Abstract
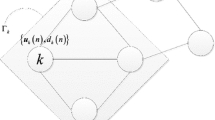
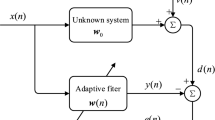
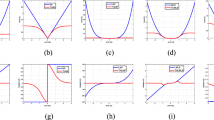
The main drawback of the diffusion least mean square algorithm (DLMS) is its performance will degrade when the impulsive noise (IN) occurs in the system. To improve the performance, a robust competitive DLMS (RCDLMS) algorithm based on two types of effective IN detection method is proposed. Because both methods estimate noise variance to determine whether impulse noise occurs or not. The first method is using the shrinkage denoising method to obtain the variance of noise, and the second method is by estimating cross-correlation of the input and error signals to acquire the variance of noise. Finally, simulation results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm has a good tracking capability and robust performance against impulsive noise.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gross, T., Sayama, H.: Adaptive Networks, pp. 1–8. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Cattivelli, F.S., Sayed, A.H.: Modeling bird flight formations using diffusion adaptation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 59(5), 2038–2051 (2011)
Chen, J., Richard, C., Sayed, A.H.: Multitask diffusion LMS over networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 63(11), 2733–2748 (2015)
Lopes, C.G., Sayed, A.H.: Diffusion least-mean squares over adaptive networks: formulation and performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56(7), 3122–3136 (2008)
Cattivelli, F.S., Sayed, A.H.: Diffusion LMS strategies for distributed estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 58(3), 1035–1048 (2010)
Wen, P., Zhang, J.: Widely-Linear complex-valued diffusion subband adaptive filter algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Inf. Process. Over Netw. 5(2), 248–257 (2018)
Ni, J., Chen, J., Chen, X.: Diffusion sign-error LMS algorithm: formulation and stochastic behavior analysis. Signal Process. 128, 142–149 (2016)
Ahn, D.C., Lee, J.W., Shin, S.J., et al.: A new robust variable weighting coefficients diffusion LMS algorithm. Signal Process. 131, 300–306 (2017)
Wen, P., Zhang, J.: A novel variable step-size normalized subband adaptive filter based on mixed error cost function. Signal Process. 138, 48–52 (2017)
Zhang, S., Zhang, J., Han, H.: Robust shrinkage normalized sign algorithm in an impulsive noise environment. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Br. 64(1), 91–95 (2017)
Wen, P., Zhang, J.: Robust variable step-size sign subband adaptive filter algorithm against impulsive noise. Signal Process. 139, 110–115 (2017)
Bhotto, M.Z.A., Ahmad, M.O., Swamy, M.N.S.: Robust shrinkage affine-projection sign adaptive-filtering algorithms for impulsive noise environments. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62(13), 3349–3359 (2014)
Bhotto, M.Z.A., Antoniou, A.: A family of shrinkage adaptive-filtering algorithms. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 61(7), 1689–1697 (2013)
Wen, P., Zhang, J.: Variable step-size diffusion normalized sign-error algorithm. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 37, 4993–5004 (2018)
Lee, H.S., Kim, S.E., Lee, J.W.: A variable step-size diffusion LMS algorithm for distributed estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 63(7), 1808–1820 (2015)
Saeed, M.O.B., Zerguine, A., Zunmo, S.A.: A variable step-size strategy for distributed estimation over adaptive networks. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 1, 1–14 (2013)
Zhang, S., Zheng, W.X., Zhang, J., et al.: A family of robust M-shaped error weighted least mean square algorithms: performance analysis and echo cancellation application. IEEE Access 5, 14716–14727 (2017)
Wen, P., Zhang, S., Zhang, J.: A novel subband adaptive filter algorithm against impulsive noise and it’s performance analysis. Signal Process. 127, 282–287 (2016)
Zhang, S., Zhang, J.: Enhancing the tracking capability of recursive least p-norm algorithm via adaptive gain factor. Digital Signal Process. 30, 67–73 (2014)
Zhang, S., Zheng, W.: Normalized least mean-square algorithm with variable step size based on diffusion strategy. In: IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems. IEEE (2018)
Zhang, S., Zheng, W.: Mean-square analysis of multi-sampled multiband-structured subband filtering algorithm. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 66(3), 1051–1062 (2019)
Wen, P., Zhang, J., Zhang, S., et al.: Augmented complex-valued normalized subband adaptive filter: algorithm derivation and analysis. J. Frankl. Inst. 356(3), 1604–1622 (2019)
Huang, F., Zhang, J., Zhang, S.: Affine projection versoria algorithm for robust adaptive echo cancellation in hands-free voice communications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 67(12), 11924–11935 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was partially supported by National Science foundation of P. R. China (Grants: 61671392, 61801401), in part by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Grant 2682018CX22 and in part by the Doctoral Innovation Fund Program of Southwest Jiaotong University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, P., Zhang, J. & Zhang, S. Robust competitive diffusion LMS algorithm. SIViP 14, 343–349 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-019-01556-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-019-01556-8