Abstract
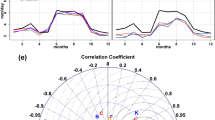
The spatio-temporal Κriging approach by using five different covariance models, has been applied into Regional Climate Model (RCM) simulated precipitation and temperature dataset in a coastal area. The results of the spatio-temporal technique were evaluated against the ERA-Interim reanalysis data during the period from 1981 to 2000. The reliability of the spatio-temporal interpolation results were estimated by using both the judgment of the wireframe plots, between the sample and the fitted covariance models, and the statistic metrics. Thus, Taylor diagrams were used and the Mean Square Error (MSE) was calculated. The analysis demonstrates that the sum-metric covariance model is highly superior to the other four covariance models as it is closer to the reanalysis data, having the highest correlation coefficient, as well as, the smallest standard deviation, resulting in the smallest Root Mean Square Error. The spatio-temporal interpolation approach improved the MPI and HadGEM2 climate model dataset. The largest enhancement is pointed out in the interpolated RCM precipitation during winter and autumn. Concerning the temperature, the interpolated MPI temperature data is negligibly improved, whereas the interpolated HadGEM2 temperature is particularly optimized during winter and autumn. The spatio-temporal interpolation technique led to the minimization of the uncertainties of the Regional Climate Models, (RCMs) simulations, and also to the best agreement between them and the ERA-Interim reanalysis data during the period from 1981 to 2000. Nevertheless, the MPI climate model is more reasonable compared to the HADGEM2 for the research area.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aalto J, Pirinen P, Heikkinen J, Venäläinen A (2013) Spatial interpolation of monthly climate data for Finland: comparing the performance of kriging and generalized additive models. Theor Appl Climatol 112:99–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-012-0716-9
Bilonick RA (1988) Monthly hydrogen ion deposition maps for the northeastern U.S. from July 1982 to September 1984. Atmos Environ 22(9):1909–1924. https://doi.org/10.1016/00046981(88)90080-7
Brassel KE, Douglas R (1979) A procedure to generate thiessen Polygons. Geogr Anal 11(3):290–303
Collins WJ, Bellouin N, Doutriaux-Boucher M, Gedney N, Halloran P, Hinton T, Hughes J, Jones CD, Joshi M, Liddicoat S, Martin G, O’Connor F, Rae J, Senior C, Sitch S, Totterdell I, Wiltshire A, Woodward S (2011) Development and evaluation of an earth-system model HadGEM2. Geosci Model Dev Discuss 4:997–1062. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmdd-4-9972011
Cressie C (1993) Statistics for Spatial Data. Wiley Series in Probability and Mathematical Statistics: Applied Probability and Statistics. John Wiley & Sons, Inc, New York
Cressie C, Wikle K (1998) The variance-based cross-variogram: you can add apples and oranges. Math Geol 30:789–799
Cressie C, Wikle K (2011) Statistics for Spatio-temporal data. Wiley
De Cesare L, Myers D, Posa D (2001) Estimating and modeling space-time correlation structures. Statist Probab Lett 51(1):9–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-7152(00)00131-0
De Iaco S, Myers D, Posa D (2001) Space-time analysis using a general product-sum model. Statist Probab Lett 52(1):21–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-7152(00)00200-5
Dee P, Uppala MS, Simmons AJ, Berrisford P, Poli P, Kobayashi S, Andrae U, Balmaseda MA, Balsamo G, Bauer P, Bechtold P, Beljaars ACM, van de Berg L, Bidlot J, Bormann N, Delsol C, Dragani R, Fuentes M, Geer AJ, Haimberger L, Healy SB, Hersbach H, Holm EV, Isaksen L, Kallberg P, Kohler M, Matricardi M, McNally AP, Monge-Sanz BM, Morcrette JJ, Park BK, Peubey C, de Rosnay P, Tavolato C, Thepaut JN, Vitart F (2011) The ERA-interim reanalysis: configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. R Meteorol Soc 137:553–597
