Abstract
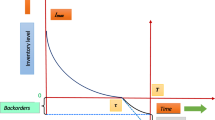
In real life situation, it is observed that demand of an item depends on the length of the credit period offered by the retailer to his customers which has a positive impact on demand of an item. But the impact of credit period on demand has received a very little attention by researchers. Furthermore, by allowing shortages as backlogging, the impact on the cost from the decay of the products can be balanced out. A profitable decision policy between a supplier and the retailers can be characterized by an agreement on the permissible delay in payments. Recently, Jaggi et al. (Eur J Oper Res 190:130–135, 2008) have investigated the impact of credit linked demand on the retailer’s optimal replenishment policy. The objective of this study is to extend Jaggi et al. (Eur J Oper Res 190:130–135, 2008) model by incorporating deterioration and backlogging. That is, we formulate a two-echelon inventory model for deteriorating items with credit period dependent demand including shortages under two-level trade credit financing and determine the retailer’s optimal replenishment policy when both the supplier as well as the retailer offers the credit period to stimulate customer demand. Furthermore, we establish some useful theorems to characterize the optimal solution and provide an easy and useful computational algorithm with the help of computer code using the software Matlab 7.0 to determine the optimal shortage point, cycle length, ordering quantity and credit period. A numerical example is included to illustrate the solution procedure for the mathematical model developed. Finally, we implement sensitivity analysis of the optimal solution with respect to the major parameters of the system and obtain some important managerial insights.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goswami A., Chaudhuri K.S.: An EOQ model for an inventory with linear trend in demand and finite rate of replenishment considering shortages. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 22, 181–187 (1991)
Chakrabarti T., Chaudhuri K.S.: An EOQ model for deteriorating items with a linear trend in demand and shortages in all cycles. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 49, 205–213 (1997)
Giri B.C., Chakrabarti T., Chaudhuri K.S.: A note on a lot sizing heuristic for deteriorating items with time varying demands and shortages. Comput. Oper. Res. 27, 495–505 (2000)
Jalan A.K., Chaudhuri K.S.: Structural properties of inventory systems with deterioration and trended demand. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 27, 851–855 (1999)
Hariga M.A., Benkherouf L.: Optimal and heuristic inventory replenishment models for deteriorating items with exponential time-varying demand. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 79, 123–137 (1994)
Wee H.M.: A deterministic lot size inventory model for deteriorating items with shortages and a declining market. Comput. Oper. Res. 22, 345–356 (1995)
Wee H.M.: A replenishment policy for item with a price dependent and a varying rate of deterioration. Prod. Plan. Control 8, 494–499 (1997)
Chakrabarti T., Giri B.C., Chaudhuri K.S.: An Economic order quantity model for items with Weibull distribution deterioration, shortages and trended demand. Comput. Oper. Res. 25, 649–657 (1998)
Lin C., Tan B., Lee W.C.: An EOQ model for deteriorating items with time varying demands and shortages. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 31, 391–400 (2000)
Goyal S.K., Gin B.C.: Recent trends in modeling of deteriorating inventory. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 134, 1–16 (2001)
Aggarwal S.P., Jaggi C.K.: Ordering policies of deteriorating items under permissible delay in payments. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 46, 658–662 (1995)
Chang H.J., Hung C.H., Dye C.Y.: An inventory model for deteriorating items with linear trend demand under conditions of permissible delay in payment. Prod. Plan. Control 12, 274–282 (2001)
Dye C.Y.: A deteriorating inventory model with stock dependent rate and partial backlogging under conditions of permissible delay in payments. Opsearch 39, 189–198 (2002)
Ouyang L.Y., Teng J.T., Chen L.H.: Optimal ordering policy for deteriorating items with partial backlogging under permissible delay in payments. J. Global Optim. 34, 245–271 (2006)
Tsao Y.C., Sheen G.J.: Dynamic pricing, promotion and replenishment policies for a deteriorating item under permissible delay in payments. Comput. Oper. Res. 35, 3562–3580 (2008)
Song X., Cai X.: On optimal payment time for a retailer under permitted delay of payment by the wholesaler. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 103, 246–251 (2006)
Soni H., Shah N.H: Optimal ordering policy for stock-dependent demand under progressive payment scheme. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 184, 91–100 (2008)
Chung K.J., Goyal S.K., Huang Y.F.: The optimal inventory policies under permissible delay in payments depending on the ordering quantity. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 95, 203–213 (2005)
Huang Y.F.: Optimal retailer’s ordering policies in the EOQ model under tade credit financing. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 54, 1011–1015 (2003)
Jaggi C.K., Goyal S.K., Goel S.K.: Retailer’s optimal replenishment decisions with credit linked demand under permissible delay in payments. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 190, 130–135 (2008)
Abad P.L.: Optimal pricing and lot sizing under conditions of partial backordering. Manag. Sci. 42, 1093–1104 (1996)
Abad P.L.: Optimal pricing and order size for a reseller under partial backordering. Comput. Oper. Res. 28, 53–65 (2001)
Chang H.J., Dye C.Y.: An EOQ model for deteriorating items with time varying demand and partial backlogging. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 50, 1176–1182 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Annadurai, K., Uthayakumar, R. Two-echelon inventory model for deteriorating items with credit period dependent demand including shortages under trade credit. Optim Lett 7, 1227–1249 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-012-0499-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-012-0499-z