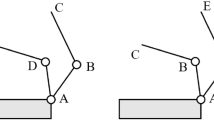
Abstract
Currently, the study of new isotopism invariants of partial Latin squares constitutes an open and active problem. This paper delves into this topic by analyzing computationally the configuration of planar bar linkage mechanisms for which the array formed by the lengths of their bars constitutes an empty-diagonal symmetric partial Latin square such that each one of its rows and columns has at least two non-empty cells. These assumptions enable one to define a series of algebraic and geometric constraints that can be readily implemented in any Computer Algebra or Dynamic Geometry System. In order to illustrate the different concepts and results introduced throughout the paper, it is explicitly determined and characterized the distribution of planar bar linkage mechanisms based on partial Latin squares of order up to five.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, R., Stolarsky, K.B.: Extremal problems of distance geometry related to energy integrals. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 193, 1–31 (1974)
Arranz, J.M., Losada, R., Mora, J.A., Recio, T., Sada, M.: Modeling the cube using Geogebra. In: Bu, L., Schoen, R. (eds.) Model-Centered Learning. Modeling and Simulations for Learning and Instruction, pp. 119–131. SensePublishers, Rotterdam (2011)
Botana, F., Abánades, M.Á., Escribano, J.: Exact internet accessible computation of paths of points in planar linkages and diagrams. Comput. Appl. Eng. Educ. 19, 835–841 (2011)
Blumenthal, L.: Theory and Applications of Distance Geometry. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1953)
Corves, B., Hüsing, M., Riedel, M.: Descriptive and Intuitive Mechanism Design and Synthesis Using Geometry-Based Computer-Aided Methods. In: Thirteenth World Congress in Mechanism and Machine Science. Curran Associates, Inc., Guanajuato, Mexico (2011)
Cox, D.A., Little, J.B., OShea, D.: Using Algebraic Geometry. Springer, New York (1998)
Crippen, G.M., Havel, T.F.: Distance Geometry and Molecular Conformation. Wiley, New York (1988)
Crippen, G.M.: Distance geometry for realistic molecular conformations. In: Distance Geometry, pp. 315–328. Springer, New York (2013)
Decker, W. Greuel, G.M., Pfister, G., Schönemann, H.: Singular 4-1-2–a computer algebra system for polynomial computations. http://www.singular.uni-kl.de (2018). Accessed 8 Nov 2019
Dénes, J., Keedwell, A.D.: Latin Squares and their Applications. Academic Press, New York (1974)
Dokuchaev, M.A., Kasyanuk, M.V., Khibina, M.A., Kirichenko, V.V.: Exponent matrices and Frobenius rings. Algebra Discrete Math. 18, 186–202 (2014)
Dong, Q., Wu, Z.: A linear-time algorithm for solving the molecular distance geometry problem with exact inter-atomic distance. J. Global Optim. 22, 365–375 (2002)
Eiran, D., Falcón, R.M., Kotlar, D., Marbach, T.G., Stones, R.J.: Two-line graphs of partial Latin rectangles. Electron. Notes Discrete Math. 68, 53–58 (2018)
Erdman, A.G., Sandor, G.N.: Mechanism Design: Analysis and Synthesis. N.J. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1984)
Falcón, R.M.: The set of autotopisms of partial Latin squares. Discrete Math. 313, 1150–1161 (2013)
Falcón, R.M.: Enumeration and classification of self-orthogonal partial Latin rectangles by using the polynomial method. Eur. J. Comb. 48, 215–223 (2015)
Falcón, R.M., Álvarez, V., Gudiel, F.: A computational algebraic geometry approach to analyze pseudo-random sequences based on Latin squares. Adv. Comput. Math. 45, 1769–1792 (2019)
Falcón, R.M., Falcón, O.J., Núñez, J.: A historical perspective of the theory of isotopisms. Symmetry 10, 1–21 (2018)
Falcón, R.M., Stones, R.J.: Classifying partial Latin rectangles. Electron. Notes Discrete Math. 49, 765–771 (2015)
Falcón, R.M., Stones, R.J.: Partial Latin rectangle graphs and autoparatopism groups of partial Latin rectangles with trivial autotopism groups. Discrete Math. 340, 1242–1260 (2017)