Demicran M, Gürkan H, Eskioǵlu O, Arabaci H, Coșkun M (2017) Climate change projections for Turkey: three models and two scenarios. Turkish J Water Sci Manage:22–43
Friedman JH (1994) An overview of predictive learning and function approximation. In “from statistics to neural networks”, Springer, Berlin, Germany, 136:1–61
Gething P, Atkinson P, Noor A, Gikandi P, Hay S, Nixon M (2007) A local space-time kriging approach applied to a national outpatient malaria data set. Comput Geosci 33(10):1337–1350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2007.05.006
Giorgetta MA, Jungclaus J, Reick CH, Legutke S, Bader J, Böttinger M, Brovkin V, Crueger T, Esch M, Fieg K, Glushak K, Gayler V, Haak H, Hollweg HD, Ilyina T, Kinne S, Kornblueh L, Matei D, Mauritsen T, Mikolajewicz U, Mueller W, Notz D, Pithan F, Raddatz T, Rast S, Redler R, Roeckner E, Schmidt H, Schnur R, Segschneider J, Six KD, Stockhause M, Timmreck C, Wegner J, Widmann H, Wieners KH, Claussen Marotzke J, Stevens B (2013) Climate and carbon cycle changes from 1850 to 2100 in MPI-ESM simulations for the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project phase 5. J Adv Model Earth Syst 5:572–597. https://doi.org/10.1002/jame.20038
Giorgi F, Coppola E, Solmon F, Mariotti L, Sylla MB, Bi X, Elguindi N, Diro GT, Nair V, Giuliani G, Turuncoglu UU, Cozzini S, Güttler I, O’Brien TA, Tawfik AB, Shalaby A, Zakey AS, Steiner AL, Stordal F, Sloan LC, Brankovic C (2012) RegCM4: model description and preliminary tests over multiple CORDEX domains. Climate Res 52:7–29. https://doi.org/10.3354/cr01018
Gräler B, Gerharz L, Pebesma E (2016) Spatio-temporal interpolation using gstat. The R Journal 8(1):204–218
Hengl T, Heuvelink GBM, Perˇcec Tadic M, Pebesma EJ (2012) Spatio-temporal prediction of daily temperatures using time-series of MODIS LST images. Theor Appl Climatol 107:265–277
Heuvelink GBM, Heuvelink GBM, Griffth DA (2010) Space-time geostatistics for geography: a case study of radiation monitoring across parts of Germany. Geog Anal 42(2):161–179. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-4632.2010.00788.x
Heuvelink GBM, Griffith DA, Hengl T, Melles SJ (2012) Sampling design optimization for space-time kriging. John Wiley, Oxford, pp 207–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-011-0464-2
Hofstra N, Haylock M, New M, Jones P, Frei C (2008) Comparison of six methods for the interpolation of daily, European climate data. J Geophys Res 113:D21110. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JD010100
Huang Y, Wong P, Gedeon T (1998) Spatial interpolation using fuzzy reasoning and genetic algorithms. J Geogr Inf Decis Anal 2:204–214
Hutchinson MF (1988) Calculation of hydrologically sound digital elevation models, third international symposium on spatial data handling at Sydney. Australia 3(1):120–127
IPCC (2007) Climate change 2007. Synthesis Report
IPCC (2013) Climate change 2013. Synthesis Report
Jones CD, Hughes JK, Belloin N, Hardiman C, Jones GS, Knight J, Liddicoat S, O’Connor FM, Andres RJ, Bell C, Boo KO, Bozzo A, Butchart N, Cadule P, Corbin KD, Doutriaux-Boucher M, Friedlingstein P, Gornall J, Gray L, Halloran PR, Hurtt G, Ingram WJ, Lamarque JF, Law RM, Meinshausen M, Osprey S, Palin EJ, Chini LP, Raddatz T, Sanderson MG MG, Sellar AA, Schurer A, Valdes P, Wood N, Woodward S, Yoshioka M, Zerroukat M (2011) The HadGEM2-ES implementation of CMIP5 centennial simulations. Geosci Model Dev 4:543–570. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-4-543-2011
Kilibarda Μ, Hengl T, Heuvelink GBM et al (2014) Spatio-temporal interpolation of daily temperatures for global land areas at1 km resolution. J Geophys Res Atmos 119:2294–2313. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013JD020803
