Abstract
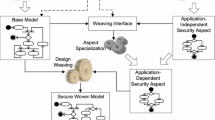
Crossutting concerns such as logging, security, and transaction, are well supported in the programming level by aspect-oriented programming technologies. However, addressing these issues in the high-level architecture design still remains open. This paper presents a novel approach to supporting crosscutting concern modelling in the software architecture design of component-based systems. We introduce a new element named “Aspect” into our architecture description language, ABC/ADL, to clearly model the behavior of crosscutting concerns. Aspect is the first class entity as Component and Connector in ABC/ADL. ABC/ADL Connectors provide the weaving points where the component and aspect crosscut. This approach effectively enables “separation of concerns” in high-level architecture design, and facilitates black-box reuse of COTS components.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perry D E, Wolf A L. Foundations for the study of software architecture. ACM SIGSOFT Software Engineering Notes, 1992, 17(4): 40–52
Marin M, Moonen L., van Deursen A. A classification of crosscutting concerns. In: Proceedings of 21st IEEE International Conference on Software Maintenance (ICSM 2005), Budapest, Hungary, Sept 2005. 673–676
Chen F, Wang Q, Mei H, et al. An architecture-based approach for omponent-oriented development. In: Proceedings of 26th International Computer Software and Applications Conference (COMPSAC’02), Los Alamitos, California, Aug 2002. 450–455
Mei H, Chen F, Wang Q, et al. ABC/ADL: An ADL supporting component composition. In: Proceedings of 4th International Conference on Formal Engineering Methods (ICFEM’02), Shanghai, China, Oct 2002. 38–47
Kiczales G, Lamping J, Mendhekar A, et al. Aspect oriented programming. In: Proceedings of 11th European Conference on Object-Oriented Programming (ECOOP’97), Finland, Jun 1997. 220–243
Duzan G, Loyall J, Schantz R, et al. Building adaptive distributed applications with middleware and aspects. In: Proceedings of 3rd International Conference on Aspect-oriented Software Developmen (AOSD’04), Lancaster, UK, Mar 2004. 66–73
Krger I H, Mathew R, Meisinger M. Efficient exploration of service-oriented architectures using aspects. In: Proceedings of 28th International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE 2006), May 2006. Shanghai, China 62–71.
Pawlak R, Seinturier L, Duchien L, et al. JAC: An aspect-based distributed dynamic framework. Software-Practice and Experience, 2004, 34: 1119–1148
Harrison W, Ossher H, Sutton S, et al. Supporting aspect-oriented software development with the concern manipulation environment. IBM Systems Journal, 2005, 44(2): 309–318
Taylor R N, Medvidovic N, Anderson K M, et al. A component-and message-based architectural style for GUI software. IEEE. Trans. Software Eng, 1996, 22(6): 390–406
Shaw M, DeLine R, Klein D V, et al. Abstractions for software architecture and tools to support them. IEEE Trans Software Eng. 1995, 21(4): 314–335
Allen R, Garlan D. A formal basis for architectural connection. ACM Transactions on Software Engineering and Methodology, 1997, 6(3): 213–249
Luckham D C, Vera J. An event-based architecture definition language. IEEE Trans Software Eng, 1995, 21(9): 717–734
Garlan D, Monroe R T, Wile D. Acme: Architectural description of component-based systems. In: Leavens G T, Sitaraman M, eds. Foundations of Component-Based Systems. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2000, 47–68
Palma K, Eterovic Y, Murillo J M. Extending the Rapide ADL to specify aspect oriented software architectures. In: Proceedings of 15th International Conference on Software Engineering and Data Engineering (SEDE 2006), Los Angeles, USA, Jul 2006, 170–177
Pinto M, Fuentes L, Troya J M. DAOP-ADL: An architecture description language for dynamic component and aspect-based development. In: Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Generative Programming and Component Engineering (GPCE 2003), Erfurt, Germany, Sep 2003, 118–137
Prez J, Ramos I, Martłnez J J, et al. PRISMA: Towards quality, aspect oriented and dynamic software architectures. In: Proceedings of 3rd International Conference on Quality Software (QSIC 2003), Dallas, USA, Nov 2003. 59–66
Pessemier N, Seinturier L, Duchien L. Components ADL and AOP: Towards a common approach. In: Workshop ECOOP on Reflection, AOP and Meta-Data for Software Evolution (RAM-SE 2004), Oslo, Norway, Jun 2004
Huang G, Wang Q, Cao D, et al. PKUAS: A domain-oriented component operating platform. Cta Electronica Sinica, 2002, 30(12a): 39–43
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, D., Mei, H. & Zhou, M. Supporting crosscutting concern modelling in software architecture design. Front. Comput. Sc. China 1, 50–57 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-007-0006-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-007-0006-3