Summary
During the last few decades we have seen a convergence among ideas and hypotheses regarding functional principles underlying human memory. Hebb’s now more than fifty years old conjecture concerning synaptic plasticity and cell assemblies, formalized mathematically as attractor neural networks, has remained among the most viable and productive theoretical frameworks. It suggests plausible explanations for Gestalt aspects of active memory like perceptual completion, reconstruction and rivalry.
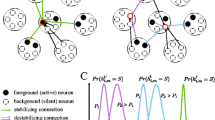
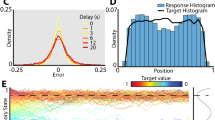
We review the biological plausibility of these theories and discuss some critical issues concerning their associative memory functionality in the light of simulation studies of models with palimpsest memory properties. The focus is on memory properties and dynamics of networks modularized in terms of cortical minicolumns and hypercolumns. Biophysical compartmental models demonstrate attractor dynamics that support cell assembly operations with fast convergence and low firing rates. Using a scaling model we obtain reasonable relative connection densities and amplitudes. An abstract attractor network model reproduces systems level psychological phenomena seen in human memory experiments as the Sternberg and von Restorff effects.
We conclude that there is today considerable substance in Hebb’s theory of cell assemblies and its attractor network formulations, and that they have contributed to increasing our understanding of cortical associative memory function.
The criticism raised with regard to biological and psychological plausibility as well as low storage capacity, slow retrieval etc has largely been disproved. Rather, this paradigm has gained further support from new experimental data as well as computational modeling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amari, S. I. (1989) Characteristics of sparsely encoded associative memory. Neural Networks 5: 451–457.
Amit, D. J. (1995) The Hebbian paradigm reintegrated: Local reverberations as internal representations. Behavioral and Brain Sciences 18: 617–657.
Amit, D. J. and M. V. Tsodyks (1991) Quantitative study of attractor neural network retrieving at low spike rates: I Substrate — spikes, rates and neuronal gain. Network: Computation in Neural Systems 2: 259–273.
Bao, J.-X., E. R. Kandel and R. D. Hawkins (1997) Involvement of pre- and postsynaptic mechanisms in posttetanic potentiation at Aplysia synapses. Science 275: 969–973.
Braitenberg, V. (1978) Cell assemblies in the cerebral cortex. Theoretical Approaches to Complex Systems. R. Heim and G. Palm, Eds. Berlin, Springer: 171–188.
Carandini, M., D. J. Heeger and J. A. Movshon (1997) Linearity and normalization in simple cells of the macaque primary visual cortex. J. Neurosci. 17: 8621–44.
Cartling, B. (1993) Control of the complexity of associative memory dynamics by neuronal adaptation. Int. J. Neural Systems 4: 129–141.
Cartling, B. (1995) Autonomous neuromodulatory control of associative processes. Network: Computation in Neural Systems 6: 247–260.
Connors, B. W. and M. J. Gutnick (1990) Intrinsic firing patterns of diverse neocortical neurons. Trends Neurosci. 13: 99–104.
Eichenbaum, H. (1993) Thinking About Brain Cell Assemblies. Science 261: 993–994.
Fransén, E. (1996) Biophysical Simulation of Cortical Associative Memory, Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden, TRITA-NA-P96/28 Dept. of Numerical Analysis and Computer Science.
Fransén, E. and A. Lansner (1995) Low spiking rates in a population of mutually exciting pyramidal cells. Network: Computation in Neural Systems 6: 271–288.
Fransén, E. and A. Lansner (1998) A model of cortical associative memory based on a horizontal network of connected columns. Network: Computation in Neural Systems 9: 235–264.
Freeman, W. and C. Skarda (1985) Spatial EEG patterns, non-linear dynamics and perception: the neo-Sherringtonian view. Brain Res. Rev. 10: 147–175.
Fuster, J. and J. P. Jervey (1982) Neuronal firing in the inferotemporal cortex of the monkey in a visual task. J. Neurosci. 2: 361–375.
