Abstract
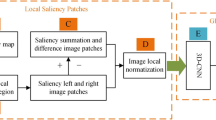
In this paper, we present a depth-perceived 3D visual saliency map and propose a no-reference stereoscopic image quality assessment (NR SIQA) algorithm using 3D visual saliency maps and convolutional neural network (CNN). Firstly, the 2D salient region of stereoscopic image is generated, and the depth saliency map is calculated, and then, they are combined to compute 3D visual saliency map by linear weighted method, which can better use depth and disparity information of 3D image. Finally, 3D visual saliency map, together with distorted stereoscopic pairs, is fed into a three-channel CNN to learn human subjective perception. We call proposed depth perception and CNN-based SIQA method DPCNN. The performances of DPCNN are evaluated over the popular LIVE 3D Phase I and LIVE 3D Phase II databases, which demonstrates to be competitive with the state-of-the-art NR SIQA algorithms.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appina, B., Khan, S., Channappayya, S.S.: No-reference stereoscopic image quality assessment using natural scene statistics. Signal Process. Image Commun. 43, 1–14 (2016)
Moorthy, A.K., Su, C.C., Mittal, A., et al.: Subjective evaluation of stereoscopic image quality. Signal Process. Image Commun. 28(8), 870–883 (2013)
Zhang, W., Borji, A., Wang, Z., et al.: The application of visual saliency models in objective image quality assessment: a statistical evaluation. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 27(6), 1266–1278 (2016)
Häkkinen, A.J., Kawai, T., Takatalo, J., et al.: What do people look at when they watch stereoscopic movies? In: Proceedings of SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering, vol. 7524, pp. 75240E-75240E-10 (2010)
Jansen, L., Onat, S., König, P.: Influence of disparity on fixation and saccades in free viewing of natural scenes. J. Vis. 9(1), 1–19 (2009)
Yang, J., An, P., Ma, J., Li, K., Shen, L.: No-reference stereo image quality assessment by learning gradient dictionary-based color visual characteristics. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), pp. 1–5 (2018)
Maki, A., Nordlund, P., Eklundh, J.-O.: Attentional scene segmentation: integrating depth and motion. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 78(3), 351–373 (2000)
Wang, W., Shen, J., Yu, Y., Ma, K.-L.: Stereoscopic thumbnail creation via efficient stereo saliency detection. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graphics 23(8), 2014–2027 (2017)
Fang, Y., Wang, J., Narwaria, M., Le Callet, P., Lin, W.: Saliency detection for stereoscopic images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 23(6), 2625–2636 (2014)
Perazzi, F., Krähenbühl, P., Pritch, Y., Hornung, A.: Saliency filters: contrast based filtering for salient region detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 733–740 (2012).
Li, N., Sun, B., Yu, J.: A weighted sparse coding framework for saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5216–5223 (2015)
Liu, Y., Yang, J.C., Meng, Q.G., et al.: Stereoscopic image quality assessment method based on binocular combination saliency model. Signal. Process. 125, 237–248 (2016)
Li, Y.F., Yang, F., Wan, W.B., et al.: No-reference stereoscopic image quality assessment based on visual attention and perception. IEEE Access 7, 46706–46716 (2019)
Benoit, A., Le Callet, P., Campisi, P., et al.: Quality assessment of stereoscopic images. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2008, 659024 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1155/2008/659024
You, J., Xing, L., Perkis, A., et al.: Perceptual quality assessment for stereoscopic images based on 2D image quality metrics and disparity analysis. In: Proceedings of International Workshop on Video Processing and Quality Metrics for Consumer Electronics, Arizona, U.S.A., pp. 1–6 (2010)
Chen, M.J., Cormack, L.K., Bovik, A.C.: No-reference quality assessment of natural stereopairs. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 22(9), 3379–3391 (2013)
Akhter, R., Sazzad, Z.M.P., Horita, Y., et al.: No-reference stereoscopic image quality assessment. In: Proceedings of Stereoscopic Displays and Applications XXI. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 75240T-75240T-12 (2010)
Zhou, W., Wu, J., Lei, J., et al.: Salient object detection in stereoscopic 3D images using a deep convolutional residual autoencoder. In: IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, pp. 1–12 (2020)
Zhang, W., Zhang, Y., Ma, L., et al.: Multimodal learning for facial expression recognition. Pattern Recogn. 48(10), 3191–3202 (2015)
Zhou, W., Yuan, J., Lei, J., et al.: TSNet: three-stream self-attention network for RGB-D indoor semantic segmentation. In: IEEE intelligent systems, pp. 1–5 (2020).
