Abstract
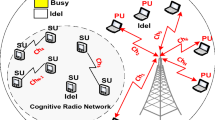
Cognitive radio (CR) is a promising wireless technology that provides efficient spectral usage. Medium Access Control (MAC) has an important role in several cognitive radio functions such as sensing, spectrum mobility, resource allocation and spectrum sharing. We focus on the opportunistic spectrum access (OSA) functionality of the CR network MAC layer by which the secondary users (SUs) access licensed spectrum in space and time with no harmful interference to primary users (PUs), without prior information on spectral usage. To achieve this, the unlicensed users should have the ability to adaptively and dynamically seek and exploit opportunities in licensed spectrum in time, polarization and frequency domains. There have been several OSA MAC schemes proposed for CR networks. This article presents a detailed review of such state-of-the-art schemes. First the differences between the conventional MAC protocols and OSA based MAC protocols are discussed. Existing OSA MAC protocols are classified according to their key attributes and their performances. Finally, future research directions are discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Federal Communications Commission (2002) Spectrum policy task force, pp 2–135
Mitola J (2000) Cognitive radio: an integrated agent architecture for software defined radio. PhD thesis, KTH Royal Institute of Technology. Stockholm
Akyildiz I, Lee W, Vuran M, Mohanty S (2006) Next generation/ dynamic spectrum access/cognitive radio wireless networks: a survey. Elsevier Comput Netw 50(13):2127–2159
Haykin S (2005) Cognitive radio: brain-empowered wireless communications. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun (JSAC) 23(2):201–220
Hijazi S, Natarajan B, Michelini M, Wu Z, Nassar C (2004) Flexible spectrum use and better coexistence at the physical layer of future wireless systems via a multicarrier platform. IEEE Wirel Comm 11 (2):8–14
Zahmati AS, Fernando X, Grami A (2010) Steady-State Markov chain analysis for heterogeneous cognitive radio networks. IEEE Sarnoff Symposium, pp 1–5
IEEE Standard for Information Technology, Telecommunications and information exchange between systems WRAN Specific requirements - Part 22: Cognitive Wireless RAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications, IEEE 802.22a (Amendment to the IEEE Std-802.22-2011(TM)) (2014). [Online]. Available: https://standards.ieee.org/about/get/802/802.22.html
Standard for Wireless LAN in TV White Space, IEEE 802.11af (2014). [Online]. Available: https://standards.ieee.org/news/2014/ieee802.11af
IEEE 1900 Standards. [Online]. Available: http://grouper.ieee.org/groups/dyspan/
IEEE 802.19: TV white space coexistence methods. [Online]. Available: https://standards.ieee.org/about/get/802/802.19.html
ETSI (2013) Mobile Broadband Services in the 2,300 MHz 2,400 MHz Frequency Band under Licensed Shared Access regime
Matinmikko M, Palola M, Saarnisaari H, Heikkila M, Prokkola J, Kippola T, Hanninen T, Jokinen M, Yrjola S (2013) Cognitive Radio Trial Environment: First live authorized shared access-based spectrum-sharing demonstration. IEEE Veh Technol Mag 8(3):30–37
IEEE 802.15 Working Group (2012) Wireless medium access control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) specifications for low-rate wireless personal area networks (WPANs). [Online]. Available: http://www.ieee802.org/15/pub/TG4m.html,accessedJun.2012
Gavrilovska L, Denkovsk D, Rakovic V, Angjelichinoski M (2014) Medium access control protocols in cognitive radio networks: Overview and general classification. IEEE Commun Surv Tutorials 16(4):2092–2124
Chowdhury M, Asaduzzaman, Kader MF (2014) Cognitive Radio MAC Protocols: A Survey, Research Issues, and Challenges. Smart Comput Rev 5(1):19–29
Ren P, Wang Y, Du Q, Xu J (2012) A survey on dynamic spectrum access protocols for distributed cognitive wireless networks. EURASIP J Wirel Commun Netw 2012(60):1–21
Domenico AD, Strinati EC, Benedetto M.-G. D (2012) A survey on MAC strategies for cognitive radio networks. IEEE Commun Surv Tutorials 14(1):21–44
Xiang J, Zhang Y, Skeie T (2010) Medium access control protocols in cognitive radio networks. Wirel Commun Mob Comput 10(1):31–49
Cormio C, Chowdhury KR (2009) A survey on MAC protocols for cognitive radio networks. Ad Hoc Netw (ELSEVIER) 7(7):1315–1329
JHA SC, Rashid MM, Bhargava VK (2011) Medium access control in distributed cognitive radio networks. IEEE Wirel Commun 18(4):41–51