Fuster, J. M. (1995) Memory in the Cerebreal Cortex. Cambridge, Massachusetts, The MIT Press.
Gilbert, C. D., J. A. Hirsch and T. N. Wiesel (1990) Lateral interactions in the visual cortex. Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantiative Biology, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. LV: 663–676.
Goldman-Rakic, P. S. (1995) Cellular basis of working memory. Neuron 14: 477–485.
Gray, C. M. and W. Singer (1989) Stimulus-specific neuronal oscillations in orientation columns of cat visual cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86: 1698–1702.
Hebb, D. O. (1949) The Organization of Behavior. New York, John Wiley Inc.
Hertz, J., A. Krogh and R. G. Palmer (1991) Introduction to the theory of neural computation. Redwood City, California, Addison-Wesley Publishing Company.
Hirsch, J. A. and C. D. Gilbert (1991) Synaptic physiology of horizontal connections in the cat visual cortex. J. Neurosci. 11(6): 1800–1809.
Hopfield, J. J. (1982) Neural Networks and physical systems with emergent collective computational properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81: 3088–3092.
Hubel, D. and T. N. Wiesel (1977) The functional architecture of the macaque visual cortex. The Ferrier lecture. Proc. Royal. Soc. B 198: 1–59.
Johansson, C., A. Sandberg and A. Lansner (2001) A Capacity Study of a Bayesian Neural Network with Hypercolumns, Dept. Numerical Analysis and Computer Science, KTH (TRITA-NA-P0120).
Lansner, A. (1982) Information processing in a network of model neurons. A computer simulation study. Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden, Dept. of Numerical Analysis and Computer Science (TRITA-NA-8211).
Lansner, A. and Ö. Ekeberg (1989) A one-layer feedback artificial neural network with a Bayesian learning rule. Int. J. Neural Systems 1: 77–87.
Lansner, A. and E. Fransén (1992) Modeling Hebbian cell assemblies comprised of cortical neurons. Network: Computation in Neural Systems 3: 105–119.
Lansner, A. and A. Holst (1996) A higher order Bayesian neural network with spiking units. Int. J. Neural Systems 7(2): 115–128.
Lansner, A. and A. Sandberg (2001) Functionality and Performance of Brain-Inspired Neural Networks. NOLTA 2001, Zao, Sendai, Japan.
LeVay, S. and C. D. Gilbert (1976) Laminar patterns of geniculocortical projections in the cat. Brain Res. 113: 1–19.
Levy, W. B. and O. Steward (1979) Synapses as associative memory elements in the hippocampal formation. Brain. Res. 175: 233–245.
MacGregor, R. J. and T. McMullen (1978) Computer simulations of diffusely connected neuronal populations. Biol. Cybernetics 28: 121–127.
Martinez, J. L., G. Schulteis and S. B. Weinberger (1991) Learning and Memory: A Biological View. J. L. Martinez and R. P. Kesner, Eds., Academic Press 149–198.
McCormick, D. A., B. W. Connors and J. W. Lighthall (1985) Comparative electrophysiology of pyramidal and sparsely spiny stellate neurons of the neocortex. J. Neurophysiol. 54: 782–806.
McGaugh, J. L. (2000) Memory — a Century of Consolidation. Science 287: 248–251.
Merzenich, M. M., R. J. Nelson, M. P. Stryker, M. S. Cynander, A. Schoppmann and J. M. Zook (1984) Somatosensory map changes following digit amputation in adult monkey. J. Comp. Neurol. 224: 591–605.
Miller, K. D. (1995) Receptive Fields and Maps in the Visual Cortex: Models of Ocular Dominance and Orientation Columns. Models of Neural Networks III. E. Domany, J. L. van Hemmen and K. Schulten, Eds. New York, Springer-Verlag 55–78.
Milner, P. M. (1957) The cell assembly: Mark II. Psychological Review 64: 242–252.
Mountcastle, V. B. (1957) Modality and topographic properties of single neurons of cat’s somatic sensory cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 20: 408–434.
