Abstract
Multicast is a group communication paradigm which aims at reducing, as much as possible, the amount of data generated into the network. Thus, IP Multicast presents itself as a technology that allows data to be distributed in such a way that the least amount of replicas of the same packet is placed into the network. However, the limited deployment of IP level Multicast protocols has lead to new approaches, in the application-level, implementing multicast using end systems and not routers. This concept has resulted in different approaches denominated as Application-Layer Multicast (ALM) or Overlay Multicast based systems. In this context, this work presents and analyzes an overlay multicast system envisioned to be highly reconfigurable and adaptable to different usability contexts. Such system versatility is not only present in the capability to construct distinct multicast distribution trees, but also in the integration of several advanced Traffic Engineering mechanisms based on collaborative efforts between the overlay and the Internet Service Provider (ISP) levels. Results from the proposed overlay system and associated mechanisms are obtained using a real system implementation which has been tested in a network emulation tool, with the experimental scenarios encompassing both single and multiple Autonomous Systems (AS).





















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
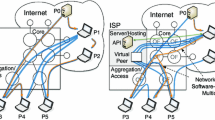
From this point on, in all the tests, a similar representation of the overlay network will be used to make easier the results perception.
References
Hardwick J (2004) IP Multicast explained, Metaswitch, http://kambing.ui.ac.id/onnopurbo/library/library-ref-eng/ref-eng-3/network/multicast.pdf, 71
Cisco IP Multicast, https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/ios-nx-os-software/ip-multicast/index.html, as seen in 2017
Cisco (2000) IP Multicast Technology Overview, https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/ios-nx-os-software/ip-multicast/white-paper-listing.html (as seen in 2017), p 24
Arora H What is IP Multicasting? Concept of IP Multicast Address Explained, http://www.thegeekstuff.com/2013/05/ip-multicasting/, 2013, as seen in 2017
Diot C., Levine B.N., Lyles B., Kassem H., Balensiefen D. (2000) Deployment issues for the IP multicast service and architecture. IEEE Netw 14(1):78–88
GalubaAffiliated W, Girdzijauskas S (2009) Peer to peer overlay networks: Structure, routing and maintenance, Encyclopedia of Database Systems, pp 2056–2061
Vlachou A., Doulkeridis C., Norvag K., Kotidis Y. (2012) Peer-to-peer query processing over multidimensional data. SpringerBriefs in Computer Science Chapter 2:5–12
Banerjee Suman, Bhattacharjess Bobby (2002) A comparative study of application layer multicast protocols, University of Maryland
Bittorrent Available at http://www.bittorrent.com/
Gnutella Described and available at http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/Gnutella
Zhang X, Liu J, Li B, Yum T-SP (2005) CoolStreaming/DONet: A data-driven overlay network for peer-to-peer live media streaming, Proc IEEE INFOCOM, pp 2102–2111
Skype Available at https://www.skype.com/
Stanford University Folding Coin, available at http://foldingcoin.net/
UC Berkeley SETI@home, available at https://setiathome.berkeley.edu/
Malatras A (2015) State-of-the-art survey on P2P overlay networks in pervasive computing environments. J Netw Comput Appl 55:1–23
Eng Keong Lua J, Crowcroft M, Pias R, Sharma S, Lim A (2005) Survey and comparison of peer-to-peer overlay network schemes. IEEE Commun Surv Tutorials 7:72–93
Rodrigues R, Druschel P (2010) Peer-to-peer systems. Commun ACM 53(10):72–82
Napster Available at http://www.napster.com/
Castro M, Druschel P, Ganesh A, Rowstron A, Wallach DS (2002) Secure routing for structured peer-to-peer overlay networks, 5th Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation, pp 2909–314
Stoica I, Morris R, Karger D, Kaashoek MF, Balakrishnan H (2001) Chord: A scalable peer-to-peer lookup service for internet applications, SIGCOMM, Conference on Applications, technologies, architectures, and protocols for computer communications, pp 149–160
Bisnik N, Alhussein A (2007) Abouzeid Optimizing random walk search algorithms in P2P networks. Comput Netw 51(6):1499– 1514
Aggarwal V, Feldmann A, Scheideler C (2007) Can ISPs and P2P users cooperate for improved performance?. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review 37(3):29–40