Yau AK-L, Komisarczuk P, Teal PD (2008) On multi-channel MAC protocols in cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference Australasian telecommunication networks and applications conference (ATNAC08), Adelaide, pp 300–305
Wang H, Zhou H, Qin H (2008) Overview of Multi-channel MAC Protocols in Wireless Networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference wireless communications, networking and mobile computing, pp 1–5
Pawelczak P, Pollin S, So H, Bahai A, Prasad R, Hekmat R (2008) Comparison of opportunistic spectrum multichannel medium access control protocols. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference globecom, pp 1–6
Mo J, So HSW, Walrand J (2008) Comparison of multi-channel MAC protocols. IEEE Trans Mobile Comput 7(1):50–65
Sun Y, Zhou B, Wu Z, Ni Q, Zhu R (2013) Multi-channel MAC Protocol in Cognitive Radio Networks. J Netw 8(11):2478–2490
Wang H, Qin H, Zhu L (2008) Performance analysis of multichannel medium access control algorithms for opportunistic spectrum access. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference computer and science software engineering, vol 1, Wuhan, pp 214–218
Pawelczak E.-Y. P, Pollin S, So H.-S. W, Bahai A, Prasad RV, Hekmat R (2008) Quality of service assessment of opportunistic spectrum ccess: a medium access control approach. IEEE Wirel Commun 15 (5):20–29
Krishna TV, Das A (2009) A survey on MAC protocols in OSA networks. Comput Netw (ELSEVIER) 53(9):1377– 1394
Wang H, Qin H, Zhu L (2008) A survey on MAC protocols for opportunistic spectrum access in cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference computer science and software engineering (CSSE), vol 1, pp 214–218
Cordeiro C, Challapali K, Birru D, Shankar S (2006) IEEE 802.22: An introduction into the first wireless standard based on cognitive radios. J Commun 1(1):38–47
Choi N, Patel M, Venkatesan S (2006) A full duplex multi-channel MAC protocol for multi-hop cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference cognitive radio oriented wireless networks and communications, pp 1–5
Hossain E, Niyato D, Han Z (2009) Dynamic spectrum access and management in cognitive radio networks. Cambridge University Press
Sharma SK, Chatzinotas S, Ottersten B (2015) 3D Beamforming for spectral coexistence of satellite and terrestrial networks. In: IEEE vehicular technology conference
Goldsmith A, Jafar SA, Maric I, Srinivasa S (2009) Breaking spectrum gridlock with cognitive radios: an information theoretic perspective. Proc IEEE 97(5):894–914
Zhao Q, Sadler B (2007) A survey of dynamic spectrum access. IEEE Signal Process Mag 24(3):79–89
Akyildiz I, Lee W, Chowdury K (2009) CRAHNS: cognitive radio ad hoc networks. J Ad Hoc Netw 7 (5):810–836
Jia J, Zhang Q, Shen XS (2008) HC-MAC: a hardware-constrained cognitive MAC for efficient spectrum management. IEEE J Selected Areas in Commun 26(1):233–242
Shah MA, Safdar GA, Maple C (2011) DDH-MAC: a novel dynamic De-Centralized hybrid MAC protocol for cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings IEEE international conference roedunet international conference (RoEduNet), pp 1–6
Safdar G, Neill M (2009) Common control channel security framework for cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings IEEE 69th vehicular technology conference, pp 1–5
Zhao J, Zheng H, Yang G.-H (2005) Distributed coordination in dynamic spectrum allocation networks. In: Proceedings of 1st IEEE international symposium new frontiers DySpan, Baltimore, pp 259–268
Chen T, Zhang H, Maggio G, Chlamtac I (2007) Topology management in CogMesh: a cluster-based cognitive radio mesh network. In: Proceedings of IEEE ICC, Glasgow, pp 6516– 6521
Liu S, Lazos L, Krunz M (2012) Cluster-based control channel allocation in opportunistic cognitive radio networks. IEEE Trans Mobile Comput 11(10):1436–1449
Lazos L, Liu S, Krunz M (2009) Topology management in CogMesh: a cluster-based cognitive radio mesh network. In: Proceedings of 6th annual IEEE communication. SECON, Rome, pp 135–143
Cordeiro C, Challapali K (2007) c-MAC: a cognitive MAC protocol for multi-channel wireless networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE symposium new frontiers in dynamic spectrum access networks (DySPAN), pp 147–157
Rozovsky R, Kumar P (2001) SEEDEX: a MAC protocol for Ad Hoc networks. In: Proceedings of ACM MobiHoc, pp 67–75
Lo BF (2011) A survey of common control channel design in cognitive radio networks. Phys Commun 4(1):26–39
