Abstract
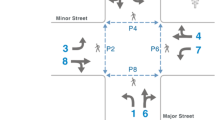
In this paper, the problem of setting traffic light cycles at crossroads and intersections is considered in order to reduce traffic congestion by minimizing total vehicle waiting time. In general, a signal light cycle should have the least number of phases. A method to determine the family \(\wp \) of all discrete cycle phasing systems with the minimum number of phases is presented. The aim is to detect from among all the components of \(\wp \) the most appropriate phasing sequence for traffic control corresponding to a current traffic situation, taking into account the activity of all pedestrian crosswalks at the intersection. The method is applied to both a typical and a complex multi-cross intersection. The problem, dealing with traffic movements and the conflicting relations that arise, is stated within the framework of graph theory.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aho, A., Hopcroft, J., Ullmanm, J.: Data Structures and Algorithms. Addison-Wesley, Boston (1987)
Alexiou, D., Katsavounis, S.: Determining the minimum number of ware-houses and their space-size for storing compatible items, optimization theory, decision making, and operations research applications. In: Springer Proceedings in Mathematics & Statistics, pp. 189–198 (2013)
Christofides, N.: Graph Theory. An Algorithmic Approach. Academic Press, New York (1975)
Diakaki, C., Papageorgiou, M., Aboudolas, K.: A multivariable regulator approach to traffic-responsive network-wide signal control. Control Eng. Pract. 10(2), 183–195 (2002)
Garey, M.R., Johnson, D.S.: Computer Intractability: A Guide to the theory of NP-Completeness. Freeman, San Francisco (1979)
Harary, F.: Graph Theory. Addison Wesley, Boston (1969)
Jinwoo, L., Baher, A., Amer, S., Eui-Hwan, C.: Real-time optimization for adaptive traffic signal control using genetic algorithms. J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 9(3) (2005)
Kouvelas, A., Aboudolas, K., Papageorgiou, M., Kosmatopoulos, E.B.: IEEE transactions on a hybrid strategy for real-time traffic signal control of urban road networks, intelligent transportation systems, vol. 12, no. 3 (2011)
Leena, S., Sudhanshu, T., Himakshi, A.: Time optimization for traffic signal control using genetic algorithm. Int. J. Recent Trends Eng. 2(2). Academic Publisher, New York (2009)
Michaels, J.G., Kenneth, H.R.: Application of Discrete Mathematics. McGraw-Hill Inc, New York (1991)
Mathew, T., Krishna R.: Traffic signal design-I, Chap. 41, NPTEL (2006). www.cdeep.iitb.ac.in/nptel/Civil%20Engineering/Transportation%20Engg%201/41-Ltexhtml/nptel_ceTEI_L41.pdf
Opsut, R.J., Roberts, F.S.: I-Colorings. I-Phasings and I-intersection assignments for graphs, and their applications. Networks 13, 327–345 (1983b)
Raychaudhuri, A.: Optimal multiple interval assignments in frequency assignment and traffic phasing. Discrete Appl. Math. 40(3), 319–332 (1992)
Roberts, F.S.: Some applications of graph theory. Department of Mathematics and DIMACS, Rutgers University, draft October 1 (2000). http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.76.5815&rep=rep1&type=pdf
Stoffers, K.E.: Scheduling of traffic lights–a new approach. Transport. Res. 2, 199–234 (1968)
Traffic Signal Design, Section 7, Phasing and Signal Groups, Department of Transportation, Minnesota (2013). http://www.dot.state.mn.us/trafficeng/publ/signaloperations/2013_Signal_Opt_and_Timing_Manual.pdf
Traffic Signal Design, Section7, Phasing and Signal Group display sequence, Roads and Traffic (2011). http://www.rms.nsw.gov.au/documents/business-industry/partners-and-suppliers/guidelines/complementary-traffic-material/tsdsect7v12-i.pdf
Traffic Signal Guidelines, 2004, Boston Transportation Department, Massachussets. https://www.cityofboston.gov/transportation/pdfs/traf_signal_oper_design_guide.pdf
Traffic Signal Operation Handbook, Texas Transportation Institute, The Texas A&M University System, Research and Technology Implementation Office, Austin, Texas (2009). http://d2dtl5nnlpfr0r.cloudfront.net/tti.tamu.edu/documents/0-5629-P1.pdf
Vogel, A., Goerick, C, von Werner, A.: Evolutionary Algorithms for Optimizing Traffic Signal Operation, ESIT 2000. Aachen, Germany, pp. 14–15 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alexiou, D. Generating the family of all traffic signal light cycles coordinated with pedestrian crosswalks. Optim Lett 10, 473–484 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-015-0871-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-015-0871-x