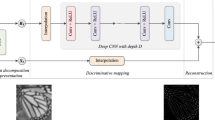
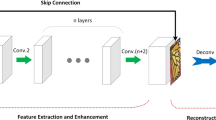
Abstract
For single-image super-resolution (SR), deep learning-based approaches have attained superior performance that overshadow all previous approaches. Most recently published deep learning-based single-image SR approaches rely on either deeper or more complex network to achieve further improved results, which are time and space intensive. In this paper, we propose a new method to effectively improve the quality of the final magnified image: a dark channel prior-based network is first designed and then used to regularize the previously existed SR networks. The motivation of this work is an interesting observation that the dark channel of the magnified image contains less dark pixels than that of the original high-resolution image. Since the proposed dark channel prior-based network is a fixed network and does not contain any trainable parameters, the combined hybrid network thus can maintain its original complexity and achieve state-of-the-art results.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, D., He, J.: Hybrid sparse representation based approach to image super-resolution reconstruction. J. Electron. Imaging 26(2), 023008 (2017)
Huang, Y., Wang, W., Wang, L.: Video super resolution via bidirectional recurrent convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 40(4), 1015–1028 (2018)
Di, Z., He, J., Du, M.: Morphable model space based face super-resolution reconstruction and recognition. Image Vis. Comput. 30(2), 100–108 (2012)
Li, Y., Cai, C., Qiu, G., Lam, K.-M.: Face hallucination based on sparse local-pixel structure. Pattern Recogn. 47(3), 1261–1270 (2014)
Bevilacqua, M., Roumy, A., Guillemot, C., Morel, M.-L.A.: Single-image super-resolution via linear mapping of interpolated self examples. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 23(12), 5334–5347 (2014)
Freedman, G., Fattal, R.: Image and video upscaling from local self examples. ACM Trans. Graph. 30(2), Art. no. 12 (2011)
Glasner, D., Bagon, S., Irani, M., Super-resolution from a single image. In: ICCV, pp. 349–356 (2009)
Pathak, H.N., Li, X., Minaee, and S., Cowan, B.: Efficient super resolution for large-scale images using attentional GAN. arXiv:1812.04821v4 [cs CV] (2019)
Yang, J., Lin, Z., Cohen, S.: Fast image super-resolution based on in-place example regression. In: CVPR, pp. 1059–1066 (2013)
Timofte, R., De Smet, V., Gool, L.V.: Anchored neighborhood regression for fast example-based super resolution. In: Proceedings of ICCV, pp. 1920–1927 (2013)
Timofte, R., De Smet, V., Gool, L.V: A + : adjusted anchored neighborhood regression for fast super-resolution. In: Proceedings of ACCV, pp. 111–126 (2014)
Yang, J., Wright, J., Huang, T., Ma, Y.: Image super-resolution via sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 19(11), 2861–2873 (2010)
Dong, W., Zhang, L., Shi, G., Wu, X.: Image deblurring and super-resolution by adaptive sparse domain selection and adaptive regularization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 20(7), 1838–1857 (2011)
Dong, C., Loy, C.C., He, K., Tang, X.: Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 38(2), 295–307 (2016)
Kim, J., Lee, J.K., Lee, K.M.: Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1646–1654 (2016)
Johnson, J., Alahi, A., Li, F.: Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 694–711 (2016)
Wang, Z., Liu, D., Yang, J., Han, W., Huang, T.: Deep networks for image super-resolution with sparse prior. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 370–378 (2015)
Yang, W., Feng, J., Yang, J., Zhao, F., Liu, J., Guo, Z., Yan, S.: Deep edge guided recurrent residual learning for image super-resolution. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(12), 5895–5907 (2017)
Ledig, C., Theis, L., Huszar, F., Caballero, J., Cunningham, A., Acosta, A., Aitken, A., Tejani, A., Totz, J., Wang, Z., Wenzhe, S.T.: Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. In: CVPR (2017)
Lim, B., Son, S., Kim, H., Nah, S., Lee, K.M.: Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution. In: CVPRW (2017)
Zhang, Y., Li, K., Li, K., Wang, L., Zhong, B., Fu, Y.: Image super-resolution using very deep residual channel attention networks. In: ECCV (2018)
Aadil, M., Rahim, R., ul Hussain, S.: Improving super resolution methods via incremental residual learning. In: ICIP (2019)
Sun, X., Zhao, Z., Zhang, S., Liu, J., Yang, X., Zhou, C.: Image super-resolution reconstruction using generative adversarial networks based on wide-channel activation. IEEE Access 8, 33838–33854 (2020)
He, K., Sun, J., Tang, X.: Single image haze removal using dark channel prior. IEEE Trans. PAMI 33(12), 2341–2353 (2011)
Wang, X., Yu, K., Wu, S., Gu, J., Liu, Y. Dong, C., Loy, C.C., Qiao, Y., Tang, X.: ESRGAN: enhanced super-resolution generative adversarial networks. In: CVPR (2018)
Xueyang, F., Huang, J., Ding, X., Liao, Y., Paisley, J.: Clearing the skies: a deep network architecture for single-image rain removal. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(6), 2944–2956 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81871433) and Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Grant No. 2016A030307045).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., He, J., Zhao, Y. et al. Single-image super-resolution reconstruction using dark channel regularization network. SIViP 15, 431–438 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-020-01762-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-020-01762-9