Standard for Recommended Practice for Installation and Deployment of IEEE 802.22 Systems, IEEE 802.22.2-2012(TM), Sep. 28 2012
Mauriand JL, Ghafoor KZ, Rawat DB, Perez JMA (2014) Cognitive networks: applications and deployments. CRC Press-Taylor and Francis Group, USA. ISBN=9781482236996
Sengupta S, Subbalakshmi KP (2013) Open research issues in Multi-Hop cognitive radio networks. IEEE Commun Mag 51(4):168–176
So J, Vaidya N (2004) Multi-Channel MAC for ad hoc networks: handling multi-channel hidden terminals using a single transceiver. In: Proceedings of ACM MobiHoc, pp 222–233
Hussain S, Fernando X (2014) Closed-form analysis of relay-based cognitive radio networks over nakagami-m fading channels. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 63(02):1193–1203
Tripathi SB, Shah M.B (2014) A dynamic opportunistic spectrum access MAC protocol for cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference advances in computing, communications and informatics (ICACCI), pp 1195–1198
Kim KJ, Kwak KS, Choi BD (2013) Performance analysis of opportunistic spectrum access protocol for multi-channel cognitive radio networks. J Commun Netw 15(1):77–86
Benslimane A, Ali A, Kobbane A, Taleb T (2009) A new opportunistic MAC layer protocol for cognitive IEEE 802.11-based wireless networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference personal, indoor and mobile radio communications, pp 2181–2185
Debroy S, De S, Chatterjee M (2013) A new opportunistic MAC layer protocol for cognitive IEEE 802.11-based wireless networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE global communications conference (GLOBECOM), pp 1221–1226
Hamdaoui B, Shin KG (2008) OS-MAC: an efficient MAC protocol for spectrum-agile wireless networks. IEEE Trans Mobile Comput 7(8):915–930
Hsu AC-C, Wei DSL, Kuo C-CJ (2007) A cognitive MAC protocol using statistical channel allocation for wireless ad-hoc networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE wireless communications and networking conference(WCNC), pp 105–110
Hung S-Y, Cheng Y-C, Wu EH-K, Chen G-H (2008) An opportunistic cognitive MAC protocol for coexistence with WLAN. In: Proceedings of IEEE ICC, Beijing, pp 4059–4063
Hung S-C, Hung S-Y, Wu EH-K, Chen G-H (2006) A decentralized CR system algorithm for cognitive borrowing scheme from primary users. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference personal, indoor and mobile radio communications, pp 1–5
Ma L, Han X, Shen C-C (2005) Dynamic open spectrum sharing MAC protocol for wireless ad hoc networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE symposium on new frontiers in dynamic spectrum access networks (DySPAN), pp 203–213
Su H, Zhang X (2008) Channel-Hopping based single transceiver MAC for cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE annual conference on information sciences and systems (CISS, pp 197–202
Shih C. -F., Wu TY, Liao W (2010) DH-MAC: a dynamic channel hopping MAC protocol for cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE ICC. Cape Town, pp 1–5
Msumba J, Xu H (2013) Throughput optimization MAC scheme for cognitive radio networks: a POMDP framework. In: Proceedings of AFRICON, pp 1–5
Yoo S.-J., Nan H, Hyon T.-I. (2009) DCR-MAC: distributed cognitive radio MAC protocol for wireless ad hoc networks. J Wirel Commun Mob Comput 9(5):631–653
Fourati S, Hamouda S, Tabbane S (2011) RMC-MAC: a reactive multi-channel MAC protocol for opportunistic spectrum access. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference new technologies, mobility and security (NTMS), pp 1–5
Yucek T, Arslan H (2009) A survey of spectrum sensing algorithms for cognitive radio applications. IEEE Commun Surv Tutorials 11(1):116–130
Park J, Paweczak P, Cabric D (2010) To buffer or to switch: design of multichannel MAC for OSA Ad Hoc networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE symposium new frontiers in dynamic spectrum access networks (DySPAN), pp 1–10
Park J, Paweczak P, Cabric D (2011) Performance of joint spectrum sensing and MAC algorithms for multichannel opportunistic spectrum access ad hoc networks. IEEE Trans Mobile Comput 10(7):1011–1027
Al-Mahdi H, Wahed M, El-Aziz SA (2014) Design and analysis of an OSA-BR MAC protocol for cognitive radio ad hoc networks. Int J Commun, Netw Syst Sci 7(7):223–234
Oo TZ, Tran NH, Dang DNM, Han Z, Le LB, Hong CS OMF-MAC: an opportunistic matched filter-based MAC in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Trans Veh Technol
