksel O, Büchler P, Kistler M, Bousleiman H, Reyes M, Cattin P (2012) Statismo-a framework for PCA based statistical models. Insight J 1:1–18
Moshfeghi M, Ranganath S, Nawyn K (1994) Three-dimensional elastic matching of volumes. IEEE Trans Image Process 3(2):128–138
Gunz P, Mitteroecker P, Bookstein FL (2005) Semilandmarks in three dimensions. In: Slice DE (ed) Modern morphometrics in physical anthropology. Developments in primatology: progress and prospects. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, Chicago, pp 73–98
Bookstein FL (1997) Landmark methods for forms without landmarks: morphometrics of group differences in outline shape. Med Image Anal 1(3):225–243
Meyer M, Barr A, Lee H, Desbrun M (2002) Generalized barycentric coordinates on irregular polygons. J Gr Tools 7(1):13–22
Metzger MC, Hohlweg-Majert B, Schön R, Teschner M, Gellrich N-C, Schmelzeisen R, Gutwald R (2007) Verification of clinical precision after computer-aided reconstruction in craniomaxillofacial surgery. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endodontol 104(4):e1–e10
Wilde F, Cornelius CP, Schramm A (2014) Computer-assisted mandibular reconstruction using a patient-specific reconstruction plate fabricated with computer-aided design and manufacturing techniques. Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr 7(2):158–166
Brief J, Hassfeld S, Däuber S, Pernozzoli A, Münchenberg J, Redlich T, Walz M, Krempien R, Weisser H, Poeckler C (2000) 3D norm data: the first step towards semiautomatic virtual craniofacial surgery. Computer aided surgery 5(5):353–358
Dean D, Min K-J, Bond A (2003) Computer aided design of large-format prefabricated cranial plates. J Craniofac Surg 14(6):819–832
Semper-Hogg W, Fuessinger MA, Schwarz S, Ellis E, Cornelius C-P, Probst F, Metzger MC, Schlager S (2016) Virtual reconstruction of midface defects using statistical shape models. J Cranio-Maxillo-Fac Surg 45(4):461–466
Schmelzeisen R, Gellrich NC, Schoen R, Gutwald R, Zizelmann C, Schramm A (2004) Navigation-aided reconstruction of medial orbital wall and floor contour in cranio-maxillofacial reconstruction. Injury 35(10):955–962
Kwon T-G, Park H-S, Ryoo H-M, Lee S-H (2006) A comparison of craniofacial morphology in patients with and without facial asymmetry–a three-dimensional analysis with computed tomography. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 35(1):43–48
Metzger M, Bittermann G, Dannenberg L, Schmelzeisen R, Gellrich N-C, Hohlweg-Majert B, Scheifele C (2013) Design and development of a virtual anatomic atlas of the human skull for automatic segmentation in computer-assisted surgery, preoperative planning, and navigation. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 8(5):691–702
Besson A, Leger J, Doual A (2000) A study of craniofacial asymmetry using computed tomography. Bulletin du Groupement international pour la recherche scientifique en stomatologie & odontologie 43(2):68–73
Katsumata A, Fujishita M, Maeda M, Ariji Y, Ariji E, Langlais RP (2005) 3D-CT evaluation of facial asymmetry. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endodontol 99(2):212–220
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fuessinger, M.A., Schwarz, S., Cornelius, CP. et al. Planning of skull reconstruction based on a statistical shape model combined with geometric morphometrics. Int J CARS 13, 519–529 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-017-1674-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-017-1674-6