Abstract
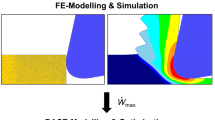
This paper deals with machine tool components for use in a small machine tool for micro machining. The goal is an automated manufacturing process and to reduce manual handling by the operator as far as possible. This includes a miniaturized clamping device for fixing a test workpiece via freezing of water. Using the Finite Element Method, the thermal deformation of the test workpiece made of 100Cr6 could be analyzed as well as the static stiffness and dynamic behavior of the clamping device. Additionally, an automated workpiece supply using electromagnets and a pneumatic cylinder is presented. For extraction of chips, an adapted extraction hood was developed. The paper presents first results of performed Computational Fluid Dynamic simulations regarding velocity and streamlines of particles. Furthermore, a demonstrator of the micro machine tool shows the current installation space, enabled with the developed machine tool components. Here, the machine tool frame is made of CFRP due to its thermal stability.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steinhagen R (2008) Vorstellung eines Konzepts für den Bau von Sondermaschinen für die Mikro-zerspanung. In: Workshop zur Fertigung von kleinen Präzisionsteilen für die Medizintechnik und Analytik, Berlin
Wulfsberg JP, Grimske S, Kohrs P, Kong N Kleine Werkzeuge für kleine Werkstücke, wt werkstattstechnik online, Edition 11/12, Internet: www.werkstattstechnik.de, Springer, pp 887–891
Kämmerer G HSC-Mikrofräsen nach dem Mini-Max-Prinzip. In: Mikroproduktion 02/11. Verlag MIKROvent GmbH, pp 14–19
Verl A, Hoffmeister H-W, Wurst K-H, Heinze T, Gerdes A Kleine Werkzeugmaschine für kleine Werkstücke, wt Werkstatttechnik online, Springer, Edition 11/12, pp 744–749
Hoffmeister H-W, Gerdes A, Verl A, Heinze T Kompakte Maschinenmodule für kleine Werkzeugmaschinen, VDI-Z, Springer-VDI-Verlag, Edition 09/2012, pp 60–63
Grimske S, Röhlig B, Kong N, Wulfsberg JP (2012) Repeatable positioning accuracy of mechanical interfaces for micro manufacturing. In: Proceedings of the 12th euspen international conference, Stockholm
Brinksmeier E, Gläbe E, Brandao C Grindball—Ein innovatives Konzept zum achsenlosen Mikroschleifen, wt Werkstatttechnik online, Springer, Edition 06/12, pp 370–376
Röhlig B, Kong N, Grimske S, Wulfsberg (2012) JP modular workpiece carrier and clamping system for micro machining. In: Proceedings of the 12th euspen international conference, Stockholm
Wulfsberg JP, Lehmann J Spanntechnik für die Mikrofertigung, wt Werkstatttechnik online, Springer, Edition 03/2003, p 146
Hoffmeister H-W, Gerdes A (2011) Mikrostiftschleifen hochlegierter Stähle. In: Jahrbuch Schleifen, Honen, Läppen und Polieren, 65. Edition, Vulkan-Verlag, pp 222–231
Gumz W Zur Berechnung der Fallgeschwindigkeit von Teilchen beliebiger Gestalt, Archiv für die gesamte Wärmetechnik, Edition 01/1950, pp 25–26
Kroeger FR, Swenson CA Absolute linear thermal-expansion measurements on copper and aluminium from 5 to 320 K. J Appl Phys 48. Edition, 1977
Acknowledgments
The authors of this work wish to acknowledge the financial support of the German Research Foundation (DFG) within the Priority Programme 1476 “Small Machine Tools for Small Parts”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoffmeister, HW., Gerdes, A. Development and design of micro machine tool components via numerical simulation. Prod. Eng. Res. Devel. 7, 527–533 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11740-013-0476-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11740-013-0476-0