Abstract
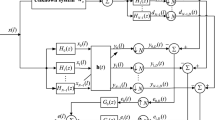
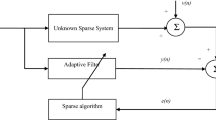
Proportionate-type adaptive filtering (PtAF) algorithms have been successfully applied to sparse system identification. The major drawback of the traditional PtAF algorithms based on the mean square error (MSE) criterion show poor robustness in the presence of impulsive noises or abrupt changes because MSE is only valid and rational under Gaussian assumption. However, this assumption is not satisfied in most real-world applications. To improve its robustness under non-Gaussian environments, we incorporate the maximum correntropy criterion (MCC) into the update equation of the PtAF to develop proportionate MCC (PMCC) algorithm. The mean and mean square convergence performance analysis are also performed. Simulation results in sparse system identification and echo cancellation applications are presented, which demonstrate that the proposed PMCC exhibits outstanding performance under the impulsive noise environments.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akyildiz, I.F., Pompili, D., Melodia, T.: Underwater acoustic sensor networks: research challenges. Ad hoc Netw. 3(3), 257–279 (2005)
Liang, J., Zhang, M., Zeng, X., et al.: Distributed dictionary learning for sparse representation in sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 23(6), 2528–2541 (2014)
Forni, F., Galeani, S., Nešić, D., et al.: Event-triggered transmission for linear control over communication channels. Automatica 50(2), 490–498 (2014)
Liang, J., Zhang, M., Liu, D., et al.: Robust ellipse fitting based on sparse combination of data points. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 22(6), 2207–2218 (2013)
Chen, Y., Gu, Y., Hero A. O.: Sparse LMS for system identification, In: ICASSP Conference, pp. 3125–3128 (2009)
Gu, Y., Jin, J., Mei, S.: l0 norm constraint LMS algorithm for sparse system identification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 16(9), 774–777 (2009)
Aliyu, M.L., Alkassim, M.A., Salman, M.S.: A p-norm variable step-size LMS algorithm for sparse system identification. Signal Image Video Process. 9(7), 1559–1565 (2015)
Jahromi, M.N.S., Salman, M.S., Hocanin, A., et al.: Convergence analysis of the zero-attracting variable step-size LMS algorithm for sparse system identification. Signal Image Video Process. 9(6), 1353–1356 (2015)
Duttweiler, D.L.: Proportionate normalized least-mean-squares adaptation in echo cancellers. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 8(5), 508–518 (2000)
Deng, H., Doroslovački, M.: Proportionate adaptive algorithms for network echo cancellation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 54(5), 1794–1803 (2006)
Das, R.L., Chakraborty, M.: On convergence of proportionate-type normalized least mean square algorithms. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express. Briefs 62(5), 491–495 (2015)
Haddad, D.B., Petraglia, M.R.: Transient and steady-state MSE analysis of the IMPNLMS algorithm. Digit. Signal Process. 33, 50–59 (2014)
Jelfs, B., Mandic, D.P.: A unifying framework for the analysis of proportionate NLMS algorithms. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 29(9), 1073–1085 (2015)
Sayin, M.O., Yilmaz, Y., Demir, A., et al.: The Krylov-proportionate normalized least mean fourth approach: formulation and performance analysis. Signal Process. 109, 1–13 (2015)
Nikias, C.L., Shao, M.: Signal processing with alpha-stable distributions and applications. Wiley, New York (1995)
Zhang, S., Zhang, J.: Enhancing the tracking capability of recursive least p-norm algorithm via adaptive gain factor. Digital Signal Process. 30, 67–73 (2014)
Arikan, O., Cetin, A.E., Erzin, E.: Adaptive filtering for non-Gaussian stable processes. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 1(11), 163–165 (1994)
Erdogmus, D., Principe, J.C.: An error-entropy minimization algorithm for supervised training of nonlinear adaptive systems. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 50(7), 1780–1786 (2002)
Wu, Z., Peng, S., Chen, B., Zhao, H., Principe, J.C.: Proportionate minimum error entropy algorithm for sparse system identification. Entropy 17(9), 5995–6006 (2015)
Liu, W., Puskal, P.P., Principe, J.C.: Correntropy: properties and applications in non-Gaussian signal processing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 55(11), 5286–5298 (2007)
Singh, A., Principe, J. C.: Using correntropy as cost function in adaptive filters, In: IJCNN Conference, pp. 2950–2955 (2009)
Wu, Z., Shi, J., Zhang, X., Ma, W., Chen, B.: Kernel recursive maximum correntropy. Signal Process. 117, 11–26 (2015)
Liang, J., Wang, D., Su, L., et al.: Robust MIMO radar target localization via non-convex optimization. Signal Process. 122, 33–38 (2016)
Ma, W., Chen, B., Duan, J., et al.: Diffusion maximum correntropy criterion algorithms for robust distributed estimation. Digit. Signal Process. 58, 10–19 (2016)
Qu, H., Ma, W., Zhao, J., et al.: Prediction method for network traffic based on maximum correntropy criterion. China Commun. 10(1), 134–145 (2013)
Chalasani, R., Principe, J.C.: Self-organizing maps with information theoretic learning. Neurocomputing 147, 3–14 (2015)
Ma, W., Qu, H., Gui, G., et al.: Maximum correntropy criterion based sparse adaptive filtering algorithms for robust channel estimation under non-Gaussian environments. J. Franklin Inst. 352(7), 2708–2727 (2015)
Chen, B., Xing, L., Liang, J., Zheng, N., Principe, J.C.: Steady-state mean-square error analysis for adaptive filtering under the maximum correntropy criterion. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 21(7), 880–884 (2014)
Chen, B., Principe, J.C.: Maximum correntropy estimation is a smoothed MAP estimation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 19(8), 491–494 (2012)
Rousseeuw, P.J., Leroy, A.M.: Robust regression and outlier detection. Wiley, New York (2005)
Das, R.L., Chakraborty, M.: Improving the performance of the PNLMS algorithm using norm regularization. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process 24(7), 1280–1290 (2016)
Shi, K., Shi, P.: Convergence analysis of sparse LMS algorithms with \(\text{ l }_{1}\)-norm penalty based on white input signal. Signal Process. 90(12), 3289–3293 (2010)
Papoulis, E.V., Stathaki, T.: A normalized robust mixed-norm adaptive algorithm for system identification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 11(1), 5286–5298 (2004)
Shao, M., Nikias, C.L.: Signal processing with fractional lower order moments: stable processes and their applications. Proc. IEEE 81(7), 986–1010 (1993)
Aydin, G., Arikan, O., Cetin, A.E.: Robust adaptive filtering algorithms for \(\alpha \)-stable random processes. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Analog Digit Signal Process. 46(2), 198–202 (1999)
Ma, W., Chen, B., Qu, H., et al.: Sparse least mean p-power algorithms for channel estimation in the presence of impulsive noise. Signal Image Video Process. 10(3), 503–510 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (No.2015AA042301), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.61372152), and the Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shanxi (No.2017JM6033). The authors would like to thank the chief editor, associate editor, and the reviewers for their valuable comments and help, which help us to improve the quality of the manuscript. Furthermore, we would like to give thanks for the JEO assistant handling our manuscript timely.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, W., Zheng, D., Zhang, Z. et al. Robust proportionate adaptive filter based on maximum correntropy criterion for sparse system identification in impulsive noise environments. SIViP 12, 117–124 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-017-1137-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-017-1137-0