Kühlewind M, Seedorf J, Gurbani V ALTO Status Page, IETF Group, https://datatracker.ietf.org/wg/alto/charter/
Sousa P (2015) Towards effective control of P2P traffic aggregates in network infrastructures. J Commun Soft Syst 11(1):37–47
Sousa P (2013) A framework for highly reconfigurable P2P trackers. J Commun Soft Syst 9(4):236–246
Sousa P (2013) Traffic engineering approaches in P2P environments. In: 5th international conference on advanced infocomm technology (ICAIT 2012). LNCS, vol 7593. Springer, Paris, pp 61–74
Shi SY, Turner JS, Waldvogel M (2001) Dimensioning server access bandwidth and multicast routing in overlay networks, NOSSDAV: Proceedings of the 11th international workshop on Network and operating systems support for digital audio and video, pp 83–91
Ke K-W, Huang C-H (2013) Performance evaluation of multisource Application Layer Multicast (ALM): Theoretical and simulative aspects. Comput Netw 57(6):1408–1424
Banerjee S, Bhattacharjee B, Kommareddy C (2002) Scalable application layer multicast, Proceedings of conference on Applications, technologies, architectures, and protocols for computer communications, pp 205–217
Hosseini M, Ahmed DT, Shirmohammadi S, Georganas ND (2007) A survey of Application-Layer multicast protocols. IEEE Commun Surv Tutorials 9(3):58–74
Jannotti J, Gifford DK, Johnson KL, Kaashoek MF, O’Toole JR JW (2000) Overcast: Reliable multicasting with an overlay network, Proc Of the 4th conference on Symposium on Operating System Design and Implementation, 4:197–212
Banerjee S, Kommareddy C, Kar K, Bhattacharjee B, Khuller S (2003) Construction of an efficient overlay multicast infrastructure for real-time applications. IEEE Societies INFOCOM 2:1521– 1531
Chawathe Y, McCanne S, Brewer E (2000) An architecture for internet content distribution as an infrastructure service. Ph.D. Thesis University of California, Berkeley
Lao L, Cui J-H, Gerla M, Chen S (2007) A scalable overlay multicast architecture for Large-Scale applications. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 4:449–459
Lao L, Cui J-H, Gerla M (2005) Multicast service overlay design, proc. of international symposium on performance evaluation of computer and telecommunication systems (SPECTS’05), Philadelphia,PA, USA
Mokhtarian K, Jacobsen H-A (2013) Minimum-delay overlay multicast. Proceedings IEEE INFOCOM, pp 1771–1779
Lin H-C, Lin T-M, Wu C-F (2014) Constructing application-layer multicast trees for minimum-delay message distribution. Inf Sci 279:433–445
Li Y, Cai W, Tang X (2013) Application layer multicast in P2P distributed interactive applications. In: International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems, pp 396–403
Besharati R, Bag-Mohammadi M, Dezfouli MA (2010) A topology-aware application layer multicast protocol. In: Consumer communications and networking conference (CCNC). IEEE. pp 1–5
Cui J, Xiong N, Park JH, Jia K, Wu L (2013) A novel and efficient source-path discovery and maintenance method for application layer multicast. Comput Electr Eng 39(1):67–75
Wydrych P, Cholda P (2011) ISP - Supported traffic reduction for Application-Level multicast. In: IEEE International Conference on Communications, pp 1–6
Picconi F, Massoulie L (2009) ISP Friend Or Foe? Making P2P Live Streaming ISP-aware. In: IEEE International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems, pp 413–422
Graph Library http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/41graph/SymbolGraph.java.html, as seen in 2017
Graphs data structures for library, http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/, as seen in 2017
PRIM algorithm, http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/greedy-algorithms-set-5-prims-minimum-spanning-tree-mst-2/, as seen in 2017
CORE network emulator, https://www.nrl.navy.mil/itd/ncs/products/core, version 4.8
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by COMPETE: POCI-01-0145-FEDER-007043 and FCT Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia within the Project Scope: UID/CEC/00319/2013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sampaio, A., Sousa, P. An adaptable and ISP-friendly multicast overlay network. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 12, 809–829 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-018-0680-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-018-0680-y