Abstract
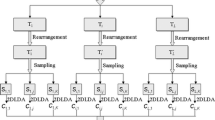
According to the research results reported in the past decades, it is well acknowledged that face recognition is not a trivial task. With the development of electronic devices, we are gradually revealing the secret of object recognition in the primate’s visual cortex. Therefore, it is time to reconsider face recognition by using biologically inspired features. In this paper, we represent face images by utilizing the C1 units, which correspond to complex cells in the visual cortex, and pool over S1 units by using a maximum operation to reserve only the maximum response of each local area of S1 units. The new representation is termed C1 Face. Because C1 Face is naturally a third-order tensor (or a three dimensional array), we propose three-way discriminative locality alignment (TWDLA), an extension of the discriminative locality alignment, which is a top-level discriminate manifold learning-based subspace learning algorithm. TWDLA has the following advantages: (1) it takes third-order tensors as input directly so the structure information can be well preserved; (2) it models the local geometry over every modality of the input tensors so the spatial relations of input tensors within a class can be preserved; (3) it maximizes the margin between a tensor and tensors from other classes over each modality so it performs well for recognition tasks and (4) it has no under sampling problem. Extensive experiments on YALE and FERET datasets show (1) the proposed C1Face representation can better represent face images than raw pixels and (2) TWDLA can duly preserve both the local geometry and the discriminative information over every modality for recognition.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alex OM, Terzopoulos D. Multilinear subspace analysis for image ensembles. Int Conf ComputVis Pattern Recognit. 2003;2:93–9.
Belhumeur P, Hespanha J, Kriegman D. Eigenfaces vs. Fisherfaces: recognition using class specific linear projection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 1997;19(7):711–20.
Belkin M, Niyogi P, Sindhwani V. On manifold regularization. In: Proc. Int’l Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. 2005.
Belkin M, Niyogi P. Laplacian eigenmaps and spectral techniques for embedding and clustering. Neural Inf Process Syst. 2002;14:585–91.
Bian W, Tao D. Harmonic mean for subspace selection. International conference on pattern recognition; 2008. p. 1–4.
Cai D, He X, Han J. Spectral regression for efficient regularized subspace learning. IEEE international conference on computer vision; 2007. p. 1–8.
Cai D, He X, Han J, Zhang H. Orthogonal Laplacian faces for face recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2006;15(11):3608–14.
Fukushima K. Neocognitron: a self organizing neural network model for a mechanism for pattern recognition unaffected by shift in position. Biol Cybern. 1980;36(4):193–202.
Gao X, Yang Y, Tao D, Li X. Discriminative optical flow tensor for video semantic analysis. Comput Vis Image Underst. 2009;113(3):372–83.
He X, Niyogi P. Locality preserving projections. Neural information processing systems; 2003. p. 20.
He X, Yan S, Hu Y, Niyogi P, Zhang H. Face recognition using Laplacian faces. IEEE Trans Patten Anal Mach Intell. 2005;27(3):328–40.
Hotelling H. Analysis of a complex of statistical variables into principal components. J Educ Psychol. 1933;24:417–41.
Huang Y, Huang K, Tao D, Tan T, Li X. Enhanced biologically inspired model. Int Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit. 2008;1–8.
Li X, Lin S, Yan S, Xu D. Discriminant locally linear embedding with high-order tensor data. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern. 2008;38(2):342–52.
Liu C, Wechsler C. Gabor feature based classification using the enhanced fisher linear discriminant model for face recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2002;11(4):467–76.
Liu W, Tao D, Liu J. Transductive component analysis. IEEE international conference on data mining; 2008. p. 433–42.
Lowe D. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int J Comput Vis. 2003;60(2):91–100.
Meyers E, Wolf L. Using biologically inspired features for face processing. Int J Comput Vis. 2008;76:93–104.
Mutch J, Lowe D. Multiclass object recognition using sparse, localized features. International conference on computer vision and pattern recognition; 2006. p. 11–8.
Ojala T, Pietikäinen M, Mäenpää T. Multiresolution grayscale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns. IEEE Trans Patten Anal Mach Intell. 2002;24(7):971–87.
