Abstract
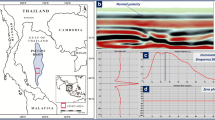
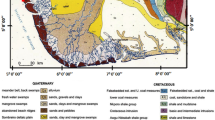
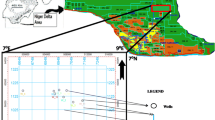
The Wubaochang structure is located at the edge of the eastern Sichuan structural belt, at the intersection of the Dabashan and eastern Sichuan arcuate fold-and-thrust belts. The tectonic setting is complex and yields poor seismic imaging results. Within this structure, the Jurassic Shaximiao Formation is a low-efficiency tight sandstone gas reservoir with low single-well production. Currently, horizontal wells are installed in the main horizons to enhance productivity and efficiency. The drilled wells show that the reservoir consists of multiple horizons with rapid lateral facies changes and highly heterogeneous physical properties. Production well pressure patterns are segmented in striped zones and significantly controlled by the sedimentary microfacies. The microfacies, geometry, and distribution patterns of the sand beds are poorly understood. As a result, there have been few high-quality horizontal wells drilled in the reservoir, significantly restricting the exploration and development efficiency of the Shaximiao Formation in this area. In this study, we examined the regional sedimentary background and relative paleo topography of the study area and synthesized the results of core descriptions, rock composition analysis, and well log and seismic response feature evaluations. Finally, we determined that the sandstones in the study area are braided river delta deposits, mainly developed with the microfacies of braided channel, flood plain, mid-channel bar, mid-channel bar complex, underwater distributary channel, and interdistributary bay. We also examined the planar distribution pattern of the sand bodies with different microfacies, based on single-well microfacies division, paleo topographic feature evaluation, and seismic information entropy analysis. The results show that the mid-channel bar and mid-channel bar complex sands are the most favorable reservoir sands in this gas reservoir, followed by the braided channel sands and underwater distributary channel sands. The topography controlled the sand deposition distribution patterns and the development of the different microfacies. Seismic entropy reflected the amount of seismic signal information and degree of chaos. The examination of seismic entropy information provides a more stable and effective stratigraphic interpretation than the use of conventional seismic methods for identifying different microfacies of braided river deltas. Seismic entropy information can provide a reliable seismic and geological basis for optimizing microfacies targets and horizontal well placement.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deng HY, Sima LQ, Wu W et al (2018) Fractal characteristics of pore structure and permeability calculation for tight sandstone reservoirs: a case of Penglaizhen formation and Shaximiao formation in Western Sichuan depression. Lithol Reserv 30(6):76–82
Fan H, Li J, Xian Y, Hu Q (2007) Application of seismic frequency—division technology in the study of fan delta evolution. Oil Gas Geol 28(5):683–686
Fan R, Zhou L, Wu J, Zeng T, Zhou X (2015) Research on tight sandstone reservoir fluids identification in Xujiahe formation, northeastern Sichuan Basin. Pet Geol Recover Effic 22(3)
Gao Z, Bin B, Zhu R, Liuhong L, Jiarui F, Jialuo MReservior sedimentary response to tectonic movement of the late Triassic in front of Daba Shan and Longmen Mountains. J Palaeogeogr 14(6)
Jiang Y, Lin Q, Haibo D, Yujun W, Chan J, Ming Sheng L (2010) Hydrocarbon accumulation conditions and exploration potentials of the Jurassic reservoirs in the Sichuan Basin. Nat Gas Ind 30(3):22–26
Li W (2015) Study on distribution characteristics of fault damage zone in tight sandstone of Xujiahe formation in the northeastern Sichuan Basin. China University of Petroleum, Beijing
Li J, Tao S-Z, Wang Z-C, Zou C-N, Gao X-H, Wang S-Q (2010) Characteristics of Jurassic petroleum geology and main factors of hydrocarbon accumulation in Ne Si Chuan Basin. Nat Gas Geosci 21(5)