Zahmati AS, Fernando X, Grami A (2013) Application-specific spectrum sensing method for cognitive sensor networks. IET Wireless Sens Syst 3(3):193–204
Gilbert EN (1960) Capacity of burst-noise channels. Bell Syst Tech J 39:1253–1265
Rabiner L, Juang H (1986) An introduction to hidden Markov models. IEEE ASSP Mag 3(1):4–16
Akyildiz IF, Lo BF, Balakrishnan R (2011) Cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks: a survey. J Phys Commun (ELSEVIER) 4(1):40–62
Alshamrani A, Shen X, Xie L-L (2009) A cooperative MAC with efficient spectrum sensing algorithm for distributed opportunistic spectrum networks. J Commun 4(10):728–740
Hu D, Mao S (2009) Design and analysis of a sensing error-aware MAC protocol for cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE global telecommunications conference (GLOBECOM), pp 1–6
Chowdhury M, Asaduzzaman, Kader MF, Rahman MO (2012) Design of an efficient MAC protocol for opportunistic cognitive radio networks. Int J Comput Sci Inf Technol (IJCSIT) 4(5):233–242
Zheng S, Liang Y-C, Kam PY, Hoang AT (2009) Cross-layered design of spectrum sensing and MAC for opportunistic spectrum access. In: Proceedings of IEEE wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC), pp 1–6
Zhao Q, Tong L, Swami A, Chen Y (2007) Decentralized cognitive MAC for opportunistic spectrum access in ad hoc networks: a POMDP framework. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 25(3):589–600
Mehanna O, Sultan A, Gamal HE (2009) Cognitive MAC protocols for general primary network models. IEEE Trans Mob Comput 1–12
Liu K, Zhao Q (2010) Indexability of restless bandit problems and optimality of Whittle index for dynamic multichannel access. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 56(11):5547–5567
Park J, van der Schaar M (2011) Cognitive MAC protocols using memory for distributed spectrum sharing under limited spectrum sensing. IEEE Trans Commun 59(9):2627–2637
Jiang L, Jiang H, Wu S, Zhou X (2012) Decentralized cognitive MAC protocol based on SARSA. In: Proceedings of IEEE 14th international conference communication technology (ICCT), pp 392–396
Koivunen V, Kulkarni SR, Poor HV (2011) Reinforcement learning based distributed multiagent sensing policy for cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE symposium new frontiers in dynamic spectrum access networks (DySPAN), pp 642–646
Teng YL, Richard F, Han YK (2011) Reinforcement-Learning-Based double auction design for dynamic spectrum access in cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC) , pp 90–95
Sharma M, Sahoo A (2013) Residual white space distribution based opportunistic multichannel access protocol for dynamic spectrum access networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE 5th international conference communication systems and networks (COMSNETS), pp 1–10
Chen Q, Wong W-C, Motani M, Liang Y-C (2013) Decentralized cognitive MAC for opportunistic spectrum access in ad hoc networks: a POMDP framework. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 31(11):2289–2300
Liu G, Chen C, Li Y, Guo J (2009) Priority-based variable multi-channel MAC protocols in cognitive radio wireless network: a fair channel access strategy. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference communications technology and applications (ICCTA), pp 488–492
Salameh HAB, Krunz M, Manzi D (2014) Spectrum bonding and aggregation with Guard-Band awareness in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Trans Mobile Comput 13(3):569– 581
Timalsina SK, Moh S, Chung I, Kang M (2013) A concurrent access MAC protocol for cognitive radio ad hoc networks without common control channel. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process 2013(69):1–13
Joshi GP, Kim SW, Kim B-S (2009) An efficient MAC protocol for improving the network throughput for cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference next generation mobile applications, services and technologies (NGMAST), pp 271–275
Ansari J, Zhang X, Mahonen P (2010) A decentralized MAC for opportunistic spectrum access in cognitive wireless networks. Comput Commun 36(13):1399–1410
Hsu C-S, Chen Y-S, He C-E (2010) An efficient dynamic adjusting MAC protocol for multichannel cognitive wireless networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference wireless communications, networking and information security (WCNIS), pp 556–560
Liu X, Xie J (2014) A Slot-Asynchronous MAC protocol design for blind rendezvous in cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE global communications conference (GLOBECOM), pp 4641–4646
