Abstract
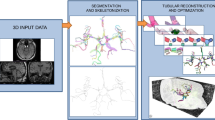
The human cerebrovasculature is extremely complicated and its three dimensional (3D) highly parcellated models, though necessary, are unavailable. We constructed a digital cerebrovascular model from a high resolution, 3T 3D time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography scan. This model contains the arterial and venous systems and is 3D, geometric, highly parcellated, fully segmented, and completely labeled with name, diameter, and variants. Our approach replaces the tedious and time consuming process of checking and correcting automatic segmentation results done at 2D image level with an aggregate and faster process at 3D model level. The creation of the vascular model required vessel pre-segmentation, centerline extraction, vascular segments connection, centerline smoothing, vessel surface construction, vessel grouping, tracking, editing, labeling, setting diameter, and checking correctness and completeness. For comparison, the same scan was segmented automatically with 59.8% sensitivity and only 16.5% of vessels smaller than 1 pixel size were extracted. To check and correct this automatic segmentation requires 8 weeks. Conversely, the speedup of our approach (the number of 2D segmented areas/the number of 3D vascular segments) is 34. This cerebrovascular model can serve as a reference framework in clinical, research, and educational applications. The wealth of information aggregated with its quantification capabilities can augment or replace numerous textbook chapters. Five applications of the vascular model were described. The model is easily extendable in content, parcellation, and labeling, and the proposed approach is applicable for building a whole body vascular system.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
ADAM (1996). Animated Dissection of Anatomy for Medicine User’s Guide. Washington, D.C.: ADAM.
Bayer (1996). Microvascular atlas of the head and neck. CD-ROM for Macintosh and Windows.
Berkovitz, B., Kirsch, C., Moxham, B., Alusi, G., & Cheeseman, T. (2003). Interactive head & neck. CD-ROM PC and Mac compatible, Primal, London.
Bookstein, F. L. (1979). Fitting conic sections to scattered data. Computer Graphics and Image Processing, 9, 56–71.
Catmull, J. E., & Clark, J. (1978). Recursively generated B-spline surfaces on arbitrary topological meshes. Computer-Aided Design, 10, 350–355.
Doris, H. U., Kochanek, D., & Bartels, R. (1984). Interpolating splines with local tension, continuity, and bias control. Proc. ACM SIGGRAPH, 18, 33–41.
Douglas, D., & Peucker, T. (1973). Algorithms for the reduction of the number of points required to represent a digitized line or its caricature. The Canadian Cartographer, 10(2), 112–122.
Federative Committee on Anatomical Terminology (FCAT) (1999). Terminologia anatomica. Stuttgart: Thieme.
Fitzgibbon, A., Pilu, M., & Fisher, R. (1999). Direct least-square fitting of Ellipses. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 21, 476–480.
Grand, W., & Hopkins, L. N. (1999). Vasculature of the brain and cranial base: Variations in clinical anatomy. Stuttgart: Thieme.
Harnsberger, H. R., Osborn, A. G., Ross, J., & Macdonald, A. (2006). Diagnostic and surgical imaging anatomy: Brain, head and neck, spine. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Hoehne, K. H. (1995). VOXEL-MAN, part 1: Brain and skull. Heidelberg: Springer.
Huber, P. (1982). Cerebral angiography (2nd ed.). Stuttgart: Thieme.
Kirbas, C., & Quek, F. (2003). Vessel extraction in medical images by 3D wave propagation and traceback. IEEE Third Symposium on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering BIBE 2003, Bethesda, USA, 2003–03, pp. 174–181.
Kockro, R. A., Serra, L., Yeo, T. T., Chan, C., Sitoh, Y. Y., Chua, G. G., et al. (2000). Planning and simulation of neurosurgery in a virtual reality environment. Neurosurgery, 46(1), 118–137.
Kretschmann, H. J., & Weinrich, W. (2004). Cranial neuroimaging and clinical neuroanatomy (3rd ed.). Stuttgart: Thieme.
Lorensen, W. E., & Cline, H. E. (1987). Marching cubes: A high resolution 3D surface construction algorithm. Computer Graphics (Proceedings of SIGGRAPH ‘87), 21(4), 163–169.
Lorigo, L. M., Faugeras, O. D., Grimson, W. E., Keriven, R., Kikinis, R., Nabavi, A., et al. (2001). CURVES: Curve evolution for vessel segmentation. Medical Image Analysis, 5(3), 195–206.
Luo, S., Lee, S. Y., Ma, X., Aziz, A., Hu, Q., & Nowinski, W. L. (2005). Automatic extraction of cerebral arteries: Algorithm and validation. Proc. Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, CARS 2005, 19th International Congress and Exhibition; International Congress Series, 1281, 375–380.
Luo, S., & Zhong, Y. (2005). Extraction of brain vessels from magnetic resonance angiographic images: Concise literature review, challenges, and proposals. Conference Proceeding IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2, 1422–1425.
Marchenko, Y., Volkau, I., & Nowinski, W. L. (2008). Vascular Editor: From images to 3D vascular models. Journal of Digital Imaging (in press).
