Abstract
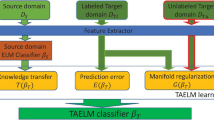
In this paper, we propose a general framework for Extreme Learning Machine via free sparse transfer representation, which is referred to as transfer free sparse representation based on extreme learning machine (TFSR-ELM). This framework is suitable for different assumptions related to the divergence measures of the data distributions, such as a maximum mean discrepancy and K-L divergence. We propose an effective sparse regularization for the proposed free transfer representation learning framework, which can decrease the time and space cost. Different solutions to the problems based on the different distribution distance estimation criteria and convergence analysis are given. Comprehensive experiments show that TFSR-based algorithms outperform the existing transfer learning methods and are robust to different sizes of training data.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen CP, Zhang CY (2014) Data-intensive applications, challenges, techniques and technologies: A survey on big data. Inform Sci 275:314–347
Zhou ZH, Chawla N, Jin Y, Williams G (2014) Big data opportunities and challenges: Discussions from data analytics perspectives. IEEE Comput Intell Mag 9(4):62–74
Kasun LLC, Zhou H, Huang GB, Vong CM (2013) Representational learning with extreme learning machine for big data. IEEE Intell Syst 28(6):31–34
Platt J (1999) Fast training of support vector machines using sequential minimal optimization, Advances in kernel methods—support vector learning 3
Suykens JAK, Vandewalle J (1999) Least squares support vector machine classifiers. Neural Process Lett 9(3):293–300
Hetch-Neilsen R (1989) Theory of the backpropagation neural network, In International Joint Conference on Neural Networks 593–605
Cortes C, Vapnik VN (1995) Support vector networks. Mach Learn 20(3):273–297
Huang GB, Chen L, Siew CK (2006) Universal approximation using incremental constructive feedforward networks with random hidden nodes. IEEE Trans Neural Networks 17(4):879–892
Han F, Huang DS (2006) Improved extreme learning machine for function approximation by encoding a priori information. Neurocomputing 69:2369–2373
Kim CT, Lee JJ (2008) Training two-layered feedforward networks with variable projection method. IEEE Trans Neural Networks 19:371–375
Zhu QY, Qin AK, Suganthan PN, Huang GB (2005) Evolutionary extreme learning machine. Patt Recogn 38:1759–1763
Wang Y, Cao F, Yuan Y (2011) A study on effectiveness of extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 74:2483–2490
Li GH, Liu M, Dong MY (2010) A new online learning algorithm for structure-adjustable extreme learning machine. Comp Math Appl 60:377–389
Huang GB, Chen L (2007) Convex incremental extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 70:3056–3062
Huang GB, Li MB, Chen L, Siew CK (2008) Incremental extreme learning machine with fully complex hidden nodes. Neurocomputing 71:576–583
Feng G, Huang GB, Lin Q, Gay R (2009) Error minimized extreme learning machine with growth of hidden nodes and incremental learning. IEEE Trans Neural Networks 20:1352–1357
Rong HJ, Ong YS, Tan AH, Zhu Z (2008) A fast pruned-extreme learning machine for classification problem. Neurocomputing 72:359–366
Rong HJ, Huang GB, Sundararajan N, Saratchandran P (2009) Online sequential fuzzy extreme learning machine for function approximation and classification problems. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cyber Part B Cyber 39:1067–1072
Yoan M, Sorjamaa A, Bas P, Simula O, Jutten C, Lendasse A (2010) OP-ELM: optimally pruned extreme learning machine. IEEE Trans Neural Networks 21:158–162
Lan Y, Soh YC, Huang GB (2010) Constructive hidden nodes selection of extreme learning machine for regression. Neurocomputing 73:3191–3199
Zong WW, Huang GB, Chen Y (2013) Weighted extreme learning machine for imbalance learning. Neurocomputing 101:229–242
Fu H, Vong CM, Wong PK, et al (2014) Fast detection of impact location using kernel extreme learning machine. Neural Comp Appl 1–10
Dai W, Yang Q, Xue G, Yu Y (2007) Boosting for transfer learning. Proc. 24th Int Confe Mach Learn 193–200
Pan SJ, Yang Q (2010) A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Trans Know Data Eng 22:1345–1359
Pan J, Wang X, Cheng Y et al (2014) Multi-source transfer ELM-based Q learning. Neurocomputing 137:57–64
Zhang L, Zhang D (2015) Domain adaptation extreme learning machines for drift compensation in E-nose systems. IEEE Trans Instru Measur 64:1790–1801. doi:10.1109/TIM.2014.2367775
Huang G, Song S, Gupta JND, Wu C (2014) Semi-supervised and unsupervised extreme learning machines. IEEE Trans Cyber 44(12):2405–2417
Huang GB (2014) An insight into extreme learning machines: Random neurons, random features and kernels. Cogn Comp 6(3):376–390
Huang GB, Bai Z, Kasun LLC et al (2015) Local receptive fields based extreme learning machine. IEEE Comp Intell Magaz 10(2):18–29
Tang J, Deng C, Huang GB (2015) Extreme learning machine for multilayer perceptron. IEEE Trans Neural Networks Learn Syst. doi:10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2424995
Huang GB, Zhu QY, Siew CK (2006) Extreme learning machine: Theory and applications. Neurocomputing 70:489–501
Widrow B, Greenblatt A, Kim Y, Park D (2013) The no-prop algorithm: A new learning algorithm for multilayer neural networks. Neural Networks 37:182–188
Rao CR, Mitra SK (1971) Generalized inverse of matrices and its applications. Wiley, New York
Huang GB, Zhou H, Ding X, Zhang R (2012) Extreme learning machine for regression and multiclass classification. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cyber Part B Cyber 42:513–529
Belkin M, Niyogi P (2003) Laplacian eigenmaps for dimensionality reduction and data representation. Neural Comput 15(6):1373–1396
Zheng M, Bu J, Chen C, Wang C et al (2011) Graph regularized sparse coding for image representation. IEEE Trans Image Process 20(5):1327–1336
Lee H, Battle A, Raina R, Ng A (2006) Efficient sparse coding algorithms. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 801–808
ORL Face Database (2005) AT&T Laboratories Cambridge, http://www.camorl.co.uk/facedatabase.html
Yale Face Database (2005) Columbia Univ., http://www.cs.columbia.edu/belhumeur/pub/images/yalefaces/
The USPS dataset, http://www-i6.informatik.rwth-aachen.de/~keysers/usps.html
The MNIST dataset, http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/
Feng L, Ong YS, Lim MH (2013) ELM-guided memetic computation for vehicle routing. IEEE Intell Syst 8(6):38–41
Cambria E, Huang GB, Kasun LLC et al (2013) Extreme learning machines [trends & controversies]. IEEE Intell Syst 28(6):30–59
Kan EM, Lim MH, Ong YS et al (2013) Extreme learning machine terrain-based navigation for unmanned aerial vehicles. Neural Comp Appl 22(3–4):469–477
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the anonymous reviewers for the valuable comments. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61473252) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61375049).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Mao, W., Jiang, W. et al. Extreme learning machine via free sparse transfer representation optimization. Memetic Comp. 8, 85–95 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12293-016-0188-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12293-016-0188-z