Abstract
Purpose
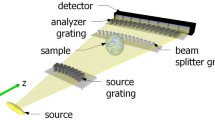
Two phase gratings in an X-ray grating interferometers can solve several technical challenges for clinical use of X-ray phase contrast. In this work, we adapt and evaluate this setup design to clinical X-ray sources and detectors in a simulation study.
Methods
For a given set of gratings, we optimize the remaining parameter space of a dual-phase grating setup using a numerical wave front simulation. The simulation results are validated with experimentally obtained visibility measurements on a setup with a microfocus tube and a clinical X-ray detector. We then confirm by simulation that the Lau condition for the \(G_0\) grating also holds for two phase gratings. Furthermore, we use a \(G_0\) grating with a fixed period to search for periods of matching phase grating configurations.
Results
Simulated and experimental visibilities agree very well. We show that the Lau condition for a dual-phase grating setup requires the interference patterns of the first phase grating to constructively overlay at the second phase grating. Furthermore, a total of three setup variants for given \(G_{0}\) periods were designed with the simulation, resulting in visibilities between 4.5 and 9.1%.
Conclusion
Dual-phase gratings can be used and optimized for a medical X-ray source and detector. The obtained visibilities are somewhat lower than for other Talbot–Lau interferometers and are a tradeoff between setup length and spatial resolution (or additional phase stepping, respectively). However, these disadvantage appears minor compared to the overall better photon statistics, and the fact that dual-phase grating setups can be expected to scale to higher X-ray energies.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonse U, Hart M (1965) An X-ray interferometer. Appl Phys Lett 6(8):155
Momose A (2005) Recent advances in x-ray phase imaging. Jpn J Appl Phys 44(9R):6355
Endrizzi M (2018) X-ray phase-contrast imaging. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect A Accel Spectrom Detect Assoc Equip 878:88
Pfeiffer F, Weitkamp T, Bunk O, David C (2006) Phase retrieval and differential phase-contrast imaging with low-brilliance X-ray sources. Nat Phys 2(4):258
Stampanoni M, Wang Z, Thüring T, David C, Roessl E, Trippel M, Kubik-Huch RA, Singer G, Hohl MK, Hauser N (2011) The first analysis and clinical evaluation of native breast tissue using differential phase-contrast mammography. Investig Radiol 46(12):801
Scherer K, Birnbacher L, Willer K, Chabior M, Herzen J, Pfeiffer F (2016) Correspondence: quantitative evaluation of X-ray dark-field images for microcalcification analysis in mammography. Nat Commun 7:10863
Hellbach K, Beller E, Schindler A, Schoeppe F, Hesse N, Baumann A, Schinner R, Auweter S, Hauke C, Radicke M, Meinel FG (2018) Improved detection of foreign bodies on radiographs using X-ray dark-field and phase-contrast imaging. Investig Radiol 53:352
Stutman D, Beck TJ, Carrino JA, Bingham CO (2011) Talbot phase-contrast X-ray imaging for the small joints of the hand. Phys Med Biol 56(17):5697
Hellbach K, Yaroshenko A, Meinel FG, Yildirim AÖ, Conlon TM, Bech M, Mueller M, Velroyen A, Notohamiprodjo M, Bamberg F, Auweter S, Reiser M, Eickelberg O, Pfeifer F (2015) In vivo dark-field radiography for early diagnosis and staging of pulmonary emphysema. Investig Radiol 50(7):430
Yaroshenko A, Hellbach K, Yildirim AÖ, Conlon TM, Fernandez IE, Bech M, Velroyen A, Meinel FG, Auweter S, Reiser M, Eickelberg O, Pfeifer F (2015) Improved in vivo assessment of pulmonary fibrosis in mice using X-ray dark-field radiography. Sci Rep 5:17492
Scherer K, Yaroshenko A, Bölükbas DA, Gromann LB, Hellbach K, Meinel FG, Braunagel M, Von Berg J, Eickelberg O, Reiser MF, Pfeifer F, Meiners S, Herzen J (2017) X-ray dark-field radiography-in-vivo diagnosis of lung cancer in mice. Sci Rep 7(1):402
