Abstract
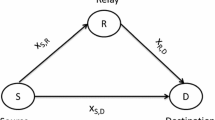
Wireless cooperative communications require appropriate power allocation (PA) between the source and relay nodes. In selfish cooperative communication networks, two partner user nodes could help relaying information for each other, but each user node has the incentive to consume his power solely to decrease its own symbol error rate (SER) at the receiver. In this paper, we propose a fair and efficient PA scheme for the decode-and-forward cooperation protocol in selfish cooperative relay networks. We formulate this PA problem as a two-user cooperative bargaining game, and use Nash bargaining solution (NBS) to achieve a win-win strategy for both partner users. Simulation results indicate that the NBS is fair in that the degree of cooperation of a user only depends on how much contribution its partner can make to decrease its SER at the receiver, and efficient in the sense that the SER performance of both users could be improved through the game.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. N. Laneman, D. N. C. Tse, G. M. Wornell. Cooperative diversity in wireless networks: Efficient protocols and outage behavior. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, vol. 50, no. 12, pp. 3062–3080, 2004.
W. F. Su, A. K. Sadek, K. J. R. Liu. SER performance analysis and optimum power allocation for decode-and-forward cooperation protocol in wireless networks. In Proceedings of IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, IEEE, New Orleans, USA, vol. 2, pp. 984–989, 2005.
Z. G. Cao, X. G. Yang. Coalition formation in weighted simple-majority games under proportional payoff allocation rules. International Journal of Automation and Computing, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 217–222, 2009.
S. M. Lucas. Computational intelligence and games: Challenges and opportunities. International Journal of Automation and Computing, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 45–57, 2008.
G. P. Zhang, L. Cong, E. Ding, K. Yang, X. D. Yang. Fair and efficient resource sharing for selfish cooperative communication networks using cooperative game theory. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Communications, IEEE, Tokyo, Japan, pp. 1–5, 2011.
S. Q. Xu, Q. Y. Zhang, W. Lin. PSO-based OFDM adaptive power and bit allocation for multiuser cognitive radio system. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing, IEEE, Beijing, PRC, pp. 1–4, 2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 60972059), Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (Nos. 2010QNA27 and 2011QNB26), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 20100481185), the Ph.D. Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (Nos. 20090095120013 and 20110095120006), Talent Introduction Program, and Young Teacher Sailing Program of China University of Mining and Technology.
Guo-Peng Zhang graduated from Xuzhou Normal University, PRC in 2001. He received the M. Sc. degree from South China Normal University in 2005 and the Ph.D. degree from the Xidian University, PRC in 2009. He is currently a lecturer at the Internet of Things Research Center, China University of Mining and Technology (CUMT), and works as postdoctoral fellow under the direction of Prof. E. J. Ding.
His research interests include micro and macro economics, game theory, wireless OFDM/MIMO communication systems, cooperative communication networks, sensor networks and cognitive radio networks.
Peng Liu received his B. Sc. and M. Sc. degrees in computer science from Nanjing University, PRC in 1999 and 2002, respectively. Currently, he is an associate professor in China University of Mining and Technology (CUMT) and pursuing his doctor degree in information and communication engineering.
His research interests include wireless sensor networks and cloud computing.
En-Jie Ding received his M. Sc. and Ph.D. degrees both in information and communication engineering from China University of Mining and Technology (CUMT). He is currently a professor at Internet of Things Research Center of CUMT.
His research interests include wireless sensor networks and their applications in coal mines.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, GP., Liu, P. & Ding, EJ. Bargaining game theoretic power control in selfish cooperative relay networks. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 9, 221–224 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-012-0637-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-012-0637-1