Abstract
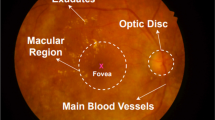
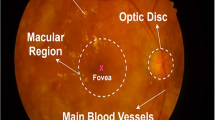
Diabetic macular edema (DME) is the main cause of visual impairment in diabetic patients. Early detection of DME will significantly reduce the risk of vision loss for the patients. According to the clinical DME grading standard, the positional relationship between Hard Exudates (HEs) and macular center is an important basis for DME grading. Accurate DME grading is thus predicated on properly locating the macular center and segmenting HEs. HEI-MED and E-ophtha EX data sets were tested by the proposed DME grading method, reaching an average accuracy of 94.4% and 87%, respectively. The proposed method was also tested by comparison against other commonly used methods as per its potential to assist doctors in initially screening DME; it was found to not only improve the efficiency of DME detection, but also to save Optical Coherence Tomography medical resources over the other methods tested.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deepak, K.S., Sivaswamy, J.: Automatic assessment of macular edema from color retinal images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 31, 766–776 (2011)
Girish, G.N., Thakur, B., Chowdhury, S.R., Kothari, A.R., Rajan, J.: Segmentation of intra-retinal cysts from optical coherence tomography images using a fully convolutional neural network model. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 23, 296–304 (2018)
Ji, L., Chen, T.Y., Liang, Y.: Early diagnosis and treatment of diabetic macular edema. I.E.S. 14, 1809–1811 (2014)
Cebulla, C.M., Flynn, H.W.: Calcification of combined hamartoma of the retina and retinal pigment epithelium over 15 years. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 251, 1455–1456 (2013)
Deepak, K.S., Sivaswamy, J.: Automatic assessment of macular edema from color retinal image. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 31, 766–776 (2012)
Huang, L.F., He, X.X., Fang, L.Y., Rabbani, H., Chen, X.D.: Automatic classification of retinal optical coherence tomography images with layer guided convolutional neural network. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 26, 1026–1030 (2019)
Li, H.Q., Opas, C.: Automated feature extraction in color retinal image by a model based approach. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 51, 246–254 (2004)
Dharitri, D., Jyoti, P.M., Nirmala, S.R.: Detection of macular and fovea for disease analysis in color fundus image. In: International Conference on Recent Trends in Information Systems, pp. 231–236. (2015)
Zheng, S.H., Chen, J., Pan, L.: Yu L (2014) Automatic analysis method of macular edema classification for diabetic retinopathy images. Chin. J. Biomed. Eng. 33, 687–695 (2014)
Baidaa, A.B., Waleed, A.N., Bryan, M.W., Zheng, Y.L.: Multiscale sequential convolutional neural networks for simultaneous detection of fovea and optic disc. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 40, 91–101 (2018)
Sundaresan, V., Ram, K., Joshi, N., Sivaprakasam, M., Gandhi, R.: Computer-assisted classification of diabetic macular edema on retinal color fundus image. In: Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp. 4330–4333. (2015)
Mehdi, G.F.E., Hamidreza, P.: Localization of hard exudates in retinal fundus image by mathematical morphology operations. Int. Conf. Comput. Knowl. Eng. 90, 323–359 (2012)
Sinthanayothin, C., Boyce, J.F., Williamson, T.H., Cook, H.L., Mensah, E., Lal, S., Usher, D.: Automated detection of diabetic retinopathy on digital fundus image. Diabetic Med 19, 105–112 (2012)
Amel, F., Mohammed, M., Abdelhafid, B.: Improvement of the hard exudates detection method used for computer-aided diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy. Int. J. Image Graph. Signal Process. 4, 19–27 (2012)
Harangi, B., Lazar, I., Hajdu, A.: Automatic exudate detection using active contour model and centerwise classification. Comput. Biol. Med. 54, 156–171 (2012)
Abràmoff, M.D., Niemeijer, M., Suttorp-Schulten, M.S.A., Viergever, M.A., Russell, S.R., van Ginneken, B.: Evaluation of a system for automatic detection of diabetic retinopathy from color fundus photographs in a large population of patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care 31, 193–198 (2008)
