Abstract
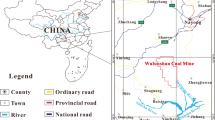
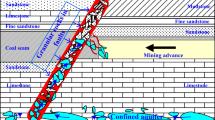
The accurate prediction of mine inflow plays an important role in the design of mine drainage capacity and the formulation of prevention and control measures for water disasters. Mine inflow is a dynamic system that is affected by many factors and is characterized by random fluctuation. The currently commonly used water inflow prediction methods often need more detailed mine geological data and complicated parameter solving process, and are limited in application. According to historical water inflow observation data of typical coal mines, a mine inflow prediction model based on unbiased grey and markov theory was established. Besides, the water inflow of a typical coal mine was predicted; and the accuracy was verified. The prediction results showed that: the mean relative error (MRE) between the predicted value of the mine inflow prediction model based on unbiased grey theory and the actual value was 3.85%. The MRE of the predicted value corrected by the markov model was improved to 2.42%. The data required for the mine inflow prediction model based on unbiased grey-markov theory are readily available. In addition, this model can eliminate the inherent bias of the traditional model and the effects of the random fluctuation of data on prediction results, and has higher computational accuracy. The relevant research results can provide some basis for the improvement of the mine inflow method.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahrami S, Ardejani FD, Baafi E (2016) Application of artificial neural network coupled with genetic algorithm and simulated annealing to solve groundwater inflow problem to an advancing open pit mine. J Hydrol 536:471–484
Booth CJ (1986)Strata-movment concepts and the hydrogeological impact of underground coal-mining. Ground Water 24(4):507–515
Deng JL (1989) Introduction to grey system theory. Journal of Grey Systems 1(1):1–24
Dong DL, Wang HZ, Wu CX (2009) Seepage characters of roof aquifers in faults and sliding structure and risk analysis of water inrush. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 28(2):373–379
Hamzacebi C, Es HA (2014) Forecasting the annual electricity consumption of Turkey using an optimized grey model. Energy 70(1–7):165–171
Hill JG, Price DR (1983) The impact of deep mining on an overlying aquifer in western Pennsylvania. Ground Water Monitoring and Remediation 3(1):138–143
Hu WY, Wang GC (1997) Development of technique of controlling water hazard on coal mine. Coal Geol Explor 25(S1):17–23
Islam MR, Shinjo R, Faruque MO, Shimada H, Howladar MF (2016) Finite element method (FEM) groundwater inflow modeling associated with an unconfined aquifer into the open-pit coalmine of the Phulbari area, NW Bangladesh. Arab J Geosci 9(5):394
Jia ZQ, Zhou ZF, Zhang HJ (2020) Forecast of coal consumption in Gansu Province based on Grey-Markov chain model. Forecast of coal consumption in Gansu Province based on Grey-Markov chain model Energy 199:199
Jovanov K, Mitrev S (2016) Forecast of influx and calculation of the balance of groundwater in "Suvodol" mine-Bitola, republic of Macedonia. Comptes Rendus de L Academie Bulgare Des Sciences 69(2):161–168
Li B, Wu Q (2019) Catastrophic evolution of water inrush from a water-rich fault in front of roadway development: a case study of the Hongcai coal mine. Mine Water Environ 38(2):421–430
Li B, Wu Q, Liu ZJ (2020) Identification of mine water inrush source based on PCA-FDA: Xiandewang coal mine case. Geofluids 2020:2584094
Li B, Wang XQ, Liu ZJ, Li T (2021) Study on multi-field catastrophe evolution laws of water inrush from concealed karst cave in roadway excavation: a case of Jiyuan coal mine. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk 12(1):222–243
Lo Russo S, Gnavi L, Peila D, Suozzi E (2013) Rough evaluation of the water-inflow discharge in abandoned mining tunnels using a simplified water balance model: the case of the Cogne iron mine (Aosta Valley, NW Italy). Environ Earth Sci 70(6):2753–2765
Mao DQ, Liu ZB, Wang WK, Li SC, Gao YQ, Xu ZH, Zhang C (2018) An application of hydraulic tomography to a deep coal mine: combining traditional pumping tests with water inrush incidents. J Hydrol 567:1–11
Meng QL, Dong ZJS, He L (2018) Forecasting service quality dynamics based on integrated method with GM(1,1) model and Markov chain. Tehnicki Vjesnik-Technical Gazette 25(5):1437–1446
Miladinovic B, Vakanjac VR, Bukumirovic D (2015) Simulation of mine water inflow:case study of the STAVALJ coal mine(southwestern Serbia). Arch Min Sci 60(4):955–969
Roy DK, Barzegar R, Quilty J, Adamowski J (2020) Using ensembles of adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system and optimization algorithms to predict reference evapotranspiration in subtropical climatic zones. J Hydrol 591:125509
Surinaidu L, Rao VVSG, Ramesh G (2013) Assessment of groundwater inflows into Kuteshwar limestone mines through flow modeling study, Madhya Pradesh, India. Arab J Geosci 6(4):1153–1161
Wang WX, Sui WH, Faybishenko B (2016) Permeability variations within mining-induced fractured rock mass and its influence on groundwater inrush. Environ Earth Sci 75(4):1–15
Wu Q, Cui QF, Zhao SQ (2013) Type classification and main characteristics of mine water disasters. J China Coal Soc 38(4):561–565
Wu Q, Li B, Chen YL (2016) Vulnerability assessment of groundwater inrush from underlying aquifers based on variable weight model and its application. Water Resour Manag 30(10):3331–3345
Xing ZG, Peng SP, Du WF (2018) Hydrogeological changes caused by opencast coal mining in steppe zone: a case study of Shengli 1 open-pit coal mine. Desalin Water Treat 121:126–133
Zeng B, Duan HM, Bai Y, Meng W (2018) Forecasting the output of shale gas in China using an unbiased grey model and weakening buffer operator. ENERGY 151:238–249
Zhang R, Jiang ZQ, Zhou HY (2014) Groundwater outbursts from faults above a confined aquifer in the coal mining. Nat Hazards 71(3):1861–7872
Zhang K, Cao B, Lin G (2017) Using multiple methods to predict mine water inflow in the Pingdingshan no. 10 coal mine, China. Mine Warer and the Environment 36(1):154–160
Zhao Y, Liang B, An ZZ (2020) Prediction equipment and water damage prevention based on microscopic image and mine water inflow. Acta Microscopica 29(6):3233–3241
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation (42162022; 41702270), Guizhou Science and Technology Department Project (Qian Ke He Ji Chu [2019]1413; Qian Ke He Zhi Cheng [2020]4Y048; Qian Ke He Zhi Cheng [2020]4Y007), Guizhou Provincial Department of Education Foundation ([2018]113; Shanxi Province Coal Mine Water Hazard Prevention and Control Technology Open Fund (2020SKMS01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: H. Babaie
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, B., Zhang, H., Luo, Y. et al. Mine inflow prediction model based on unbiased Grey-Markov theory and its application. Earth Sci Inform 15, 855–862 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-022-00770-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-022-00770-2