Wang XY, Wong A, Ho P-H (2011) Stochastic medium access for cognitive radio ad hoc networks. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 29(4):770–783
Hastings WK (1970) Monte carlo sampling methods using markov chains and their applications. Biometrika 57(1):97–109
Joshi GP, Kim SW (2011) An enhanced synchronized MAC protocol for cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference wireless communications, networking and mobile computing (WiCOM), pp 1–4
Xue D, Ekici E, Wang X (2010) Opportunistic periodic MAC protocol for cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE global telecommunications conference (GLOBECOM), pp 1–6
Cox DR (1967) Renewal theory, Butler and Tanner Ltd, London
Htike Z, Lee J, Hong CS (2012) A MAC protocol for cognitive radio networks with reliable control channels assignment. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference information networking (ICOIN), pp 81–85
Anamalamudi S, Jin M (2014) Hybrid common control channel based MAC protocol for cognitive radio Ad-Hoc networks. Int J Inf Electron Eng 4(3):216–224
Park J, Jain R, cabric D (2009) Spectrum sensing design framework based on cross-layer optimization of detection efficiency. In: Proceedings of IEEE ICC, Dresden, pp 1–6
Sun C, Zhang W, Letaief KB (2007) Cluster-based cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio systems. In: Proceedings of ICC, pp 2511–2515
Kalil MA, Puschmann A, Mitschele-Thiel A (2012) SWITCH: a multichannel MAC protocol for cognitive radio ad hoc networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Fall), pp 1–5
Gu Z, Hua Q-S, Wang Y, Lau FC (2013) Nearly optimal asynchronous blind rendezvous algorithm for cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE sensor mesh and ad hoc communications and networks (SECON), pp 371–379
Wang S, Zhang J, Tong L (2012) A characterization of delay performance of cognitive medium access. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 11(2):800–809
Liu Y, Gong W (2003) On fluid queueing systems with strict priority. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 48(12):2079–2088
Elmachkour M, Kobbane A, Sabir E, Koutbi ME (2012) New insights from a delay analysis for cognitive radio networks with and without reservation. In: Proceedings of IEEE wireless communications and mobile computing conference (IWCMC), pp 65–70
Su H, Zhang X (2008) Cross-layer based opportunistic MAC protocols for QoS provisionings over cognitive radio wireless networks. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 26(1):118–129
Azarfar A, Frigon J-F, Sanso B (2015) Delay analysis of multichannel opportunistic spectrum access MAC protocols. IEEE Trans Mob Comput PP(99):1–14
Wang Y, Ren P, Wu G (2010) A throughput-aimed MAC protocol with QoS provision for cognitive ad hoc networks. IEICE Trans Commun E93-B(6):1426–1429
Le L, Hossain E (2008) OSA-MAC: a MAC protocol for opportunistic spectrum access in cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC), pp 1426–1430
Botong L, Jing L, Zhi N, Xiaoying G, Youyun X (2009) An improvement on opportunistic spectrum access MAC protocol. In: Proceedings of IEEE 15th Asia-Pacific conference on communications (APCC), pp 766–769
Jha SC, Phuyal U, Rashid MM, Bhargava VK (2011) Design of OMC-MAC: an opportunistic multi-channel MAC with QoS provisioning for distributed cognitive radio networks. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 10(10):3414–3425
Hasan R, Murshed M (2011) A novel multichannel cognitive radio network with throughput analysis at saturation load. In: Proceedings of IEEE international symposium on network computing and applications (NCA), pp 211–218
Hasan R, Murshed M (2012) Unsaturated throughput analysis of a novel interference-constrained multi-channel random access protocol for cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE 23rd international symposium on personal, indoor and mobile radio communications (PIMRC), pp 178–184
Song H, Lin X (2008) A group based MAC protocol for QoS provisioning in cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference communication systems (ICCS), pp 1489–1493
Li J, Luo T, Gao J, Yue G (2015) A MAC protocol for link maintenance in multichannel cognitive radio ad hoc networks. IEEE J Commun Netw 17(2):172–183
Li J, Gao J, Luo T, Yue G (2012) Design of QSPM-MAC quasi-synchronous priority multichannel MAC access protocol. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference wireless communications and signal processing (WCSP), pp 1–6