Li D, Li J, Zhang B et al (2017) Formation condition, resource potential and sweetspot area prediction of Jurassic tight oil in Sichuan Basin. Acta Pet Sin 38(7):740–752
Li M, Li F, Yang Z, Wang J, Liang F, Zhengyon LJ, Tang Q (2019) Precise depicting channel sandbodies based on seismic sedimentology: an example from tight gas reservoirs of Shaximiao formation, Longgang area, Sichuan Basin. Nat Gas Explor Dev 42(2):76–80
Liang D, Ran L, Dai D et al (2011) A recognition of the prospecting potential of Jurassic large-area unconventional oils in the central-northern Sichubasin[J]. Acta Pet Sin 32(1):8–17
Liao QH, Hua LJ et al (2011) People exploration prospect of the Jurassic tight reservoirs in China Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil Gas Geol 32(6):815–822, 838
Mao J-B, Wei-Li Y, Huai-Yi F, Wei-Dong C, Zhao-Qing J (2007) Reservoir characteristics of Shaximiao formation in Wubaochang structure, northeastern Sichuan Basin. Nat Gas Ind 27(5)
Mao Q, Zheng R-C, Guang-Fu Z, Yang K, Wang F, Zhi-Yong ZUpper Triassic sedimentary facies and sedimentary evolution in the northeastern Sichuan Foreland Basin. Sediment Geol Tethyan Geol 32(1)
Pan C-L, Liu S-G, Ma Y-S, Guo X-S, Guo T-L (2011) Reservoir characteristics and main controlling factors of the Xujiahe formation in northeastern Sichuan Basin. J Southwest Pet Univ Sci Technol Ed 33(3)
Pang Z, Tao S, Zhang Q et al (2018) Secondary migration mechanism and accumulation controlling factors of Jurassic tight oil in Sichuan Basin. Acta Pet Sin 39(11):1211–1222
Rojas J, Marin CE, García PA, Forero J, Crespo RG (2018) Analysis of physico-chemical variables and their influence on water quality of the Bogota River using data mining. Int J High Perform Syst Archit 8(1/2):3
Shan R, Li Y, Wang Q (2015) Application of seismic sedimentology in sedimentary facies analysis in Yb area. Coal Geol Explor 43(2):91–95
Wang R, Mei L (2008) Seismic identification of oil-gas accumulation area using independent component analysis technique. Acta Petroli Seisinica 29(4):545–548
Wang T, Han X, Xu H, Sun X, Li T, Hou Y (2021) Study on sedimentary facies based on unsupervised neural network seismic attribute clustering. Oil Geophys Prospect 56(2):372–379
Xiao F-S, Ma T-H (2007) Understanding of exploration and development of Shaximiao gas Pool in Wubaochang structure, northeastern Sichuan Basin. Nat Gas Ind 27(5):4–7
Xiao F, Huang D, Zhang B, Tang D, Ran Q, Tang Q, Yin H (2019) Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of natural gas in Jurassic Shaximiao formation, Sichuan Basin. Acta Pet Sin 40(5):569–580
Xu G, Wang J, Huang W, Wang L, Yang W (2014) A method for seismic wavelet zero-phasing based on information entropy theory. OGP 49(2):239–251
Yang S (2014) Sedimentary evolution during Jurassic and faces-controlling reservoir prediction in Sichuan Basin, China, Chengdu
Yang SY, Li CX, Cai JG (2006) Geochemical compositions of Core sediments in eastern China: implication for late Cenozoic palaeoenvironmental changes. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 229:287–302
Yang D, Ramu AG, Lee Y, Kim S, Jeon H, Sathishkumar VE, Al-Mohaimeed AM, Al-onazi WA, Algarni TS, Choi D (2021) Fabrication of ZnO nanorods based gas sensor pattern by photolithography and lift off techniques. J King Saud Univ Sci 33(3):101397
Zhang M, Xiao R, Liu Q, Liu Y, Guo D, Tan Y (2007) Dynamic characteristics analysis on Wubaochang structure of Shaximiao formation gas reservoirs and Someideas about its exploitation and production. Nat Gas Ind 27(5):18–20
Zhang W, Guan P, Han D, Meng Q, Xie X, Jian X, Liu REvaluation of terrestrial hydrocarbon source rocks and oil source correlation in Triassic and Jurassic in northeastern Sichuan. Acta Sci Nat Univ Pekin 49(5)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: H. Babaie
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiao, Y., Liu, Z., Luo, W. et al. Characterization of seismic information entropy attributes of braided river delta sedimentary microfacies for the upper Shaximiao formation in the Wubaochang area, northeastern Sichuan Basin, China. Earth Sci Inform 15, 1371–1383 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-021-00748-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-021-00748-6