Abstract
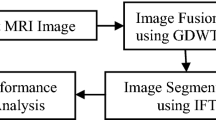
In humans, the abnormality in brain arises due to various reasons and the ischemic-stroke (IS) is one of the major brain syndromes to be diagnosed and treated with appropriate procedures. The brain-signals and brain-images are widely considered for the clinical level diagnosis of IS. The proposed research considered the brain-image (MRI) based assessment of IS, due to its accuracy and multi modality nature. The MRI slices with modalities, such as diffusion-weighted (DW), flair and T1 are considered for the assessment. This work implements the following procedures to extract the IS lesion (ISL); (i) pixel level image fusion based on principal-component-analysis (PCA), (ii) image thresholding using cuckoo-search (CS) and Tsallis entropy, (iii) watershed based ISL extraction, and (iv) comparison of segmented ISL with the ground-truth-image (GTI). To confirm the clinical significance of the proposed work, the test images are collected from the benchmark ISLES2015 database. The results of this research confirms that, the fused brain MRI slices with DW and flair (DW + flair) modality facilitate to attain improved mean values of Jaccard-Index (83.17 ± 7.32%), Dice (88.51 ± 4.76%) and segmentation accuracy (97.34 ± 1.62%) compared to other images. This research confirms that, pixel level fusion will help to achieve better result during the clinical level disease diagnosis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
STROKE: http://www.world-stroke.org/
Thanaraj P, Parvathavarthini B (2017) Multichannel interictal spike activity detection using time–frequency entropy measure. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 40(2):413–425
Rajinikanth V, Satapathy SC (2018) Segmentation of Ischemic Stroke Lesion in brain MRI based on social group optimization and fuzzy-Tsallis entropy. Arab J Sci Eng 43:4365–4378
Rajinikanth V, Palani TK, Satapathy SC, Fernandes SL, Dey N (2019) Shannon’s entropy and watershed algorithm based technique to inspect ischemic stroke wound. Smart Innov Syst Technol 105:23–31
Kanchana R, Menaka R (2015) Computer reinforced analysis for ischemic stroke recognition: a review. Indian J Sci Technol 8(35):81006
Rajinikanth V, Satapathy SC, Dey N, Lin H (2018) Evaluation of Ischemic Stroke region from CT/MR Images using hybrid image processing techniques. Intell Multidimens Data Image Process 7:194–219. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-5225-5246-8.ch007
Maier O, Wilms M, Von der Gablentz J, Krämer UM, Münte TF, Handels H (2015) Extra tree forests for sub-acute ischemic stroke lesion segmentation in MR sequences. J Neurosci Methods 240:89–100
Maier O, Schröder C, Forkert ND, Martinetz T, Handels H (2015) Classifiers for ischemic stroke lesion segmentation: a comparison study. PLoS ONE 10(12):e0145118
Maier O et al (2017) ISLES 2015—a public evaluation benchmark for ischemic stroke lesion segmentation from multispectral MRI. Med Image Anal 35:250–269
Mitra J, Bourgeat P, Fripp J, Ghose S, Rose S, Salvado O, Connelly A, Campbell B, Palmer S, Sharma G, Christensen S, Carey L (2014) Lesion segmentation from multimodal MRI using random forest following ischemic stroke. NeuroImage 98:324–335
Jahmunah V et al (2019) Automated detection of schizophrenia using nonlinear signal processing methods. Artif Intell Med 100:101698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2019.07.006
Sharma M, Patel S, Acharya UR (2020) Automated detection of abnormal EEG signals using localized wavelet filter banks. Pattern Recognit Lett 133:188–194
Acharya UR et al (2019) Automatic detection of ischemic stroke using higher order spectra features in brain MRI images. Cogn Syst Res 58:134–142
Rajinikanth V, Raj ANJ, Thanaraj KP, Naik GR (2020) A Customized VGG19 network with concatenation of deep and handcrafted features for brain tumor detection. Appl Sci 10(10):3429
