Abstract
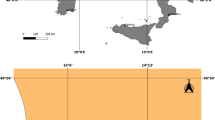
The accurate and efficient detection of the water depth of coral reefs through remote sensing imagery is crucial for navigation, marine engineering, and marine safety, among others. This study proposed a water depth inversion method that is processed using a two-step strategy. First, a log-dual-band ratio transform model is employed by combining blue, yellow, red, and red edge bands. Second, a multivariable linear regression model is constructed to determine water depth. The experimental study is conducted in a reef island in the South China Sea, and the WorldView-2 satellite data is used as the test data. Results demonstrated that the proposed method needs a few parameters in the model, and can effectively and reliably characterize the correlation between the spectral features and water depth.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Canty MJ (2011) Image analysis, classification and change detection in remote sensing: with algorithms for envi/idl and python, 3rd edn. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 23(1):129–130
Cho HJ, Lu D (2010) A water-depth correction algorithm for submerged vegetation spectra. Remote Sensing Letters 1:29–35. doi:10.1080/01431160903246709
Eugenio F, Marcello J, Martin J (2015) High-resolution maps of bathymetry and benthic habitats in shallow-water environments using multispectral remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 53:3539–3549 doi:10.1109/tgrs.2014.2377300
Froidefond JM, Gardel L, Guiral D, Parra M, Ternon JF (2002) Spectral remote sensing reflectances of coastal waters in French Guiana under the Amazon influence. Remote Sens Environ 80:225–232 doi:10.1016/s0034-4257(01)00301-7
Gavin H (2011) The Levenberg-Marquardt method for nonlinear least squares curve-fitting problems Availble Online from: http://people.duke.edu/~hpgavin/ce281/lm.pdf
Kanno A, Tanaka Y, Shinohara R, Kurosawa A, Sekine M (2014) Which spectral bands of WorldView-2 are useful in remote sensing of water depth? A case study in coral reefs. Mar Geod 37:283–292. doi:10.1080/01490419.2014.908794
Knudby A, Nordlund L (2011) Remote sensing of seagrasses in a patchy multi-species environment. Int J Remote Sens 32:2227–2244 doi:10.1080/01431161003692057
Lee ZP, Carder KL, Mobley CD, Steward RG, Patch JS (1999) Hyperspectral remote sensing for shallow waters: 2. Deriving bottom depths and water properties by optimization. App Opt 38:3831–3843. doi:10.1364/ao.38.003831
Lyzenga DR (1978) Passive remote sensing techniques for mapping water depth and bottom features. Appl Opt 17:379–383
Lyzenga DR, Malinas NR, Tanis FJ (2006) Multispectral bathymetry using a simple physically based algorithm. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 44:2251–2259 doi:10.1109/tgrs.2006.872909
Phinn SR, Roelfsema CM, Mumby PJ (2012) Multi-scale, object-based image analysis for mapping geomorphic and ecological zones on coral reefs. Int J Remote Sens 33:3768–3797 doi:10.1080/01431161.2011.633122
Polcyn FC, Brown WL, Sattinger IJ (1970) The measurement of water depth by remote sensing techniques. Michigan univ ann arbor inst of science and technology. Ann Arbor, Michigan
Richards JA, Richards J (1999) Remote sensing digital image analysis vol 3. Springer
Strome WM, David E (1990) Modern remote sensing digital image analysis technology for monitoring global change. In: Proceedings of the 23rd international symposium on remote sensing of environment, April 18, 1990 - April 25, 1990, Bangkok, Thail, 1990. Proceedings of the International Symposium on Remote Sensing of Environment. Publ by Environmental Research Inst of Michigan, p 1335
Stumpf RP, Holderied K, Sinclair M (2003) Determination of water depth with high-resolution satellite imagery over variable bottom types. Limnol Oceanogr 48:547–556
Wang D, Feng X, Ma R, Kang G (2007) A method for retrieving water-leaving radiance from Landsat TM image in Taihu Lake, East China. Chin Geogr Sci 17:364–369 doi:10.1007/s11769-007-0364-7
Wang Y (2009) Remote sensing of coastal environments. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Acknowledgements
The present study is supported by the China Ocean Center (Fax: 01062173743), which provided the WorldView-2 data set and method support. The authors are grateful to their supervisor who provided closed guidance for the completion of this study. Finally, the authors would like to thank Yonglin Shen who provided guidelines on the outline of the paper, as well as provided guidance on thesis writing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: H. A. Babaie
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, G., Chen, F. & Shen, Y. Detecting the water depth of the South China Sea reef area from WorldView-2 satellite imagery. Earth Sci Inform 10, 331–337 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-017-0299-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-017-0299-1