Abstract
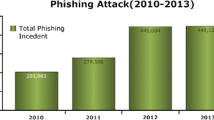
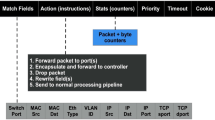
In cyber world Botnets becoming more popular and great challenge to security. Attacker by using bot net taking legacy attacks towards new dimension. Existing Intrusion Prevention / Intrusion Detection (IPS/IDS) systems can detect botnets attacks by using anomaly detection methods (or) signature. To fly the radar of IDS/IPS systems Bot master creates an attack either anomaly (or) any known signature. One possible thing is mimicking attack. Attacker hack the popular website browsing history. By using, browsing history they will simulate thousands of users through bots and will try to degrade the performance of the website. Mimicking kind of attacks can be made as distributed by using Botnet. In this paper, we are discussing about the possibility of mimicking attack by using Botnet. The first phase attacker will inject bots into the targeted systems. In second phase Bot master will inject respective mimicking profile in to targeted systems similar to their browsing behavior. We are proposing possible algorithm to identify the mimicking attack at gate way level, which will be tied up with NIDS. We worked on example of mimicking attack by using HTTP protocol. The attacker will collect the profile of users and using that mimicking profile was extracted. With that heterogeneous mimicking attack was executed. NIDS will be installed at gateway which will collect the connection statistics. The statistics will be given to the detection algorithm which will identify the similar flows based on Layer 3, Layer 4, Layer 7. The suspicious flows will be sent for challenges to prove the identity of the user. If it is in attack mimicking applications can’t respond to the challenges, the source ip address does not respond to challenges were added to the block list.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu S, Guo S, Stojmenovic I (2015) Fool me if you can: mimicking attacks and anti-attacks in cyberspace. IEEE Trans Comput 64(1):139
Krishna VR, Subhashini R (2017) Detecting HTTP based mimicking attacks at HTTP server. Int J Eng Technol 9(4):3041–3049
Peng T, Leckie C, Ramamohanarao K (2007) Survey of network-based defense mechanisms countering the dos and DDOS problems. ACM Comput Surv 39(1):1–42
Edman M, Yener B (2009) On anonymity in an electronic society: a survey of anonymous communication systems. ACM Comput Surv 42(1):1–35
Bacher P, Holz T, Kotter M, Wicherski G (2008) Know your enemy: tracking botnets (using honeynets to learn more about bots). Technical Report, The Honeynet Project
Abade MS, Habibi J, Lucas C (2005) Intrusion detection using a fuzzy genetics-based learning algorithm. J Netw Comput Appl 30:414
Olanrewaju RF, Khan BUI, Najeeb AR, Zahir KNAK, Hussain S (2018) Snort-based smart and swift intrusion detection system. Indian J Sci Technol 11(4):1–9
Gu G, Zhang J, Lee W (2008) BotSniffer: detecting botnet command and control channels in network traffic. In: Proceedings of the 15th Network and Distributed System Security Symposium (NDSS), San Diego, February
Gu G, Porras P, Yegneswaran V, Fong M, Lee W (2007) Bothunter: detecting malware infection through IDS driven dialog correlation. In: Proceedings of 16th USENIX Security Symposium on USENIX Security Symposium. USENIX Association, Berkeley, pp 1–16. Available from: http://portal.acm.org/citation
Zhisong PAN et al (2005) An integrated model of intrusion detection based on neural network and expert system. In: Proceedings of the 17th IEEE International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI’05), December
Kim G et al (2014) A novel hybrid intrusion detection method integrating anomaly detection with misuse detection. Expert Syst Appl 41:1690–1700
Kanungo T, Mount DM, Netanyahu NS, Piatko CD, Silverman R, Wu AY (2002) An efficient k-means clustering algorithm: analysis and implementation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 24(7):881
Pelleg D, Moore A (2000) X-means: extending K-means with efficient estimation of the number of clusters. ICML ’00 Proceedings of the seventeenth international conference on machine learning, pp 727–734, June 29–July 2
Abadeh MS et al (2011) Design and analysis of genetic fuzzy systems for intrusion detection in computer networks. Expert Syst Appl 38:7067–7075
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection: Special Issue on Future Networking Applications Plethora for Smart Cities
Guest Editors: Mohamed Elhoseny, Xiaohui Yuan, and Saru Kumari
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rama Krishna, V., Subhashini, R. Mimicking attack by botnet and detection at gateway. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 13, 1204–1214 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-019-00854-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-019-00854-9