Badgujar, R., Deore, P.: MBO-SVM-based exudate classification in fundus retinal image of diabetic patients. Comput. Methods. Biomed. 7, 195–206 (2018)
Prentai, P., Lonari, S.: Detection of exudates in fundus photographs using deep neural networks and anatomical landmark detection fusion. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 137, 281–292 (2016)
Mo, J., Zhang, L.: Feng YQ (2016) Exudate-based diabetic macular edema recognition in retinal image using cascaded deep residual networks. Neurocomputing 290, 161–171 (2016)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural. Inform. Process. Syst. 25, 1097–1105 (2012)
Yu, L.Q., Chen, H., Dou, Q., Qin, J., Heng, P.A.: Automated melanoma recognition in dermoscopy image via very deep residual networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 36, 994–1004 (2017)
Ren, Shaoqing, He, Kaiming, Girshick, Ross, Sun, Jian: Faster RCNN: towards real-time object detection with center proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39, 1137–1149 (2017)
Zhao, H.S., Shi, J.P., Qi, X.J., Wang, X.G., Jia, J.Y.: Pyramid scene parsing network. In: Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (Honolulu, USA), vol. 1, pp. 6230–6239. (2017)
Yu, F., Koltun, V.: Multi-Scale Context Aggregation by dilated Convolutions. In: ICLR. (2016)
He, K.M., Zhang, X.Y., Ren, S.Q., Sun, J.: Deep Residual Learning for image recognition. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 1, 770–778 (2015)
Decenciere, E., et al.: Feedback on a publicly distributed image database the Messidor database. Image Anal. Stereol. 33, 231–234 (2014)
Luca, G., Fabrice, M., Thomas, P.K., Fabrice, M., Li, Y.Q., Seema, G., Kenneth, W., Tobin, J., Edward, C.: Exudate-based diabetic macular edema detection in fundus image using publicly available data sets. Med. Image Anal. 16, 216–226 (2012)
Jeetinder, S., Gopal, D.J., Jayanthi, S.: Appearance-based object detection in color retinal image. In: IEEE International Conference on image Processing (Boston, MA), pp. 1–9. (2008)
Niemeijer, M., Abràmoff, M.D., Ginneken, B.V.: Segmentation of the optic disc, macular and vascular arch in fundus photographs. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 26, 116–127 (2007)
Jyoti, P.M., Malaya, K.N., Samarendra, D.: Automatic classification of macular degeneration from fundus image. In: World Congress on Information and Communication Technologies (IEEE). (2012)
Gandomkar, Ziba, Tay, Kevin, Ryder, Will, Brennan, Patrick C., Mello-Thoms, Claudia: iCAP: an individualized model combining gaze parameters and image-based features to predict radiologists’ decisions while reading mammograms. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 36, 1066–1075 (2017)
Zhang, X., et al.: Exudate detection in color retinal image for mass screening of diabetic retinopathy. Med. Image Anal. 18, 1026–1043 (2014)
Imani, E., Pourreza, H.R.: A novel method for retinal exudate segmentation using signal separation algorithm. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 133, 195–205 (2016)
Das, V., Puhan, N.B.: Tsallis entropy and sparse reconstructive dictionary learning for exudate detection in diabetic retinopathy. J. Med. Imaging 4, 024002 (2017)
Liu, Q., Zou, B., Chen, J., Ke, W., Yue, K., Chen, Z., Zhao, G.: A location-to-segmentation strategy for automatic exudate segmentation in colour retinal fundus image. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 55, 78–86 (2017)
Perdomo, O., Otalora, S., Rodriguez, F.: A novel machine learning model based on exudate localization to detect diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmic Med. Image Anal. Third Int. Workshop 21, 137–144 (2016)
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61601325), Tianjin Science and Technology Major Projects and Engineering (No. 17ZXSCSY00060, No. 17ZXHLSY00040), and the Program for Innovative Research Team in University of Tianjin (Grant No. TD13-5034).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Zhang, Q., Liu, M. et al. Diabetic macular edema grading based on improved Faster R-CNN and MD-ResNet. SIViP 15, 743–751 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-020-01792-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-020-01792-3