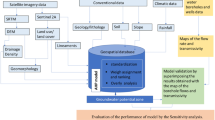
Abstract
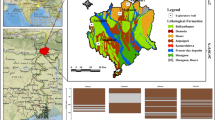
Arid to semi-arid regions are characterized by low levels of surface water and low annual precipitation (generally <350 mm/year). In such areas, groundwater must be used to meet all the needs of the population for water. As a consequence, careful management is required to ensure the sustainability of this scarce resource in response to the demands of urban centers, industry, agriculture, and tourism. The concept of the aquifer recharge rate is particularly useful in the quantification of these groundwater resources and can be used to form the basis of a decision support system. This study determined the potential recharge rate in the Haouz aquifer using a multi-criteria analysis that included both the major and minor factors influencing the rate of infiltration of water into the aquifer. The analysis was based on the use of a geographical information system supported by remote sensing techniques to develop thematic data layers. These layers were then used to describe the spatial variation of the factors influencing the recharge rate of the aquifer and were subsequently integrated and analyzed to derive the spatial distribution of the potential recharge. This approach was used to classify the Haouz Plain (Morocco) into three different zones with respect to the recharge rate, with recharge rates ranging from 3.5 to 18.2 %.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abourida A, Vincent S, Errouane S, et al. (2008) Estimation des volumes d’eau pompés dans la nappe pour l’irrigation (plaine du Haouz, Marrakech, Maroc). Comparaison d’une méthode statistique et d’une méthode basée sur l’utilisation de la télédétection J Water Sci 22:1–13. doi:10.7202/019820ar
Ait El Mekki O (2010) Etude de la relation eaux de surface-eaux souterraines au contact de Oued Rheraya avec la plaine du Haouz; Bilan et quantification des apports. Mémoire de 3ème cycle, Université Cadi Ayyad Faculté des Sciences Semlalia
Ait El Mekki O, Laftouhi N-E, Hanich L (2015) Estimate of regional groundwater recharge rate in the Central Haouz Plain, Morocco, using the chloride mass balance method and a geographical information system. Appl Water Sci:1–10. doi:10.1007/s13201-015-0335-6
Al Saud M (2010) Mapping potential areas for groundwater storage in Wadi Aurnah Basin, western Arabian peninsula, using remote sensing and geographic information system techniques. Hydrogeol J 18:1481–1495. doi:10.1007/s10040-010-0598-9
Armbruster JT (1976) An infiltration index useful in estimating low-flow characteristics of drainage basin. J Res US Geol Surv 4:533538
Badraoui M (2006) Connaissance et utilisation des ressources en sol au Maroc
Bannari A, Teillet P, Landry R (2004) Comparaison de réflectances de surfaces naturelles dans les bandes spectrales homologues des capteurs TM de landsat-5 et ETM+ de landsat-7. Télédétection 4:263–275
Belward AS, Valenzuela CR (1991) Remote sensing and geographical information systems for resource management in developing countries. Kluwer Academic Publishers
Biron P-E (1982) Le Permo-Trias de la région de l’Ourika (Haut-Atlas de Marrakech, Maroc): lithostratigraphie, sédimentologie, tectonique et minéralisations. Thèse de doctorat
Childs C (2004) Interpolating surfaces in ArcGIS spatial analyst. ArcUser:32–35
Chowdhury A, Jha MK, Chowdary VM (2010) Delineation of groundwater recharge zones and identification of artificial recharge sites in West Medinipur district, West Bengal, using RS, GIS and MCDM techniques. Environ Earth Sci 59:1209–1222. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0110-9
Concaret J (1960) Etude pédologique d’une zone du Haouz de Marrakech (Soueilah Mrabtine) (Royaume du Maroc). Génie Rural du Sud, Marrakech
Dahdouh-Guebas F (2002) The use of remote sensing and GIS in the sustainable Management of Tropical Coastal Ecosystems. Environ Dev Sustain 4:93–112. doi:10.1023/A:1020887204285
Dar IA, Sankar K, Dar MA (2011) Deciphering groundwater potential zones in hard rock terrain using geospatial technology. Environ Monit Assess 173:597–610. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1407-6