Kondareddy YR, Agrawal P (2008) Synchronized MAC protocol for multi-hop cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE ICC, Beijing, pp 3198–3202
Nguyen MV, Hong CS (2013) Interference-dependent contention control in multi-hop wireless ad-hoc networks: an optimal cognitive MAC protocol. In: Proceedings of IEEE ICC, Budapest
Standard for Recommended Practice for Installation and Deployment of IEEE 802.22 Systems, IEEE 802.22.2-2012(TM) (2012)
Mody AN, Lei Z, Ko G, Pyo C, Rahman MA (2011) Introduction to IEEE Std. 802.22-2011 and its amendment PAR for P802.22b: broadband extension and monitoring. IEEE 802 Plenary Session, Atlanta
Authorised Shared Access: an innovative model of pro-competitive spectrum management. Parcu and Associates (2012)
RSPG opinion on LSA (2013)
Matinmikko M, Okkonen H, Palola M, Yrjola S, Ahokangas P, Mustonen M (2014) Spectrum sharing using licensed shared access: the concept and its workflow for LTE -advanced networks. IEEE Wireless Commun 21(2):72–79
3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP): technical specifications; LTE (Evolved UTRA) and LTE-advanced radio technology series (Rel 11). [Online]. Available: http://www.3gpp.org/DynaReport/36-series.htm
Liu L, Chen R, Geirhofer S, Sayana K, Shi Z, Zhou Y (2012) Downlink MIMO in LTE-advanced: SU-MIMO vs. MU-MIMO. IEEE Commun Mag 50(2):140–147
Lee J-KHJ, Zhang J (2009) MIMO technologies in 3GPP LTE and LTE-advanced. EURASIP J Wirel Commun Netw 2009
Karunakaran P, Wagner T, Scherb A, Gerstacker W (2014) On simultaneous sensing and reception for cognitive LTE-A systems. In: Proceedings of IEEE international workshop on cognitive cellular systems (CCS), pp 1–5
Sesia S, Toufik I, Baker M (2011) LTE - the UMTS long term evolution: from theory to practice, 2nd edn. Wiley
Hussain S, Fernando X (2014) Performance analysis of relay-based cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks over non-identical nakagami-m channels. IEEE Trans Commun 62(8):2733–2746
Wang Y, Xu Y, Shen L, Xu C, Cheng Y (2014) Two-dimensional POMDP-based opportunistic spectrum access in time-varying environment with fading channels. IEEE J Commun Netw 16(2):217–226
Wang B, Wu Y, Liu KR (2010) Game theory for cognitive radio networks: an overview. Comput Netw (ELSEVIER) 54(14):2537–2561
Vaid V, Patel A, Merchant SN (2014) Optimal channel stopping rule under constrained conditions for CRNs. In: Proceedings of IEEE national conference on communications (NCC), pp 1–5
Sharma H, Patel A, Merchant SN, Desai UB (2014) Optimal spectrum sensing for cognitive radio with imperfect detector. In: Proceedings of IEEE vehicular technology conference (VTC Spring), pp 1–5
Xu Y, Anpalagan A, Wu Q, Shen L, Gao Z, Wang J (2013) Decision-theoretic distributed channel selection for opportunistic spectrum access: strategies, challenges and solutions. IEEE Commun Surv Tutorials 15 (4):1689–1713
Jingqi F, Qiang Z, Haikuan W (2009) A new backoff algorithm based on the dynamic modulating parameters of IEEE 802.11. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference wireless communications, networking and mobile computing (WiCom), pp 1–4
Mawlawi B, Doré J-B (2013) CSMA/CA bottleneck remediation in saturation mode with new backoff strategy. In: Proceedings of 6th International Workshop on Multiple Access Communications (MACOM), vol 8310, pp 70–81
Lo BF, Akyildiz IF, Al-Dhelaan AM (2010) Efficient recovery control channel design in cognitive radio ad hoc networks. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 59(9):4513–4526
Akyildiz IF, Lo BF, Balakrishnan R (2011) Efficient recovery control channel design in cognitive radio ad hoc networks. Phys Commun 4(1):40–62
dos Santos PMR, Kalil MA, Artemenko O, Lavrenko A, Mitschele-Thiel A (2013) Self-organized common control channel design for cognitive radio ad hoc networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE international symposium on personal indoor and mobile radio communications (PIMRC), pp 2419–2423
Lo BF, Akyildiz IF (2010) Reinforcement learning-based cooperative sensing in cognitive radio ad hoc networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE international symposium on personal indoor and mobile radio communications (PIMRC), pp 2244–2249
Chan A, Liu X, Noubir G, Thapa B (2007) Efficient broadcast control channel jamming: resilience and identification of traitors. In: Proceedings of IEEE international symposium on information theory (ISIT), pp 2496–2500