Köppen W (1954) Classification of climates and world patterns. In: Trewartha GT (ed) An Introduction to Climate. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 225–226
Lasinio GJ, Sahu SK, Mardia KV (2007) Modeling rainfall data using a Bayesian Kriged-Kalman model. In: Upadhyay SK, Singh U, Dey DK (eds) Bayesian statistics and its applications. Tunbridge Wells, UK, Anshan, pp 61–86
Mair A, Fares A (2011) Comparison of rainfall interpolation methods in a mountainous region of a tropical island. J Hydrol Eng 16:371–383
Matheron, G (1962). Traité de Geostatistique Appliquée. Memoires du Bureau de Recherches Geologiques et Minieres, Tome I(14). Paris: Editions Technip (in French)
Pal JS, Giorgi F, XBi E et al (2007) Regional climate modeling for the developing world: the ICTP RegCM3 and RegCNET. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 88:1395–1409
Pebesma E (2004) Multivariable Geostatistics in S: the gstat package. Comput Geosci 30(7):683–691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2004.03.012
Pebesma E (2012) Spacetime: Spatio-temporal data in R. J Stat Softw 51(7):1–30. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v051.i07
Pebesma E, Gräler B (2017) Introduction to Spatio-temporal Variography. Institute for Geoinformatics University of Münster:1–11
Popke D, Stevens B, Voigt A (2013) Climate and climate change in a radiative-convective equilibrium version of ECHAM6. J Adv Model Earth Syst 5:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012MS000191
R Core Team (2013) A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing Vienna, Austria., see https://www.R-project.org/
Sibson R (1981) A brief description of natural neighbour interpolation, in interpreting multivariate data. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester UK, pp 21–36
Snepvangers J, Heuvelink G, Huisman J (2003) Soil water content interpolation using spatio-temporal kriging with external drift. Geoderma 112(3–4):253–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7061(02)00310-5
Taylor ΚΕ (2001) Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram. J Geophys Res 106(D7):7183–7192
Tolika K, Maheras P, Vafiadis M, Flocas HA, Arseni-Papadimitriou A (2006) An evaluation of a general circulation model (GCM) and the NCEP-NCAR reanalysis data for winter precipitation in Greece. Int J Climatol 26:935–955
Wackernagel H (2003) Multivariate Geostatistics: an introduction with applications, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Wong KW, Wong PM, PM TDGTD, Fung CC (2003) Rainfall prediction model using soft computing technique. Soft Comput 7(6):434–438
Xoplaki E, González-Rouco JF, Luterbacher J, Wanner H (2004) Wet season Mediterranean precipitation variability: influence of large-scale dynamics and trends. Clim Dyn 23:63–78
Yang X, Xie X, Liu Ji F, Wang L (2015) Spatial interpolation of daily rainfall data for local climate impact assessment over greater Sydney region. Hindawi publishing corporation advances in meteorology, 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/563629
Zimmerman D, Pavlik C, Ruggles A, Armstrong MP (1999) An experimental comparison of ordinary and universal kriging and inverse distance weighting. Math Geol 31(4):375–390
Acknowledgments
This research has been financially supported by General Secretariat for Research and Technology (GSRT) and the Hellenic Foundation for Research and Innovation (HFRI) (Scholarship Code: 174, 95543).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: H. A. Babaie
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
P., V., C., A., A., L. et al. Minimizing the uncertainties of RCMs climate data by using spatio-temporal geostatistical modeling. Earth Sci Inform 12, 183–196 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-018-0361-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-018-0361-7