Dey N et al (2019) Social-group-optimization based tumor evaluation tool for clinical brain MRI of flair/diffusion-weighted modality. Biocybern Biomed Eng 39(3):843–856
ISLES 2015. http://www.isles-challenge.org
Yushkevich PA, Piven J, Hazlett HC, Smith RG, Ho S, Gee JC, Gerig G (2006) User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: significantly improved efficiency and reliability. Neuroimage 31(3):1116–1128
ITK-SNAP. http://www.itksnap.org/pmwiki/pmwiki.php
Rajinikanth V, Satapathy SC, Dey N, Vijayarajan R (2018) DWT-PCA image fusion technique to improve segmentation accuracy in brain tumor analysis. Lect Notes Electr Eng 471:453–462
Bhateja V, Moin A, Srivastava A, le Bao N, Lay-Ekuakille A, Le DN (2016) Multispectral medical image fusion in Contourlet domain for computer based diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Rev Sci Instrum 87(7):074303
Vijayarajan R, Muttan RS (2014) Local principal component averaging image fusion. Int J Imaging Robotics 13(2):94–103
Vijayarajan R, Muttan RS (2014) Iterative block level principal component averaging medical image fusion. Optik Int J Light Electron Opt 125(17):4751–4757
Vijayarajan R, Muttan RS (2014) Fuzzy C-means clustering based principal component averaging fusion. Int J Fuzzy Syst 16(2):153–159
Yang X-S, Deb S (2009) Cuckoo search via lévy flights. In: World congress on nature & biologically inspired computing, 2009. NaBIC 2009. IEEE, pp 210–214
Yang X-S, Deb S (2010) Engineering optimisation by cuckoo search. Int J Math Model Numer Optim 1(4):330–343
Yang X-S, Deb S (2012) Cuckoo search for inverse problems and topology optimization. In: Proceedings of international conference on advances in computing. Springer, Berlin, pp 291–295
Yang X-S, Deb S (2013) Multiobjective cuckoo search for design optimization. Comput Oper Res 40(6):1616–1624
Lakshmi VS, Tebby SG, Shriranjani D, Rajinikanth V (2016) Chaotic cuckoo search and Kapur/Tsallis approach in segmentation of T cruzi from blood smear images. Int J Comput Sci Infor Sec (IJCSIS) 14:51–56
Varsha S et al (2018) Gray scale image multi-thresholding with chaotic cuckoo search. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on system, computation, automation and networking (ICSCA), pp 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSCAN.2018.8541262
Tsallis C (1988) Possible generalization of Boltzmann–Gibbs statistics. J Stat Phys 52(1):479–487
Rajinikanth V, Satapathy SC, Fernandes SL, Nachiappan S (2016) Entropy based segmentation of tumor from brain MR images—a study with teaching learning based optimization. Pattern Recognit Lett 94:87–94
Rajinikanth V, Fernandes SL, Bhushan B, Sunder NR (2018) Segmentation and analysis of brain tumor using Tsallis entropy and regularised level set. Lect Notes Electr Eng 434:313–321
Roerdink JBTM, Meijster A (2001) The watershed transform: definitions, algorithms and parallelization strategies. Fundam Inf 41:187–228
Kaleem M, Sanaullah M, Hussain MA, Jaffar MA, Choi T-S (2012) Segmentation of brain tumor tissue using marker controlled watershed transform method. Commun Comput Inf Sci 281:222–227
Deng G, Li Z (2012) An improved marker-controlled watershed crown segmentation algorithm based on high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery. Lect Note Electr Eng 128:567–572
Ward MO (2008) Multivariate data glyphs: principles and practice. Handbook of data visualization, pp 179–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-33037-0_8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to report regarding the present study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hemanth, D.J., Rajinikanth, V., Rao, V.S. et al. Image fusion practice to improve the ischemic-stroke-lesion detection for efficient clinical decision making. Evol. Intel. 14, 1089–1099 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12065-020-00551-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12065-020-00551-0