Bian K, Park JM (2006) MAC-layer misbehaviors in multi-hop cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings of US-Korea conference on science, technology and entrepreneurship, pp 1–8
Lo BF, Akyildiz IF (2012) Multiagent jamming-resilient control channel game for cognitive radio ad hoc networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE ICC, Ottawa, pp 1821–1826
Srivastava V, Motani M (2005) Cross-layer design: a survey and the road ahead. IEEE Commun Mag 43 (12):112– 119
Peng Y, Xiang F, Long H (2009) The research of cross-layer architecture design and security for cognitive radio network. In: Proceedings of IEEE international symposium on information engineering and electronic commerce (IEEC), pp 603– 607
Ren K, Zhu H, Han Z, Poovendran R (2013) Security in cognitive radio networks. Proc IEEE Netw 27(3):2–3
Sharma RK, Rawat DB (2015) Advances on security threats and countermeasures for cognitive radio networks: a survey. IEEE Commun Surv Tutorials 17(2):1023–1043
He A, Bae KK, Newman TR, Gaeddert J, Kim K, Menon R, Morales-Tirado L, Neel JJ, Zhao Y, Reed JH, Tranter WH (2010) A survey of artificial intelligence for cognitive radios. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 59(4):1578–1592
Christian I, Moh S, Chung I, Lee J (2012) Spectrum mobility in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Commun Mag 50(6):114– 121
Liu X, Ding Z (2007) ESCAPE: a channel evacuation protocol for spectrum-agile networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE international symposium new frontiers in dynamic spectrum access networks (DySPAN), pp 292–302
Giupponi L, Prez-Neira AI (2008) Fuzzy-based spectrum handoff in cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference cognitive radio oriented wireless networks and communications, pp 1–6
Butun I, Talay AC, Altilar DT, Khalid M, Sankar R (2010) Impact of mobility prediction on the performance of cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE wireless telecommunications symposium (WTS), pp 1–5
Xing X, Jing T, Cheng W, Huo Y, Cheng X (2013) Spectrum prediction in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Wirel Commun 20(2):90–96
Akbar IA, Tranter WH (2007) Dynamic spectrum allocation in cognitive radio using hidden Markov models: poisson distributed case. In: Proceedings of IEEE Southeastcon, pp 196–201
Tumuluru VK, Wang P, Niyato D (2010) A neural network based spectrum prediction scheme for cognitive radio. In: Proceedings of ICC, Cape Town, pp 1–5
Xing X, Jing T, Huo Y, Li H, Cheng X (2013) Channel quality prediction based on bayesian inference in cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM, Turin, pp 1465–1473
Wen Z, Luo T, Xiang W, Majhi S, Ma Y (2008) Autoregressive spectrum hole prediction model for cognitive radio systems. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on communications workshops, pp 154–157
Nejatian S, Syed-Yusof SK, Latiff NMA, Asadpour V (2013) Integrated handoff management in cognitive radio mobile ad hoc networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE international symposium on personal indoor and mobile radio communications (PIMRC), pp 2887–2892
Gözüpek D, Alagöz F (2011) An opportunistic pervasive networking paradigm: multi-hop cognitive radio networks. In: Obaidat MS, Denko M, Woungang I (eds) Pervasive computing and networking. Wiley, Chichester. doi:10.1002/9781119970422.ch7
Rabbi KM, Rawat DB, Ahad MA, Amin T (2015) Analysis of multi-hop opportunistic communications in cognitive radio network. In: Proceedings of IEEE SoutheastCon, Fort Lauderdale, pp 1–8
Kartheek M, Sharma V (2012) Providing QoS in a cognitive radio network. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on communication systems and networks (COMSNETS), pp 1–9
Sahoo A, Souryal M (2015) Implementation of an opportunistic spectrum access system with disruption QoS provisioning and PU traffic parameter estimation. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC), pp 1084–1089
Ansari J, Zhang X, Achtzehn A, Petrova M, Mahonen P (2011) A flexible MAC development framework for cognitive radio systems. In: Proceedings of IEEE international wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC), pp 156– 161
Mishra V, Tong LC, Chan S, Mathew J (2014) TQCR-Media access control: two-level quality of service provisioning media access control protocol for cognitive radio network. IET Netw 3(2):74–81
