Abstract
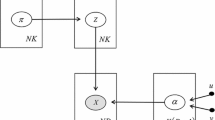
Because of too much dependence on prior assumptions, parametric estimation methods using finite mixture models are sensitive to noise in image segmentation. In this study, we developed a new medical image segmentation method based on non-parametric mixture models with spatial information. First, we designed the non-parametric image mixture models based on the cosine orthogonal sequence and defined the spatial information functions to obtain the spatial neighborhood information. Second, we calculated the orthogonal polynomial coefficients and the mixing ratio of the models using expectation-maximization (EM) algorithm, to classify the images by Bayesian Principle. This method can effectively overcome the problem of model mismatch, restrain noise, and keep the edge property well. In comparison with other methods, our method appears to have a better performance in the segmentation of simulated brain images and computed tomography (CT) images.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- f :
-
Probability distribution function
- X 1, . . . , X N :
-
Independent and identically distributed samples
- e i :
-
The orthogonal basis
- L 2([a, b]):
-
Hilbert orthogonal base of space
- 1/s :
-
The smoothing parameter
- \({(a_{0,j},a_{1,j},\ldots,a_{K_{N_{j}},j})}\) :
-
The estimate of Fourier coefficients of condition probability density function
- \({K_{N_j}}\) :
-
The point of cutoff in the expansion of cosine
- N j :
-
The number of pixels of the jth class
- g(1/s):
-
The Mean Integrated Squared Error (MISE)
- N:
-
Sample number
- h ij :
-
A spatial function
- \({P(j|\bar{{x}}_i )}\) :
-
The probability of the neighboring pixels of x i labeled as \({\bar{x}_{i}}\) belonging to the jth class
- NB(x i ):
-
A square window centered on pixel x i in the spatial domain
- n :
-
The size of neighborhood
- P NB(j|x i ):
-
The weighted posterior probability of current pixel x i with neighboring information
- w j :
-
The weight of the jth component of mixture models
- f j (x|θ j ):
-
The density function of the jth component
- K :
-
The number of classes
- j(x i ):
-
Represents the label of the class of the pixel x i
- F(I):
-
Image segmentation quality criterion
- I :
-
The image to be segmented
- R :
-
The number of regions in the segmented image
- A i :
-
The area or the number of pixels of the ith region
- e i :
-
The average number of wrongly classified pixels of region i
- C 1, C 2 :
-
The original image and segmented image of each pixel in the region
- x :
-
The gray level of the pixel
- α :
-
Threshold
- P, R :
-
The quantities precision and recall
References
Maulik U.: Medical image segmentation using genetic algorithms. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 13(2), 166–173 (2009)
Wang J., Kong J., Lu Y., Qi M., Zhang B.: A modified FCM algorithm for MRI brain image segmentation using both local and non-local spatial constraints. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph 32(8), 685–698 (2008)
Khan S.S., Ahmad A.: Cluster center initialization algorithm for K-means clustering. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 25(11), 1293–1302 (2004)
Chen J.M., Lu H., Song Y.Q.: A possibility fuzzy clustering algorithm based on the uncertainty membership. J. Comput. Res. Dev. 9, 1486–1491 (2008)
Chuang K.S., Tzeng H.L., Chen S., Wu J., Chen T.J.: Fuzzy c-means clustering with spatial information for image segmentation. Comput. Med. Imag. 30, 9–15 (2006)
Menezes R.: A kernel variogram estimator for clustered data. Scand. J. Stat. 35(1), 18–37 (2007)
Katkovnik V., Shmulevich I.: Kernel density estimation with adaptive varying window size. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 23(14), 1641–1648 (2002)
Alfó M., Nieddu L., Vicari D.: Finite mixture models for mapping spatially dependent disease counts. Biom. J. 51(1), 84–97 (2009)
Guillemaud R., Brady M.: Estimating the bias field of MR images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 16(3), 238–251 (1997)
Wells W.M., Grimson W.L., Kikinis R., Jolesz F.A.: Adaptive segmentation of MRI data. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 15(4), 429–442 (1996)
Bilmes, J.A.: A gentle tutorial of the EM algorithm and its application to parameter estimation for Gaussian mixture and hidden Markov models. Berkeley, CA: International Computer Science Institute, April (1998), ICSI-TR-97-021
Peel D., McLachlan G.J.: Robust mixture modelling using the t distribution. Stat. Comput. 10(4), 339–348 (2000)
Lin T.I., Lee J.C., Yen S.Y.: Finite mixture modelling using the skew normal distribution. Stat. Sin. 17, 909–927 (2007)
Tsung I.L., Jack C.L.: Robust mixture modeling using the skew t distribution. Stat. Comput. 17(2), 81–92 (2007)
Fan S.: Image thresholding using a novel estimation method in generalized gaussian distribution mixture modeling. Neurocomputing 72(1–3), 500–512 (2008)
Zribi M., Ghorbel F.: An unsupervised and non-parametric Bayesian classifier. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 24, 97–112 (2003)
Zivkovic Z., van der Heijden F.: Efficient adaptive density estimation per image pixel for the task of background subtraction. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 27(7), 773–780 (2006)
Chan N.H., Lee Thomas C.M., Peng L.: On nonparametric local inference for density estimation. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 54(2), 509–515 (2010)
Roettger, S., Bauer, M., Stamminger, M.: Spatialized transfer functions. Eurographics-IEEE VGTC symposium on visualization (2005)
Tang Y.G., Liu D., Guan X.P.: Multi-resolution image segmentation based on Gaussian mixture model. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 17(4), 870–874 (2006)
Cencov N.N.: Evaluation of an unknown distribution density from observations. Sov. Math. Dokl. 3, 1559–1562 (1962)
Gehringer K.R., Redner R.A.: Nonparametric probability density estimation using normalized B-Splines. Commun. Stat. Simul. Comput. 21(3), 849–878 (1992)
Kronmal R., Tarter M.: The estimation of probability densities and cumulatives by Fourier series methods. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 63, 925–952 (1968)
Dempster A.P., Laird N.M., Rubin D.B.: Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the E.M algorithm. J. R. Stat. B. 39(1), 1–38 (1977)
BrainWeb:Simulated Brain Database. http://www.bic.mni.mcgill.ca/brainweb/
Liu J., Yang Y.H.: Multiresolution color image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. 16(7), 689–700 (1994)
Martin D.R., Fowlkes C.C., Malik J.: Learning to detect natural image boundaries using local brightness, color, and texture cues. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. 26(5), 530–549 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, YQ., Liu, Z., Chen, JM. et al. Medical image segmentation based on non-parametric mixture models with spatial information. SIViP 6, 569–578 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-010-0185-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-010-0185-5