Kagias M, Wang Z, Guzenko VA, David C, Stampanoni M, Jefimovs K (2018) Fabrication of Au gratings by seedless electroplating for X-ray grating interferometry. Mater Sci Semicond Process 15:215
Ruiz-Yaniz M, Koch F, Zanette I, Rack A, Meyer P, Kunka D, Hipp A, Mohr J, Pfeiffer F (2015) X-ray grating interferometry at photon energies over 180 kev. Appl Phys Lett 106(15):151105
Sarapata A, Willner M, Walter M, Duttenhofer T, Kaiser K, Meyer P, Braun C, Fingerle A, Noël PB, Pfeiffer F, Herzen J (2015) Quantitative imaging using high-energy X-ray phase-contrast CT with a 70 kvp polychromatic X-ray spectrum. Opt Express 23(1):523. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.23.000523
Thüring T, Abis M, Wang Z, David C, Stampanoni M (2014) X-ray phase-contrast imaging at 100 kev on a conventional source. Sci Rep 4:5198
Miao H, Panna A, Gomella AA, Bennett EE, Znati S, Chen L, Wen H (2016) A universal moiré effect and application in X-ray phase-contrast imaging. Nat Phys 12:830. https://doi.org/10.1038/NPHYS3734
Kagias M, Wang Z, Jefimovs K, Stampanoni M (2017) Dual phase grating interferometer for tunable dark-field sensitivity. Appl Phys Lett 110(1):014105. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4973520
Bopp J, Gallersdörfer M, Ludwig V, Seifert M, Maier A, Anton G, Riess C (2018) Phasenkontrast Röntgen mit 2 Phasengittern und medizinisch relevanten Detektoren. Bildverarb für die Med 18:170
Bopp J, Ludwig V, Gallersdörfer M, Seifert M, Pelzer G, Maier A, Anton G, Riess C (2018) Towards a dual phase grating interferometer on clinical hardware. In: Medical imaging 2018: physics of medical imaging, vol 10573. International Society for Optics and Photonics, p 1057321
Talbot HF (1836) LXXVI. Facts relating to optical science No. IV. Lond Edinb Philos Mag J Sci 9(56):401
Takeda M, Ina H, Kobayashi S (1982) Fourier-transform method of fringe-pattern analysis for computer-based topography and interferometry. JosA 72(1):156
Bevins N, Zambelli J, Li K, Qi Z, Chen GH (2012) Multicontrast X-ray computed tomography imaging using Talbot–Lau interferometry without phase stepping. Med Phys 39(1):424
Ritter A, Bartl P, Bayer F, Gödel KC, Haas W, Michel T, Pelzer G, Rieger J, Weber T, Zang A, Anton G (2014) Simulation framework for coherent and incoherent X-ray imaging and its application in Talbot–Lau dark-field imaging. Opt Express 22(19):23276
Jahns J, Lohmann AW (1979) The Lau effect (a diffraction experiment with incoherent illumination). Opt Commun 28(3):263–267
Miller SR, Gaysinskiy V, Shestakova I, Nagarkar VV (2005). In: Penetrating radiation systems and applications VII, vol 5923. International Society for Optics and Photonics, p 59230F
Dudak J, Zemlicka J, Karch J, Hermanova Z, Kvacek J, Krejci F (2017) Microtomography with photon counting detectors: improving the quality of tomographic reconstruction by voxel-space oversampling. J Instrum 12(01):C01060
Rieger J, Meyer P, Pelzer G, Weber T, Michel T, Mohr J, Anton G (2016) Designing the phase grating for Talbot–Lau phase-contrast imaging systems: a simulation and experiment study. Opt Express 24(12):13357
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge funding by Siemens Healthineers, the German Research Foundation (DFG), and the International Max Planck Research School for the Physics of Light. Funding was provided by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Grant No. 289363653.)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
This article does not contain patient data.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bopp, J., Ludwig, V., Seifert, M. et al. Simulation study on X-ray phase contrast imaging with dual-phase gratings. Int J CARS 14, 3–10 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-018-1872-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-018-1872-x