Havel, T.F.: Some examples of the use of distances as coordinates for euclidean geometry. J. Symb. Comp. 11, 579–593 (1991)
Hohenwarter, M.: GeoGebra: Ein Softwaresystem für dynamische Geometrie und Algebra der Ebene. Ph.D. Thesis. Paris Lodron University, Salzburg, Austria (2002)
Hu, Y., Nelson-Maney, N., Anderson, P.S.L.: Common evolutionary trends underlie the four-bar linkage systems of sunfish and mantis shrimp. Evolution 71, 1397–1405 (2017)
Hulpke, A., Kaski, P., Östergård, P.R.J.: The number of Latin squares of order 11. Math. Comput. 80, 1197–1219 (2011)
Iriarte, X., Aginaga, J., Ros, J.: Teaching mechanism and machine theory with GeoGebra. In: García-Prada, J.C., Castejón, C. (eds.) New Trends in Educational Activity in the Field of Mechanism and Machine Theory, pp. 211–219. Springer International Publishing, Switzerland (2014)
Kolesova, G., Lam, C.W.H., Thiel, L.: On the number of \(8\times 8\) Latin squares. J. Combin. Theory Ser. A 54, 143–148 (1990)
Kotlar, D.: Computing the autotopy group of a Latin square by cycle structure. Discrete Math. 331, 74–82 (2014)
Kovács Z., Kovács, B.: A Compilation of LEGO Technic Parts to Support Learning Experiments on Linkages. Technical Report (2017) arXiv:1712.00440 [math.HO]
Kurita, K., Inoue, F., Furuya, N., Shiokawa T., Natori M.: Development of adaptive roof structure by variable geometry truss. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction, pp. 1–6. Krakow, Poland (2001)
Kurtenbach, S., Prause, I., Weigel, C., Corves, B.: Comparison of geometry software for the analysis in mechanism theory. In: García-Prada, J.C., Castejón, C. (eds.) New Trends in Educational Activity in the Field of Mechanism and Machine Theory, pp. 193–201. Springer International Publishing, Switzerland (2014)
Lavor, C., Liberti, L., Maculan, N., Mucherino, A.: Recent advances on the discretizable molecular distance geometry problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 219, 698–706 (2012)
Menger, K.: Untersuchungen über allgemeine Metrik. Mathematische Annalen 100, 75–163 (1928)
Menger, K.: New foundation of Euclidean geometry. Am. J. Math. 53, 721–745 (1931)
McKay, B.D., Meynert, A., Myrvold, W.: Small Latin squares, quasigroups, and loops. J. Combin. Des. 15, 98–119 (2007)
Prause, I., Fauroux, J.C., Hüsing, M., Corves, B.: Using Geometry Sketchers and CAD Tools for Mechanism Synthesis. In: Proceedings of IFToMM 2015, The 14th World Congress in Mechanism and Machine Science, paper OS3-032, 11 pp. International Federation for the Theory of Mechanisms and Machines, Taiwan (2015)
Porta, J.M., Rojas, N., Thomas, F.: Distance Geometry in Active Structures. In: Ottaviano E., Pelliccio A., Gattulli V. (eds.) Mechatronics for Cultural Heritage and Civil Engineering. Intelligent Systems, Control and Automation: Science and Engineering 92, pp. 115–136. Springer, Cham (2018)
Rojas, N.: Distance-based formulations for the position analysis of kinematic chains. PhD thesis. Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Institut de Robòtica i Informàtica Industrial, Barcelona (2012)
Saxe, J.: Embeddability of weighted graphs in \(k\)-space is strongly NP-hard. In: Proceedings of 17th Allerton Conference in Communications, Control and Computing, pp. 480–489. Monticello, IL (1979)
Stones, D.S.: Symmetries of partial Latin squares. Eur. J. Combin. 34, 1092–1107 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work is partially supported by the Research Project FQM-016 from Junta de Andalucía, and by the Departmental Research Budget of the Department of Applied Mathematics I of the University of Seville.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Falcón, R.M. Using a CAS/DGS to Analyze Computationally the Configuration of Planar Bar Linkage Mechanisms Based on Partial Latin Squares. Math.Comput.Sci. 14, 375–389 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11786-019-00428-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11786-019-00428-1