Das S, Behera SC, Kar A, et al. (1997) Hydrogeomorphological mapping in ground water exploration using remotely sensed data — a case study in keonjhar district, orissa. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 25:247–259. doi:10.1007/BF03019366
Dauteloup J (1958a) Carte des roches mères du Haouz de Marrakech, Maroc
Dauteloup J (1958b) Carte pédologique : Haouz de Marrakech : Maroc
Dauteloup J (1958c) Carte pédologique : Haouz de Marrakech (région Est) : F2
Dauteloup J (1958d) Carte pédologique : Haouz de Marrakech (région Est) : F1
Dauteloup J (1959) Carte de tri des sols : Haouz de Marrakech
Direction de Géologie (1982) Carte Structurale du Maroc
ESRI (2005) Arc Hydro Tools - Tutorial
Gad A (2002) Changes in Land Use and Land Cover in Arid Southern Mediterranean on the Long Term Using Remote Sensing and GIS — A Case Study of Northwest Egypt. In: Barnes I (ed) Global Atmospheric Change and its Impact on Regional Air Quality. Springer Netherlands, pp 195–201
Ganapuram S, Kumar GTV, Krishna IVM, et al. (2009) Mapping of groundwater potential zones in the Musi basin using remote sensing data and GIS. Adv Eng Softw 40:506–518. doi:10.1016/j.advengsoft.2008.10.001
Goodin JR, Northington DK (1985) Plant resources of arid and semiarid lands: a global perspective. Academic Press, USA
Greenbaum D (1985) Review of remote sensing applications to groundwater exploration in basement and regolith. Br Geol Surv 63
Haridas v.., Aravindan s, Girish G (1998) Remote sensing and its application for ground water favorable area identification. J Geol Assoc Res Cent 6:18–22
Harinarayanan P, Gopalakrishna GS, Balasubramanian A (2000) Remote sensing data for groundwater development and management in Keralapura watersheds of Cauvery Basin, Karnataka, India. Indian Mineral 34:11–17
Helldén U (1987) An assessment of woody biomass, community forests, land use and soil erosion in Ethiopia. A feasibility study on the use of remote sensing and GIS [geographical information system]-analysis for planning purposes in developing countries. 75 pp
Horton RE (1932) Drainage-basin characteristics. EOS Trans Am Geophys Union 13:350–361. doi:10.1029/TR013i001p00350
Horton RE (1945) Erosional development of streams and their drainage basins; Hydrophysical Approach to Quantitative Morphology. Geol Soc Am Bull 56:275–370. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1945)56[275:EDOSAT]2.0.CO;2
INRA du Maroc, Ministère de l’Agriculture du Maroc, Le groupe OCP du Maroc (2009) Carte de Fertilité des Sols
Jensen JR, Lulla DK (1987) Introductory digital image processing: A remote sensing perspective. Geocarto Int 2:65–65. doi:10.1080/10106048709354084
Jha MK, Chowdary VM (2007) Challenges of using remote sensing and GIS in developing nations. Hydrogeol J 15:197–200. doi:10.1007/s10040-006-0117-1
Jha MK, Chowdhury A, Chowdary VM, Peiffer S (2006) Groundwater management and development by integrated remote sensing and geographic information systems: prospects and constraints. Water Resour Manag 21:427–467. doi:10.1007/s11269-006-9024-4
Keane RE, Burgan R, van Wagtendonk J (2001) Mapping wildland fuels for fire management across multiple scales: Integrating remote sensing, GIS, And biophysical modeling. Int J Wildland Fire 10:301–319
Khodaei K, Nassery HR (2013) Groundwater exploration using remote sensing and geographic information systems in a semi-arid area (Southwest of Urmieh, Northwest of Iran). Arab J Geosci 6:1229–1240. doi:10.1007/s12517-011-0414-4
Kouadio KE, Savane I, Lasm T, Biemi J (2008) Hydrogeology prospecting in crystalline and metamorphic area by spatial analysis of productivity potential. Eur J Sci Res 22:373–390
Krishnamurthy J, Kumar N, Jayaraman V, Manivel M (1996) An approach to demarcate groundwater potential zones through remote sensing and a geographic information system. Int J Remote Sens 17:1867–1885
Kumar SK, Chandrasekar N, Seralathan P, et al. (2012) Hydrogeochemical study of shallow carbonate aquifers, Rameswaram Island, India. Environ Monit Assess 184:4127–4138. doi:10.1007/s10661-011-2249-6