Xu, Y., Du, J., Dai, L.-R., et al.: An experimental study on speech enhancement based on deep neural networks. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 21, 65–68 (2014)
Zhou, W., Liu, W., Lei, J.., et al.: Deep Binocular Fixation Prediction using a Hierarchical Multimodal Fusion Network. In: IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems
Kang, L., Ye, P., Li, Y., et al.: Convolutional neural networks for no-reference image quality assessment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1733–1740 (2014)
Bosse, S., Maniry, D., Wiegand, T., et al.: A deep neural network for image quality assessment. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on image processing, pp. 3773–3777 (2016)
Zhang, W., Qu, C., Ma, L., et al.: Learning structure of stereoscopic image for no-reference quality assessment with convolutional neural network. Pattern Recognit. 59(C), 176–187 (2016)
Zhou, W., Lei, J.S., Jiang, Q.P.: Blind binocular visual quality predictor using deep fusion network. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging. 6, 883–893 (2020)
Zhang, L., Gu, Z., Li. H.: SDSP: a novel saliency detection method by combining simple priors. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, pp. 171–175 (2014)
Achanta, R., Hemami, S., Estrada, F., et al.: Frequency-tuned salient region detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1597–1604 (2009)
Judd, T., Ehinger, K., Durand, F., et al.: Learning to predict where humans look. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2106–2113 (2010)
Wu, Y., Shen, X.: A unified approach to salient object detection via low rank matrix recovery. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 853–860 (2012)
Sun, D., Roth, S., Black, M.J.: Secrets of optical flow estimation and their principles. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2432–2439 (2010)
Nair, V., Hinton. G.E.: Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-10), pp. 807–814 (2010)
Hinton, G.E., Srivastava, N., Krizhevsky, A., et al.: Improving neural networks by preventing coadaptation of feature detectors. Computer Science 3(4), 212–223 (2012)
Kingma, D., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization (2014). arXiv:1412.6980
Wang, Z., Bovik, A.C., Sheikh, H.R., et al.: Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13(4), 600–612 (2004)
Shao, F., Tian, W., Lin, W., et al.: Learning sparse representation for no-reference quality assessment of multiply distorted stereoscopic images. IEEE Image Qual. Assess.: error Vis. Struct. Similarity Multimed. 19(8), 1821–1836 (2017)
Oh, H., Ahn, S., Kim, J., et al.: Blind deep S3D image quality evaluation via local to global feature aggregation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(10), 4923–4936 (2017)
Wang, X., Ma, L., Kwong, S., et al.: Quaternion representation based visual saliency for stereoscopic image quality assessment. Signal Process. 145, 202–213 (2018)
Liu, T.-J., Lin, C.-T., Liu, H.-H., et al.: Blind stereoscopic image quality assessment based on hierarchical learning. IEEE Access 7, 8058–8069 (2019)
Yang, J., Zhao, Y., Zhu, Y., et al.: Blind assessment for stereo images considering binocular characteristics and deep perception map based on deep belief network. Inf. Sci. 474, 1–17 (2019)
Yang, J., Sim, K., Jiang, B., et al.: No-reference stereoscopic image quality assessment based on hue summation-difference mapping image and binocular joint mutual filtering. Appl. Opt. 57(14), 3915–3926 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61771223).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Yun, L., Chen, H. et al. No-reference stereoscopic image quality assessment using 3D visual saliency maps fused with three-channel convolutional neural network. SIViP 16, 273–281 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-021-01987-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-021-01987-2