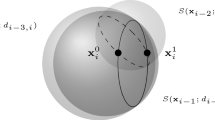
Abstract
A branch-and-prune (BP) algorithm is presented for the discretizable distance geometry problem in \(\mathbb {R}^K\) with inexact distances. The algorithm consists in a sequential buildup procedure where possible positions for each new point to be localized are computed by using distances to at least K previously placed reference points and solving a system of quadratic equations. Such a system is solved in a least-squares sense, by finding the best positive semidefinite rank K approximation for an induced Gram matrix. When only K references are available, a second candidate position is obtained by reflecting the least-squares solution through the hyperplane defined by the reference points. This leads to a search tree which is explored by BP, where infeasible branches are pruned on the basis of Schoenberg’s theorem. In order to study the influence of the noise level, numerical results on some instances with distances perturbed by a small additive noise are presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
As detailed in [19], the squared volume of the simplex defined by \(\{v_{i-K}, \dots , v_{i-1} \}\) is directly proportional to the absolute value of \(CM(\{v_{i-K}, \dots , v_{i-1} \})\).
This sort of matrix is also known in the literature as nonnegative hollow matrix [1].
In fact, if the problem is only to determine whether D is an EDM, without obtaining a realization, it is enough to obtain the smallest eigenvalue of G, e.g., by the inverse shifted power method.
Recall the Frobenius norm of a matrix A is given by \(\Vert A \Vert _F^2 = \sum _{i} \sum _{j} a_{ij}^2 = \text {trace}(A^T A)\).
References
Al-Homidan, S., Wolkowicz, H.: Approximate and exact completion problems for Euclidean distance matrices using semidefinite programming. Linear Algebra Appl. 406, 109–141 (2005)
Anderson, B.D.O., Shames, I., Mao, G., Fidan, B.: Formal theory of noisy sensor network localization SIAM. J. Discrete Math. 24, 684–698 (2010)
Borg, I., Groenen, P.J.F.: Modern Multidimensional Scaling: Theory and Applications, 2nd edn. Springer Series in Statistics. Springer, New York (2005)
Cassioli, A., Gunluk, O., Lavor, C., Liberti, L.: Discretization vertex orders in distance geometry. Discrete Appl. Math. 197, 27–41 (2015)
Drusvyatskiy, D., Krislock, N., Cheung Voronin, Y.-L., Wolkowicz, H.: Noisy Euclidean distance realization: robust facial reduction and the Pareto frontier. SIAM J. Optim. 27(4), 2301–2331 (2017)
Dokmanic, I., Parhizkar, R., Ranieri, J., Vetterli, M.: Euclidean distance matrices: essential theory, algorithms, and applications. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 32(6), 12–30 (2015)
Dong, Q., Wu, Z.: A linear-time algorithm for solving the molecular distance geometry problem with exact inter-atomic distances. J. Glob. Optim. 22, 365–375 (2002)
Dong, Q., Wu, Z.: A geometric build-up algorithm for solving the molecular distance geometry problem with sparse distance data. J. Glob. Optim. 26(3), 321–333 (2003)
Eckart, C., Young, G.: The approximation of one matrix by another of lower rank. Psychometrika 1, 211–218 (1936)
Gonçalves, D.S., Mucherino, A.: Discretization orders and efficient computation of cartesian coordinates for distance geometry. Optim. Lett. 8, 2111–2125 (2014)
Gonçalves, D.S., Mucherino, A.: Optimal partial discretization orders for discretizable distance geometry. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 23, 947–967 (2016)
Gonçalves, D.S., Mucherino, A., Lavor, C., Liberti, L.: Recent advances on the interval distance geometry problem. J. Glob. Optim. 69, 525–545 (2017)
Krislock, N., Wolkowicz, H.: Explicit sensor network localization using semidefinite representations and facial reductions. SIAM J. Optim. 20, 2679–2708 (2010)
Lavor, C., Lee, J., John, A.L.S., Liberti, L., Mucherino, A., Sviridenko, M.: Discretization orders for distance geometry problems. Optim. Lett. 6, 783–796 (2012)
Lavor, C., Liberti, L., Maculan, N., Mucherino, A.: The discretizable molecular distance geometry problem. Comput. Optim. Appl. 52, 115–146 (2012)
Lavor, C., Liberti, L., Mucherino, A.: The interval branch-and-prune algorithm for the discretizable molecular distance geometry problem with inexact distances. J. Glob. Optim. 56, 855–871 (2013)
Liberti, L., Lavor, C., Maculan, N.: A branch-and-prune algorithm for the molecular distance geometry problem. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 15, 1–17 (2008)
Liberti, L., Masson, B., Lee, J., Lavor, C., Mucherino, A.: On the number of realizations of certain Henneberg graphs arising in protein conformation. Discrete Appl. Math. 165, 213–232 (2014)
Liberti, L., Lavor, C., Maculan, N., Mucherino, A.: Euclidean distance geometry and applications. SIAM Rev. 56, 3–69 (2014)
Luo, X., Wu, Z.: Least-squares approximations in geometric buildup for solving distance geometry problems. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 149, 580–598 (2011)
Mathar, R.: The best Euclidean fit to a given distance matrix in prescribed dimensions. Linear Algebra Appl. 67, 1–6 (1985)
Mucherino, A., Lavor, C., Liberti, L.: The discretizable distance geometry problem. Optim. Lett. 6, 1671–1686 (2012)
Mucherino, A., Liberti, L., Lavor, C.: MD-jeep: an implementation of a branch and prune algorithm for distance geometry problems, lectures notes in computer science 6327. In: Fukuda, K. et al. (eds.) Proceedings of the 3rd International Congress on Mathematical Software (ICMS10), Kobe, Japan, pp. 186–197 (2010)
Saxe, J.B.: Embeddability of weighted graphs in \(k\)-space is strongly NP-hard. In: Proceedings of 17th Allerton Conference in Communications, Control and Computing, pp. 480–489. Monticello, IL (1979)
Schoenberg, I.: Remarks to Maurice Fréchet’s article “Sur la définition axiomatique d’une classe d’espaces distanciés vectoriellement applicable sur l’espace de Hilbert”. Ann. Math. 36, 724–732 (1935)
Schönemann, P.H.: A generalized solution of the orthogonal procrustes problem. Psychometrika 31, 1–10 (1966)
Sit, A., Wu, Z., Yuan, Y.: A geometric buildup algorithm for the solution of the distance geometry problem using least-squares approximation. Bull. Math. Biol. 71, 1914–1933 (2009)
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank Prof. Nathan Krislock for helping with SNLSDPClique package. I am grateful to the anonymous reviewers for their comments and suggestions that helped to improve this work. I also thank the Brazilian research agency CNPq for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gonçalves, D.S. A least-squares approach for discretizable distance geometry problems with inexact distances. Optim Lett 14, 423–437 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-017-1225-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-017-1225-7