Le Rouget G (1973a) Région Marrakech ouest - oued Tensift esquisse cartographique de la répartition des roches et dépôts superficiels
Le Rouget G (1973b) Région Marrakech ouest - oued Tensift : carte pédologique
Le Rouget G (1975) Région Marrakech est-Tahnaout : carte pédologique
Leblanc M, Favreau G, Tweed S, et al. (2007) Remote sensing for groundwater modelling in large semiarid areas: Lake Chad Basin, Africa. Hydrogeol J 15:97–100. doi:10.1007/s10040-006-0126-0
Leblanc M, Leduc C, Razack M, et al (2003) Application of remote sensing and GIS for groundwater modeling of large semiarid areas: example of the Lake Chad Basin, Africa In: Hydrology of Mediterranean and Semiarid Regions: Papers Selected for the International Conference on Hydrology of the Mediterranean and Semi-Arid Regions, Held in Montpellier, France from 1 to 4 April 2003. International Association of Hydrological Sciences, p 186e192
Machiwal D, Jha MK, Mal BC (2011) Assessment of Groundwater Potential in a Semi-Arid Region of India Using Remote Sensing, GIS and MCDM Techniques. Water Resour Manag 25:1359–1386. doi:10.1007/s11269-010-9749-y
Magesh NS, Chandrasekar N, Soundranayagam JP (2012) Delineation of groundwater potential zones in Theni district, Tamil Nadu, Using remote sensing, GIS and MIF techniques. Geosci Front 3:189–196. doi:10.1016/j.gsf.2011.10.007
Mahler P (1960a) Pédologie du périmètre des Ouled Yacoub. (IN) Royaume du Maroc
Mahler P (1960b) Pédologie de la zone de l’Oued N’Fis. (IN) Royaume du Maroc
Mahler P (1960c) Pédologie de la zone de l’Oued R’dat. (IN) Royaume du Maroc
Mahler P (1960d) OUED TENSIFT (MAROC)
Margat J, Gun J van der (2013) Groundwater around the World: A Geographic Synopsis. CRC Press, Florida
Maselli F, Conese C, Petkov L, Resti R (1992) Inclusion of prior probabilities derived from a nonparametric process into the maximum-likelihood classifier. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 58:201–207
McCall MK, Minang PA (2005) Assessing participatory GIS for community-based natural resource management: claiming community forests in Cameroon. Geogr J 171:340–356. doi:10.1111/j.1475-4959.2005.00173.x
Michard A (1976) Eléments de géologie marocaine, Éditions du Service géologique du Maroc
Moret L (1931) Recherches Géologiques dans l’Atlas de Marrakech. Université de Grenoble, Extrait des Notes et Mémoires du Service des Mines et de la Carte Géologique du Maroc
Moukhchane M (1983) Contribution à l’étude des réservoirs profonds de la bordure nord de l’Atlas entre Demnate et Imintanoute (Maroc). Thèse de 3ème cycle, Besançon
Mukherjee P, Singh CK, Mukherjee S (2012) Delineation of Groundwater Potential Zones in Arid Region of India—A Remote Sensing and GIS Approach. Water Resour Manag 26:2643–2672. doi:10.1007/s11269-012-0038-9
Münch Z, Conrad J (2007) Remote sensing and GIS based determination of groundwater dependent ecosystems in the Western Cape, South Africa. Hydrogeol J 15:19–28. doi:10.1007/s10040-006-0125-1
Muralidhar M, Raju KR, Raju KSVP, Prasad JR (2000) Remote sensing applications for the evaluation of water resources in rainfed area, Warangal district, Andhra Pradesh. Indian Mineral 34:33–40
Murthy KSR (2000) Ground water potential in a semi-arid region of Andhra Pradesh - a geographical information system approach. Int J Remote Sens 21:1867–1884. doi:10.1080/014311600209788
Musy A, Soutter M (1991) Physique du sol, 04/01/1991 edn. Presses Polytechniques et Universitaires Romandes (PPUR), Suisse
Patil MB, Desai CG, Umrikar BN (2012) Image classification tool for Land Use/Land cover analysis: A Comparative Study Of Maximum Likelihood and Minimum Distance Method. Int J Geol Earth Environ Sci 2:189–196
Philip GM, Watson DF (1982) A Precise Method for Determining Contoured Surfaces. Aust Pet Explor Assoc J 22:205–212
Piqué A, Soulaimani A, Hoepffner C, et al. (2007) Géologie du Maroc. Geode, Imprimerie El Watanya, Marrakesh, Morocco
Salomon J, Chellai EH, Guerraoui F, Lang J (1996) Dynamique sédimentaire et structuration, durant le Néogène, de la bordure nord du Haut Atlas Marocain (Haouz de Marrakech). J Afr Earth Sci 22:323–334. doi:10.1016/0899-5362(96)00007-3