Mountcastle, V. B. (1998) Perceptual neuroscience: The Cerebral Cortex. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press.
Nadal, J. P., G. Toulouse, J.-P. Changeux and S. Dehaene (1986) Networks of formal neurons and palimpsests. Europhys. Lett. 1: 535–42.
Olshausen, B. A. and D. J. Field (1997) Sparse Coding with an Overcomplete Basis Set: A Strategy Employed by V1? Vision Research 37: 3311–3325.
Palm, G. (1982) Neural Assemblies. An Alternative Approach to Artificial Intelligence. Berlin, Springer.
Pulvermuller, F. (1999) Words in the brain’s language. Behavioral and Brain Sciences 22: 280–336.
Quinlan, P. (1991) Connectionism and Psychology. A Psychological Perspective on Connectionist Research. New York, Harvester, Whaetsheaf.
Rochester, N., J. H. Holland, L. H. Haibt and W. L. Duda (1956) Tests on a cell assembly theory of the action of the brain, using a large digital computer. IRE Trans. Information Theory IT-2: 80–93.
Sandberg, A. and A. Lansner (2002) Synaptic Depression as an Intrinsic Driver of Reinstatement Dynamics in an Attractor Network. Neurocomputing 44–46: 615–622.
Sandberg, A., A. Lansner, K.-M. Petersson and Ö. Ekeberg (2002) Bayesian attractor networks with incremental learning. Network: Computation in Neural Systems 13(2): 179–194.
Sandberg, A., K. M. Petersson and A. Lansner (2001) Selective Enhancement of Recall through Plasticity Modulation in an Autoassociative Memory. Neurocomputing 38–40: 867–873.
Scannell, J. W., C. Blakemore and M. P. Young (1995) Analysis of connectivity in the cat cerebral cortex. J. Neurosci. 15: 1463–1483.
Sommer, F. T. and T. Wennekers (2001) Associative memory in networks of spiking neurons. Neural Networks 14: 825–834.
Sternberg, S. (1966) High-speed scanning in human memory. Science 153: 652–654.
Thorpe, S., D. Fize and C. Marlot (1996) Speed of processing in the human visual system. Nature 381: 520–522.
Thorpe, S. and M. Imbert (1989) Biological constraints on connectionist modelling. Connectionism in Perspective. R. Pfeiffer, Ed. Berlin, Springer-Verlag.
Traub, R. D., M. A. Whittington, S. B. Colling, G. Buzsaki and J. G. R. Jeffreys (1996) Analysis of gamma rhythms in the rat hippocampus in vitro and in vivo. J. Physiol. 493: 471–84.
von Restorff, H. (1933) Analyse von Vorgängen in Spurenfeld. Psychol. Forschung 18: 299–342.
Wahlgren, N. and A. Lansner (2001) Biological Evaluation of a Hebbian-Bayesian Learning rule. Neurocomputing 38–40, 433–438.
Wallén, P., J. Buchanan, S. Grillner, J. Christenson and T. Hökfelt (1989) The effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine on the afterhyperpolarisation, spike frequency regulation and oscillatory membrane properties in lamprey spinal cord neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 61: 759–768.
Wickens, J. and R. Kötter (1995) Cellular Models of Reinforcement. Models of Information Processing in the Basal Ganglia. J. C. Houk, J. L. Davis and D. G. Beiser, Eds. Cambridge, Massachusetts, The MIT Press 187–214.
Willshaw, D. J. and H. C. Longuet-Higgins (1969) Associative memory models. Machine Learning 5. Meltzer and Michie, Eds. Edinburgh, Scotland, Edinburgh University Press.
Yen, S.-C., E. D. Menschik and L. H. Finkel (1999) Perceptual grouping in striate cortical networks mediated by synchronization and desynchronization. Neurocomputing 26–27(1–3): 609–616.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lansner, A., Fransén, E. & Sandberg, A. Cell assembly dynamics in detailed and abstract attractor models of cortical associative memory. Theory Biosci. 122, 19–36 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12064-003-0035-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12064-003-0035-x