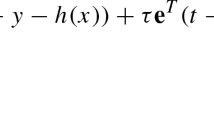Abstract
We consider the linear complementarity problem (LCP): \(Mz+q\ge 0, z\ge 0, z^{\prime }(Mz+q)=0\) as an absolute value equation (AVE): \((M+I)z+q=|(M-I)z+q|\), where \(M\) is an \(n\times n\) square matrix and \(I\) is the identity matrix. We propose a concave minimization algorithm for solving (AVE) that consists of solving a few linear programs, typically two. The algorithm was tested on 500 consecutively generated random solvable instances of the LCP with \(n=10, 50, 100, 500\) and 1,000. The algorithm solved \(100\,\%\) of the test problems to an accuracy of \(10^{-8}\) by solving 2 or less linear programs per LCP problem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chung, S.-J.: NP-completeness of the linear complementarity problem. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 60, 393–399 (1989)
Cottle, R.W., Dantzig, G.: Complementary pivot theory of mathematical programming. Linear Algebra Appl. 1, 103–125 (1968)
Cottle, R.W., Pang, J.-S., Stone, R.E.: The Linear Complementarity Problem. Academic Press, New York (1992)
ILOG, Incline Village, Nevada. ILOG CPLEX 9.0 User’s Manual. http://www.ilog.com/products/cplex/ (2003)
Mangasarian, O. L.: Solution of general linear complementarity problems via nondifferentiable concave minimization. Acta Mathematica Vietnamica, 22(1):199–205. ftp://ftp.cs.wisc.edu/math-prog/tech-reports/96-10.ps (1997)
Mangasarian, O. L.: Absolute value equation solution via concave minimization. Optimization Lett. 1(1), 3–8. ftp://ftp.cs.wisc.edu/pub/dmi/tech-reports/06-02.pdf (2007)
Mangasarian, O. L.: Absolute value programming. Comput. Optim. Appl. 36(1), 43–53. ftp://ftp.cs.wisc.edu/pub/dmi/tech-reports/05-04.ps (2007)
Mangasarian, O. L.: A generalized Newton method for absolute value equations. Technical Report 08–01, Data Mining Institute, Computer Sciences Department, University of Wisconsin, May 2008. ftp://ftp.cs.wisc.edu/pub/dmi/tech-reports/08-01.pdf. Optimization Lett. 3(1), 2009, 101–108. Online version: http://www.springerlink.com/content/c076875254r7tn38/
Mangasarian, O. L.: Absolute value equation solution via dual complementarity. Technical report, Data Mining Institute, Computer Sciences Department, University of Wisconsin, Madison, Wisconsin, September 2011. Optimization Lett. 7(4), 625–63. ftp://ftp.cs.wisc.edu/pub/dmi/tech-reports/11-03.pdf (2013)
Mangasarian, O. L.: Primal-dual bilinear programming solution of the absolute value equation. Technical report, Data Mining Institute, Computer Sciences Department, University of Wisconsin, Madison, Wisconsin, February 2011. Optimization Lett. 6(7), 1527–1533. ftp://ftp.cs.wisc.edu/pub/dmi/tech-reports/11-01.pdf (2012)
Mangasarian, O. L.: Absolute value equation solution via linear programming. Technical Report 13–01, Data Mining Institute, Computer Sciences Department, University of Wisconsin, Madison, Wisconsin, February. ftp://ftp.cs.wisc.edu/pub/dmi/tech-reports/13-01.pdf (2013)
Mangasarian, O. L., Meyer, R. R.: Absolute value equations. Linear Algebra Appl. 419, 359–367. ftp://ftp.cs.wisc.edu/pub/dmi/tech-reports/05-06.pdf (2006)
MATLAB. User’s Guide. The MathWorks, Inc., Natick, pp. 1994–2006. http://www.mathworks.com
Murty, K.G.: Linear Complementarity, Linear and Nonlinear Programming. Helderman-Verlag, Berlin (1988)
Polyak, B.T.: Introduction to Optimization. Optimization Software, Inc. Publications Division, New York (1987)
Rockafellar, R.T.: Convex Analysis. Princeton University Press, Princeton (1970)
Acknowledgments
The research described here, based on Data Mining Institute Report 13-02, March 2013, was supported by the Microsoft Corporation and ExxonMobil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mangasarian, O.L. Linear complementarity as absolute value equation solution. Optim Lett 8, 1529–1534 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-013-0656-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-013-0656-z