Abstract
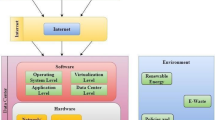
Cloud is the most trending technology used at almost in every part of the business and in every field of business. Cloud provides number of services in wider spectrum to cloud users from anywhere at any time. But, it achieved through several parameters like deployment model, resource optimization, load optimization etc. Nowadays, Load optimization is playing crucial role in cloud computing behalf system performance. The best optimization technique goal is to fulfill the user requirement efficiently with minimal resources and processing time. Parallel task processing is highly demanded in cloud application. The CPU resources are needed to move for parallelism growth due to communication and synchronization of parallel job arrival in cloud. It is difficult but highly demanded for a data center to response arrived task in parallel way. The objective of work is to design Efficient Load Optimization and Resource Minimization (ELORM) algorithm for optimizing the tasks at different Hybrid P2P Cloud data center zones and different users in cloud environment. The works provides an effective way to distribute the resources based on load prediction in the data centers for resource optimization. It enhances the load optimization, by maintaining the reliability and stability between the user base and data center during data transmission process. It also reduces the resource utilization and response time of the proposed algorithm compared than conventional methods. Proposed ELORM reduces 83.13 s Task completion time, 20.82 $ Virtual machine cost, 6.68% load balancing compare than conventional methods.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qiang G (2017) Task scheduling based on ant colony optimization in cloud environment. AIP Conference Proceedings 1834:1–11
Damodar T, Shailendra S, Sanjeev S (2017) Theoretical analysis of bio-inspired load balancing approach in cloud computing environment. International Journal of Database Theory and Application 10(11):15–26
Meenakshi S, Pankaj S (2012) Performance evaluation of adaptive virtual machine load balancing algorithm. Int J Adv Comput Sci Appl 3(2):86–88
Sankara N, Ramakrishnan M, Murtaza SB (2017) Efficient load balancing algorithm for cloud computing using divisible load scheduling and weighted round Robin methods. Advances in Natural and Applied Sciences 11(1):13–19
Pradeep S, Rawat PD, Saroha GP (2016) Tasks scheduling in cloud computing environment using Workflowsim. Res J Inf Technol 8(3):98–104
Shweta P, Mayank B (2017) Implementation of load balancing in cloud computing thorough Round Robin & Priority using cloudSim. International Journal for Rapid Research in Engineering Technology & Applied Science 3(11):1–12
Medhat T, Ashraf ES, Arabi K, Torkey F (2015) Cloud task scheduling based on ant Colony optimization. The International Arab Journal of Information Technology 12(2):129–137
Nguyen XP, Tran CH (2017) Load balancing algorithm to improve response time on cloud computing. International Journal on Cloud Computing: Services and Architecture 7(6):1–12
Amey R, Anusooya G (2017) Energy efficient load balancing for cloud data center. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research 10(1):162–165
Atyaf D, Khaldun IA (2017) An efficient load balancing scheme for cloud computing. Indian J Sci Technol 10(11):1–8
Beloglazov, Buyya R (2010) Energy efficient resource management in virtualized cloud data centers. In proceedings of the 2010 10th IEEE/ACM international conference on cluster, cloud and grid computing. IEEE Computer Society, pp 826–831
Beloglazov JA, Buyya R (2012) Energy-aware resource allocation heuristics for efficient management of data centers for cloud computing. Futur Gener Comput Syst 28(5):755–768
Krishna PV (2013) Honey bee behavior inspired load balancing of tasks in cloud computing environments. Appl Soft Comput 13(5):2292–2303
Prevost JJ, Nagothu K, Kelley B, Jamshidi M (2011) Prediction of cloud data center networks loads using stochastic and neural models. In: System of systems engineering (SoSE), 2011 sixth international conference, pp, pp 276–281
Chana, Kansal NJ (2012) Cloud load balancing techniques: a step towards green computing. International Journal of Computer Science Issues 9(1):238–246
Greenberg J, Hamilton DAM, Patel P (2008) The cost of a cloud: research problems in data center networks. ACM SIGCOMM computer communication review 39(1):68–73
Beloglazov RB, Lee YC, Zomaya A (2011) A taxonomy and survey of energy-efficient data centers and cloud computing systems. Adv Comput 82:47–111
Beloglazov, Buyya R (2012) Optimal online deterministic algorithms and adaptive heuristics for energy and performance efficient dynamic consolidation of virtual machines in cloud data centers. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience 24(13):1397–1420
R. Buyya, A. Beloglazov, and J. Abawajy, “Energy-efficient management of data center resources for cloud computing: a vision, architectural elements, and open challenges. 2010 International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Processing Techniques and Applications (PDPTA 2010), Las Vegas, USA, July 12–15, 2010, arXiv preprint arXiv:1006.0308, pp. 1–12, 2010
Luo J, Rao L, Liu X (2014) Temporal load balancing with service delay guarantees for data center energy cost optimization. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems 25(3):775–784
Preethi CK, Ramesh SM, Shanmathi S, Sathiya PB (2014) Optimization of resources in cloud computing using effective load balancing algorithms. International Advanced Research Journal in Science, Engineering and Technology 1(1):20–22
Vijaya BRB, Bala MB, Mohan R (2016) Efficient load balancing scheme in cloud using resource allocation algorithm. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering 6(12):214–217
Amanpreet K, Bikrampal K, Dheerendra S (2017) Optimization techniques for resource provisioning and load balancing in cloud environment: a review. IJ Information Engineering and Electronic Business (1):28–35
A.P. Shameer, , and A.C. Subhajini, “Optimization task scheduling techniques on load balancing in cloud using intelligent bee Colony algorithm. International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics, Vol. 116, No. 22, pp. 341–352, 2017
Adnan B, Benjamin PI (2018) Distributed virtual machine consolidation: a systematic mapping study. Computer Science Review 28:118–130
Manasrah AM, Ba Ali H (2018) Workflow scheduling using hybrid GA-PSO algorithm in cloud computing. Wirel Commun Mob Comput 2018:1–16
Boroń M, Brzeziński J, Kobusińska A (2019) P2P matchmaking solution for online games. In: Peer-to-peer networking and applications ,Vol. s12083-019-00725-3, pp 1–14
Sacha J, Biskupski B, Dahlem D, Cunningham R, Meier R, Dowling J, Haahr M (2010) Decentralising a service-oriented architecture. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications 3(4):323–350
Zhang Z, Ge L, Wang P, Zhou X (2019) Behavior reconstruction models for large-scale network service systems. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications 12(2):502–513
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection: Special Issue on P2P Computing for Intelligence of Things Guest Editors: Sunmoon Jo, Jieun Lee, Jungsoo Han, and Supratip Ghose
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Priya, B., Gnanasekaran, T. To optimize load of hybrid P2P cloud data-center using efficient load optimization and resource minimization algorithm. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 13, 717–728 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-019-00795-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-019-00795-3