Zia MT, Qureshi FF, Shah SS (2013) A energy efficient cognitive radio MAC protocols for adhoc network: a survey. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference computer modelling and simulation (UKSim), pp 140–143
Timmers M, Pollin S, Dejonghe A, der Perre LV, Catthoor F (2010) A distributed multichannel MAC protocol for multihop cognitive radio networks. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 59(1):446–459
Kamruzzaman SM (2010) An energy efficient multichannel MAC protocol for cognitive radio ad hoc networks. Int J Commun Netw Inf Secur (IJCNIS) 2(2):112–119
Hoang DT, Niyato D, Wang P, Kim DI (2015) Performance optimization for cooperative multiuser cognitive radio networks with RF energy harvesting capability. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 14(7):112–119
Suojanen M, Nurmi J (2014) Tactical applications of heterogeneous ad hoc networks – cognitive radios, wireless sensor networks and COTS in networked mobile operations. In: In the proceedings of international conference on advances in cognitive radio (COCORA), pp 1–5
Chv̈ez-Santiago R, Balasingham I (2011) Cognitive radio for medical wireless body area networks. In: In the proceedings of IEEE international workshop on computer aided modeling and design of communication links and networks (CAMAD), pp 148–152
Hu S, Yao Y-D, Yang Z (2014) MAC Protocol identification using support vector machines for cognitive radio networks. IEEE Wirel Commun 21(1):52–60
Cheng Y-C, Wu EH, Chen G-H (2015) A decentralized MAC protocol for unfairness problems in coexistent heterogeneous cognitive radio networks scenarios with collision-based primary users. IEEE Syst J PP(99):1–12
Naranjo J, Viering I, Friederichs K (2012) A cognitive radio based dynamic spectrum access scheme for lte heterogeneous networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE wireless telecommunications symposium (WTS), pp 1–7
Deaton J, Irwin R, DaSilva L (2011) The effects of a dynamic spectrum access overlay in lte-advanced networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE symposium on new frontiers in dynamic spectrum access networks (DySPAN), pp 488–497
Naranjo JD, Bauch G, Saleh AB, Viering I, Halfmann R (2013) A dynamic spectrum access scheme for an LTE-advanced HetNet with carrier aggregation. In: Proceedings of International ITG Conferenceon Systems, Communication and Coding (SCC), pp 1–6
Zhang Y, Yu R, Nekovee M, Liu Y, Xie S, Gjessing S (2012) Cognitive machine-to-machine communications: visions and potentials for the smart grid. IEEE Netw 26(3):6–13
Hoang DT, Niyato D (2012) Performance analysis of cognitive machine-to-machine communications. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on communication systems (ICCS), pp 245–249
Aijaz A, Aghvami A-H (2015) Cognitive machine-to-machine communications for internet-of-things: a protocol stack perspective. IEEE Internet Things J 2(2):103–112
Boisguene R, Chou S, Huang C (2014) A survey on cognitive machine-to-machine communications. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference wireless communications and mobile computing (ICWCMC), pp 739–744
Tarchi D, Fantacci R, Marabissi D (2015) An M2M cognitive MAC protocol for overlaid OFDMA environments. Transactions on emerging telecommunications technologies (Wiley). doi:10.1002/ett.2955
Aijaz A, Ping S, Akhavan M, Aghvami A-H (2014) CRB-MAC: a receiver-based MAC protocol for cognitive radio equipped smart grid sensor networks. IEEE Sensors J 14(12):4325– 4333
Aijaz A, Aghvami A-H (2013) A PRMA based MAC protocol for cognitive machine-to-machine communications. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference communication (ICC), pp 2753–2758
Yang M, An J (2011) Opportunistic spectrum access with spectrum heterogeneity in cognitive networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference wireless communications, networking and mobile computing (WiCOM), pp 1–5
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely acknowledge the support from Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) of Canada and support from the Ryerson University Faculty of Engineering and Architectural Science Dean’s Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sultana, A., Fernando, X. & Zhao, L. An overview of medium access control strategies for opportunistic spectrum access in cognitive radio networks. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 10, 1113–1141 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-016-0465-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-016-0465-0