MathWorks (2001). MATLAB: Curve fitting toolbox user’s guide. Natick: MathWorksMathWorks.
Nowinski, W. L., Thirunavuukarasuu, A., & Benabid, A. L. (2005a). The Cerefy Clinical Brain Atlas: Enhanced Edition with Surgical Planning and Intraoperative Support. Thieme, New York.
Nowinski, W. L., Thirunavuukarasuu, A., & Bryan, R. N. (2002). The Cerefy Atlas of Brain Anatomy. An Introduction to Reading Radiological Scans for Students, Teachers, and Researchers. Thieme, New York.
Nowinski, W. L., Thirunavuukarasuu, A., Volkau, I., Baimuratov, R., Hu, Q., Aziz, A., et al. (2005b). Three-dimensional brain atlas of anatomy and vasculature. Radiographics, 25(1), 263–271.
Nowinski, W. L., Thirunavuukarasuu, A., Volkau, I., Marchenko, Y., Aminah, B., Puspitasari, F., et al. (2008a). A three-dimensional interactive atlas of cerebral arterial variants. Proc. 46th Annual Meeting of American Society of Neuroradiology ASNR 2008, 426.
Nowinski, W. L., Thirunavuukarasuu, A., Volkau, I., Marchenko, Y., Aminah, B., Puspitasari, F., et al. (2008b). Cerebral vasculature in three dimensions and its correlation with imaging neuroanatomy based on 3T and 7T acquisitions. Neuroradiology 50 (Suppl 1), S67.
Nowinski, W. L., Thirunavuukarasuu, A., Volkau, I., Marchenko, Y., Knopp, M. V., Runge, V. M., et al. (2008c). A 3D interactive atlas of cerebral arteries from 7T. 94 Radiological Society of North America Scientific Assembly and Annual Meeting, Chicago, USA, November 30–December 5, 2008 (in press).
Nowinski, W. L., Thirunavuukarasuu, A., Volkau, I., Marchenko, Y., & Runge, V. M. (2008d). The Cerefy Atlas of Cerebral Vasculature. New York: Thieme.
Nowinski, W. L., Thirunavuukarasuu, A., Volkau, I., Runge, V. M., Salamon, N., & Salamon, G. (2006). Interactive atlas of cerebral vasculature. Program 92 Radiological Society of North America Scientific Assembly and Annual Meeting Program 2006, Chicago, USA, 25 November–1 December 2006, pp 884.
Passat, N., Ronse, C., Baruthio, J., Armspach, J. P., Maillot, C., & Jahn, C. (2005). Region-growing segmentation of brain vessels: An atlas-based automatic approach. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 21, 715–725.
Qiao, Y., Hu, Q., Qian, G., Luo, S., & Nowinski, W. L. (2007). Thresholding based on variance and intensity contrast. Pattern Recognition, 40(2), 596–608.
Rhoton, A. L. (2007). Cranial anatomy and surgical approaches. UK: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Rosenfeld, A., & Pfalz, J. L. (1968). Distance functions on digital pictures. Pattern Recognition, 1, 33–61.
Runge, V. M., Nitz, W. R., Schmeets, S. H., Faulkner, W. H., & Desai, N. K. (2004). The physics of clinical MR taught through images. New York: Thieme.
Salamon, G., & Huang, Y. P. (1976). Radiological anatomy of the brain. Berlin: Springer.
Schuenke, M., Schulte, E., Schumacher, U., Ross, L., & Lamperti, E. (2007). Head and neuroanatomy (Thieme Atlas of Anatomy Series). New York: Thieme.
Sundsten, J. W., Brinkley, J. F., Eno, K., & Prothero, J. (1994). The digital anatomist. Interactive brain atlas. CD ROM for the Macintosh, University of Washington, Seattle.
Volkau, I., Ng, T. T., Marchenko, Y., & Nowinski, W. L. (2008). On geometric modeling of the human intracranial venous system. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 27(6), 745–751.
Volkau, I., Zheng, W., Aziz, A., Baimouratov, R., & Nowinski, W. L. (2005). Geometric modeling of the human normal cerebral arterial system. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 24(4), 529–539.
Wilson, D. L., & Noble, J. A. (1999). An adaptive segmentation algorithm for extracting arteries and aneurysms from Time-of-flight MRA data. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 18(10), 938–945.
Wong, W., Le, T. M., Volkau, I., Thirunavuukarasuu, A., Ng, H. P., & Nowinski, W. L. (2008). Estimation and presentation of blood flow and velocity from radiological images of arterial system in the human brain. Proc. 30th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society 2008, Vancouver, Canada, 4936–4939.
Yan, P., & Kassim, A. A. (2006). Segmentation of volumetric MRA images by using capillary active contour. Medical Image Analysis, 10, 317–329.
Zheng, W. (2008). Improved modelling of the human cerebral vasculature. National University of Singapore, Singapore, PhD thesis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nowinski, W.L., Volkau, I., Marchenko, Y. et al. A 3D Model of Human Cerebrovasculature Derived from 3T Magnetic Resonance Angiography. Neuroinform 7, 23–36 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-008-9028-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-008-9028-8