Sander P, Chesley MM, Minor TB (1996) Groundwater Assessment Using Remote Sensing And GIS In A Rural Groundwater Project In Ghana: Lessons Learned. Hydrogeol J 4:40–49. doi:10.1007/s100400050086
Saraf AK, Choudhury PR (1998) Integrated remote sensing and GIS for groundwater exploration and identification of artificial recharge sites. Int J Remote Sens 19:1825–1841. doi:10.1080/014311698215018
Sener E, Davraz A, Ozcelik M (2005) An integration of GIS and remote sensing in groundwater investigations: A case study in Burdur, Turkey. Hydrogeol J 13:826–834. doi:10.1007/s10040-004-0378-5
Servat E, Najem W, Leduc C, Shakeel A (2003) Hydrology of Mediterranean and Semiarid Regions: Papers Selected for the International Conference on Hydrology of the Mediterranean and Semi-Arid Regions, Held in Montpellier, France from 1 to 4 April 2003. International Association of Hydrological Sciences
Service Géologique du Maroc (1957) Carte géologique du Maroc. Marrakech, Feuille
Shaban A, Khawlie M, Abdallah C (2006) Use of remote sensing and GIS to determine recharge potential zones: the case of Occidental Lebanon. Hydrogeol J 14:433–443. doi:10.1007/s10040-005-0437-6
Shaban A, Khawlie M, Kheir RB, Abdallah C (2001) Assessment of road instability along a typical mountainous road using GIS and aerial photos, Lebanon – eastern Mediterranean. Bull Eng Geol Environ 60:93–101. doi:10.1007/s100640000092
Sinan M (2000) Méthodologie d’identification, d’évaluation et de protection des ressources en eau des aquifères régionaux par couplage des SIG, de la géophysique et de la géostatistique. Application à l’aquifère du Haouz de Marrakech (Maroc). Thèse de Doctorat d’Etat, Université Mohammed V
Solomon S, Quiel F (2006) Groundwater study using remote sensing and geographic information systems (GIS) in the central highlands of Eritrea. Hydrogeol J 14:1029–1041. doi:10.1007/s10040-006-0096-2
Teeuw RM (1995) Groundwater exploration using remote sensing and a low-cost geographical information system. Hydrogeol J 3:21–30. doi:10.1007/s100400050057
Thomas A, Sharma P, Sharma M, Anil S (1999) Hydrogeomorphological mapping in assessing groundwater by using remote sensing data—A case study in Lehra Gage Block, Sangrur district, Punjab. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 27:31–42
Tiwari A, Rai B (1996) Hydromorphological mapping for groundwater prospecting using landsat e MSS imagesda case study of Part of Dhanbad District, Bihar. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 24:281–285
Tweed SO, Leblanc M, Webb JA, Lubczynski MW (2007) Remote sensing and GIS for mapping groundwater recharge and discharge areas in salinity prone catchments, southeastern Australia. Hydrogeol J 15:75–96. doi:10.1007/s10040-006-0129-x
Ulbricht KA, Teotia HS, Civco DL (1993) Supervised Classification to Land Cover Mapping in Semi-Arid Environment of NE Brazil Using Landsat-TM and SPOT Data. Int Arch Photogramm Remote Sens 29:821–827
Venkatesh M (2012) Watershed and Stream Network Delineation using ArcHydro Tools.
Watson DF, Philip GM (1985) A refinement of inverse distance weighted interpolation. Geo-Process 2:315–327
Welch R, Remillard M, Alberts J Georgia U (1992) Integration of Gps, Remote Sens, and Gis Techniques for Coastal Resource Management.
Xu Y, Usher B (2006) Groundwater Pollution in Africa. CRC Press, Florida
Yang W, Wang R, Huang J, et al. (2007) Application of inverse distance weighted interpolation method in contaminated site assessment. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao J Appl Ecol Zhongguo Sheng Tai Xue Xue Hui Zhongguo Ke Xue Yuan Shenyang Ying Yong Sheng Tai Yan Jiu Suo Zhu Ban 18:2013–2018
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: H. A. Babaie
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ait El Mekki, O., Laftouhi, NE. Combination of a geographical information system and remote sensing data to map groundwater recharge potential in arid to semi-arid areas: the Haouz Plain, Morocco. Earth Sci Inform 9, 465–479 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-016-0268-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-016-0268-0