Phillips PJ, Moon H, Rizvi SA, Rauss PJ. The FERET evaluation methodology for face-recognition algorithms. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2000;22(10):1090–104.
Riesenhuber M, Poggio T. Hierarchical models of object recognition in cortex. Nat Neurosci. 1999;2(11):1019–25.
Riesenhuber M, Poggio T. Models of object recognition. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3:1199–204.
Riesenhuber M, Poggio T. Neural mechanisms of object recognition. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2002;12:162–8.
Roweis ST, Saul LK. Nonlinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding. Science. 2000;290:2323–6.
Schneider R, Riesenhuber M. Detailed look at scale and translation invariance in a hierarchical neural model of visual object recognition. AI Memo 2002-011/CBCL Memo218, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2002.
Serre T, Riesenhuber M. Realistic modeling of simple and complex cell tuning in the HMAX model, and implications for invariant object recognition in cortex. AI Memo 2004-017/CBCL Memo239, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2004.
Serre T, Wolf L, Poggio T. Object recognition with features inspired by visual cortex. Int Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit. 2005;2:994–1000.
Serre T, Wolf L, Bileschi S, Riesenhuber M, Poggio T. Robust object recognition with cortex-like mechanisms. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2007;29(3):411–26.
Song D, Tao D. Biologically inspired feature manifold for scene classification. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2009;18:1–30.
Song D, Tao D. C1 units for scene classification. International conference on pattern recognition; 2008. p. 1–4.
Sun J, Tao D, Papadimitriou S, Yu P, Faloutsos C. Incremental tensor analysis: theory and applications. ACM Trans Knowl Discov Data. 2008;2(3):11.1–11.37.
Tao D, Sun J, Shen J, Wu X, Li X, Maybank S, Faloutsos S. Probabilistic tensor analysis with Akaike and Bayesian information criteria. In: Ishikawa M, et al. editors. The 14th international conference on neural information processing. 2008;791–801.
Tao D, Li X, Wu X, Maybank S. Human carrying status in visual surveillance. Int Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit. 2006;2:1670–7.
Tao D, Li X, Wu X, Maybank S. General tensor discriminant analysis and Gabor feature for gait recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2007;29(10):1700–15.
Tao D, Li X, Wu X, Hu W, Maybank S. Supervised tensor learning. Knowl Inf Syst. 2007;13:1–42.
Tao D, Sun J, Shen J, Wu X, Li X, Maybank S, Faloutsos C. Bayesian tensor analysis. IEEE international joint conference on neural networks; 2008. p. 1403–10.
Tao D, Song M, Li X, Shen J, Sun J, Wu X, et al. Bayesian tensor approach for 3-D Face modeling. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol. 2008;18(10):1397–410.
Tao D, Li X, Wu X, Maybank S. Tensor rank one discriminant analysis–a convergent method for discriminative multilinear subspace selection. Neurocomputing. 2008;71(10–12):1866–82.
Tao D, Li X, Wu X, Maybank S. Geometric mean for subspace selection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2009;31(2):260–74.
Turk M, Pentlanbd A. Eigenfaces for recognition. J Cogn Neurosci. 1991;3:71–86.
Ye J, Janardan R, Li Q. Two-dimensional linear discriminant analysis. Neural information processing systems; 2005. p. 1569–76.
Zhang T, Tao D, Li X, Yang J. A unifying framework for spectral analysis based dimensionality reduction. IEEE international joint conference on neural networks; 2008. p. 1671–8.
Zhang T, Tao D, Yang J. Discriminative locality alignment. European conference on computer vision; 2008. p. 725–38.
Zhang T, Tao D, Li X, Yang J. Patch alignment for dimensionality reduction. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng. 2009;21(9):1299–313.
Acknowledgments
This project was partially supported by the Nanyang Technological University Start-Up Grant (under project number M58020010), 100 Talents Program of The Chinese Academy of Sciences and K. C. WONG Education Foundation Award of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mu, Y., Tao, D., Li, X. et al. Biologically Inspired Tensor Features. Cogn Comput 1, 327–341 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-009-9028-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-009-9028-5