Abstract
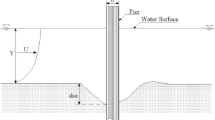
In this paper, for the first time, the scour pattern around twin bridge piers was predicted using an optimized hybrid algorithm. The hybrid algorithm (ANFIS-FA) was developed through the combination of the Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS) as well as the Firefly algorithm (FA). After that, four ANFIS and ANFIS-FA models were developed by implementing the parameters influencing the scour depth around twin piers. To assess the performance of soft computing models, the Monte Carlo simulations were employed. In addition, the validation of the numerical models was carried out by the k-fold cross validation approach. It is worth noting that the value of k in the k-fold cross validation was considered as 5. Based on the modeling results, the analysis of the results indicated that ANFIS-FA models are more precise than ANFIS models. Then, the superior model was detected through the establishment of a sensitivity analysis. The superior model is a function of all input parameters. This model estimated scour values with reasonable accuracy. For example, the values of R2, MAPE and RMSE were calculated 0.991, 5.876 and 0.015, respectively. Furthermore, the results of the error distribution demonstrated that about 66% of the results obtained from the superior model have an error less than 5%. Next, the Froude number (Fr) was identified as the most effective input parameter in estimating the scour hole around twin bridge piers. The study showed that the firefly algorithm could successfully optimize the ANFIS network and the performance of the hybrid model (ANFIS-FA) was better than the simple model (ANFIS). Finally, by performing an uncertainty analysis, it was concluded that the superior model has an overestimated performance. The uncertainty analysis proved that the hybrid model had a narrower uncertainty band in comparison with the ANFIS model.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be available on request.
References
Afzali SH (2016) New model for determining local scour depth around Piers. Arab J Sci Eng 41:3807–3815. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1983-4
Amini A, Melville BW, Ali TM, Ghazali AH (2011) Clear-water local scour around pile groups in shallow-water flow. J Hydraul Eng 138(2):177–185
Azamathulla HM (2012) Gene-expression programming to predict scour at a bridge abutment. J Hydroinf 14(2):324–331
Azimi H, Bonakdari H, Ebtehaj I (2019) Gene expression programming-based approach for predicting the roller length of a hydraulic jump on a rough bed. ISH J Hydraul Eng 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/09715010.2019.1579058
Azimi H, Bonakdari H, Ebtehaj I, Shabanlou S, Talesh SHA, Jamali A (2019) A pareto design of evolutionary hybrid optimization of ANFIS model in prediction abutment scour depth. Sādhanā 44(7):1–14
Azimi H, Bonakdari H, Ebtehaj I, Talesh SHA, Michelson DG, Jamali A (2017) Evolutionary Pareto optimization of an ANFIS network for modeling scour at pile groups in clear water condition. Fuzzy Sets Syst 319:50–69
Azimi H, Shiri H (2020a) Dimensionless groups of parameters governing the ice-seabed interaction process. J Offshore Mech Arctic Eng 142(5):051601
Azimi H, Shiri H (2020b) Ice-seabed interaction analysis in sand using a gene expression programming-based approach. Appl Ocean Res 98:102120
Azimi H, Shiri H (2021) Sensitivity analysis of parameters influencing the ice–seabed interaction in sand by using extreme learning machine. Nat Hazards 106(3):2307–2335
Bateni SM, Jeng DS (2007) Estimation of pile group scour using adaptive neuro-fuzzy approach. Ocean Eng 34(8):1344–1354
Firat M, Gungor M (2009) Generalized regression neural networks and feed forward neural networks for prediction of scour depth around bridge piers. Adv Eng Softw 40(8):731–737
Fouli H, Elsebaie IH (2016) Reducing local scour at bridge piers using an upstream subsidiary triangular pillar. Arab J Geosci 9(12):598
Jang JS (1993) ANFIS: adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 23(3):665–685
Jang JSR, Sun CT and Mizutani E 1997 Neuro-fuzzy and soft computing. Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-261066-3
Kardan N, Hassanzadeh Y, Hakimzadeh H (2017) The effect of combined countermeasures on main local scouring parameters using physical models. Arab J Geosci 10(23):516
Liriano SL, Day RA (2001) Prediction of scour depth at culvert outlets using neural networks. J Hydroinf 3(4):231–238
Mohammadpour R (2017) Prediction of local scour around complex piers using GEP and M5-tree. Arab J Geosci 10(18):416
Muzzammil M (2010) ANFIS approach to the scour depth prediction at a bridge abutment. J Hydroinf 12(4):474–485
Najafzadeh M, Barani GA, Hessami Kermani MR (2013) Abutment scour in clear-water and live-bed conditions by GMDH network. Water Sci Technol 67(5):1121–1128
Oliveto G, Marino MC (2016) Temporal scour evolution at non-uniform bridge piers. Proc Inst Civil Eng Water Manag 170(5):254–261 Thomas Telford Ltd.
Omara H, Elsayed SM, Abdeelaal GM, Abd-Elhamid HF, Tawfik A (2018) Hydromorphological numerical model of the local scour process around bridge Piers. Arab J Sci Eng 44:4183–4199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3359-z
Onen F (2014) Prediction of scour at a side-weir with GEP, ANN and Regression models. Arab J Sci Eng 39:6031–6041. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1244-y
Petersen TU, Sumer BM, Fredsøe J, Raaijmakers TC, Schouten JJ (2015) Edge scour at scour protections around piles in the marine environment-laboratory and field investigation. Coast Eng 106:42–72
Shabanlou S, Azimi H, Ebtehaj I, Bonakdari H (2018) Determining the scour dimensions around submerged vanes in a 180 bend with the gene expression programming technique. J Mar Sci Appl 17(2):233–240
Sharafi H, Ebtehaj I, Bonakdari H, Zaji AH (2016) Design of a support vector machine with different kernel functions to predict scour depth around bridge piers. Nat Hazards 84(3):2145–2162
Trent R, Gagarin N, Rhodes J (1993) Estimating pier scour with artificial neural networks. Hydraul Eng (1043-1048). ASCE
Wang H, Tang H, Liu Q, Wang Y (2016) Local scouring around twin bridge piers in open-channel flows. J Hydraul Eng 142(9):06016008
Yang X-S (2010) Firefly algorithm, stochastic test functions and design optimization. Int J Bio Ins Comp 2(2):78–84
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by: H. Babaie
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kohansarbaz, A., Kohansarbaz, A., Yaghoubi, B. et al. An integration of adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system and firefly algorithm for scour estimation near bridge piers. Earth Sci Inform 14, 1399–1411 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-021-00652-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-021-00652-z