Abstract
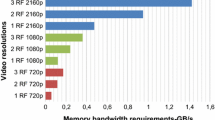
Video-coding systems require a large external memory bandwidth to encode a single video frame. Many modules of the current video encoders must access the external memory to read and write data resulting in large power consumption, since memory-related power is dominant in current digital systems. Moreover, external memory access represents an important performance bottleneck in current multimedia systems. In this sense, this article presents the Reference Frame Context Adaptive Variable-Length Coder (RFCAVLC), which is a low-complexity lossless solution to compress the reference data before storing them in the external memory. The proposed approach is based on Huffman codes and employs eight static code tables to avoid the cost of the on-the-fly statistical analysis. The best table to encode each block is selected at run time using a context evaluation, resulting in a context-adaptive configuration. The proposed RFCAVLC reaches an average compression ratio superior to 32 % for the evaluated video sequences. The RFCAVLC architectures, encoder, and decoder were designed and synthesized targeting FPGA and 65 nm TSMC standard cell library. The RFCAVLC design is able to reach real-time encoding for WQSXGA (3,200 × 2,048 pixels) at 33 fps. The RFCAVLC also achieves power savings related to external memory communication that exceed 30 % when processing HD 1,080p videos at 30 fps.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
ISO/IEC: International Organization for Standardization. ISO/IEC 14496-10 mpeg-4 part 10 information technology—coding of audio-visual objects—part 10: advanced video coding. Technical Report 2012
Wiegand, T., Sullivan, G.J., Bjontegaard, G., Luthra, A.: Overview of the H.264/AVC video coding standard. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 13(7), 560–576 (2003)
Sullivan, G.J., Wiegand, T.: Video compression—from concepts to the H.264/AVC standard. Proc. IEEE 93(1), 18–31 (2005)
ITU-T Recommendation H.265: high efficiency video coding, audiovisual and multimedia systems (2013)
Ren, J., Kehtarnavaz, N.: Fast adaptive termination mode selection for H.264 scalable video coding. J. Real-Time Image Process. 4, 13–21 (2009)
Correa, G., Assuncao, P., Agostini, L., Silva Cruz, L.: “Complexity scalability for real-time HEVC encoders”. J. Real-Time Image Process., pp 1–16 (2014)
Zatt, B., Shafique, M., Sampaio, F., Agostini, L., Bampi, S., Henkel, J.: “Run-time adaptive energy-aware motion and disparity estimation in multiview video coding”. In: IEEE DAC, pp. 1026–1031 (2011)
Li, Y., Zhang, T.: Reducing DRAM image data access energy consumption in video processing. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 14(2), 303–313 (2012)
Kim, S., Han, J., Kim, J.: An efficient scheme for motion estimation using multireference frames in H.264/AVC. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 8(3), 457–466 (2006)
Vetro, A., Wiegand, T., Sullivan, G.J.: Overview of the stereo and multiview video coding extensions of the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC standard. Proc. IEEE 99(4), 626–642 (2011)
Jaspers, E., With, P.: Bandwidth reduction for video processing in consumer systems. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 47(4), 885–894 (2001)
Tuan, J., Chang, T., Jen, C.: On the data reuse and memory bandwidth analysis for full-search block-matching VLSI architecture. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 12(1), 61–72 (2002)
Grellert, M., Sampaio, F., Mattos, J.C.B., Agostini, L: “A multilevel data reuse scheme for motion estimation and its VLSI design”. In: IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), pp. 583–586 (2011)
Chen, C., Huang, C., Chen, Y., Chen, L.: Level C+ data reuse scheme for motion estimation with corresponding coding orders. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 16(4), 553–558 (2006)
Budagavi, M., Zhou, M.: “Video coding using compressed reference frames”. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, pp. 1165–1168 (2008)
Gupte, D., Amrutur, B., Mehendale, M., Rao, A., Budagavi, M.: Memory bandwidth and power reduction using lossy reference frame compression in video encoding. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 21(2), 225–230 (2011)
Ivanov, Y., Moloney, D.: “Reference frame compression using embedded reconstruction patterns for H.264/AVC decoder”. In: International Conference on Digital Telecommunications, pp. 168–173, (2008)
Bao, X., Zhou, D., Goto S.: “A lossless frame recompression scheme for reducing DRAM power in video encoding”. In: IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 677–680 (2010)
Yng, T., Lee, B., Yoo, H.: A low complexity and lossless frame memory compression for display devices. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 54, 1453–1458 (2008)
Guo, L., Zhou, D., Goto, S.: “Lossless embedded compression using multi-mode DPCM & averaging prediction for HEVC-like video codec”. In: European Signal Processing Conference, pp. 1–5 (2013)
Cheng, C., Tseng, P., Chen, L.: Multimode embedded compression codec engine for power-aware video coding system. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 19(2), 141–150 (2009)
Song, T., Shimamoto, T.: Reference frame data compression method for H.264/AVC. IEICE Electron. Express 4(3), 121–126 (2007)
Kim, J., Kyung, C.: A lossless embedded compression using significant bit truncation for HD video coding. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 20(6), 848–860 (2010)
Lee, Y., Chen, C., You, Y.: Design of VLSI architecture of autocorrelation-based lossless recompression engine for memory-efficient video coding systems. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 33(2), 459–482 (2014)
Sze, V., Finchelstein, D.F., Sinangil, M.E., Chandrakasan, A.P.: A 0.7-V 1.8-mW H.264/AVC 720p Video Decoder. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 44(11), 2943–2956 (2009)
Tikekar, M., Huang, C.-T., Juvekar, C., Sze, V., Chandrakasan, A.P.: A 249-Mpixel/s HEVC Video-Decoder Chip for 4 K Ultra-HD Applications. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 49(1), 61–72 (2014)
Silveira, D., Sanchez, G., Grellert, M., Possani, V., Agostini, L.: “Memory bandwidth reduction in video coding systems through context adaptive lossless reference frame compression”. In: IEEE Southern Programmable Logic Conference (2012)
Silveira, D., Porto, M., Agostini, L.: “A lossless approach for external memory bandwidth reduction in video coding systems and its VLSI architecture”. In: IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (2013)
Xiph.org: test media, available at http://media.xiph.org/video/derf/. Jan 2012
Huffman, D.A.: “A method for the construction of minimum-redundancy codes”. In: Proceedings of the I.R.E, pp. 1098–1101 (1952)
Salomon, D.: Data compression—the complete reference, 4th edn. Springer, London (2007)
Sullivan, G.J., Topiwala, P., Luthra, A.: “The H.264/AVC advanced video coding standard: overview and introduction to the fidelity range extensions”. In: SPIE Conference on Applications of Digital Image Processing (2004)
Altera Corporation: FPGA CPLD and ASIC from Altera, available at http://www.altera.com/. Nov 2012
Synopsys, “Design compiler user guide” (2010)
Micron MT47H32M16HR: 512 Mb DDR2 SDRAM, available: http://www.micron.com
Micron Technical Note: Calculating Memory System Power for DDR2, available: http://www.micron.com
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silveira, D., Zatt, B., Agostini, L. et al. Reference frame context-adaptive variable-length coder: a real-time hardware-friendly approach for lossless external memory bandwidth reduction in current video-coding systems. J Real-Time Image Proc 14, 249–265 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-014-0443-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-014-0443-9