Abstract
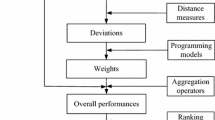
To cope with the hesitancy and uncertainty of the decision makers’ cognitions to decision-making problems, this paper introduces a new type of fuzzy sets called linguistic interval hesitant fuzzy sets. A linguistic interval hesitant fuzzy set is composed of several linguistic terms with each one having several interval membership degrees. Considering the application of linguistic interval hesitant fuzzy sets in decision making, an ordered relationship is offered, and several operational laws are defined. After that, several aggregation operators based on additive and fuzzy measures are introduced, by which the comprehensive attribute values can be obtained. Based on the defined distance measure, models for the optimal weight vectors are constructed. In addition, an approach to multi-attribute decision making with linguistic interval hesitant fuzzy information is developed. Finally, two numerical examples are provided to show the concrete application of the procedure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atanassov KT. Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1986;20(1):87–96.
Atanassov KT, Gargov G. Interval valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1989;31(3):343–9.
Akusok A, Miche Y, Hegedus J, Nian R, Lendasse A. A two-stage methodology using K-NN and false-positive minimizing ELM for nominal data classification. Cogn Comput. 2014;6(3):432–45.
Andrea G, Eiko Y, Giorgio G. Cognitive dissonance and social influence effects on preference judgments: an eye tracking based system for their automatic assessment. Int J Hum Comput Stud. 2015;73(1):12–8.
Akusok A, Miche Y, Hegedus J, Rui N, Amaury L. A two-stage methodology using K-NN and false-positive minimizing ELM for nominal data classification. Cogn Comput. 2014. doi:10.1007/s12559-014-9253-4.
Bellman RE, Zadeh LA. Decision-making in a fuzzy environment. Manage Sci. 1970;17(4):141–64.
Bryson N, Mobolurin A. An action learning evaluation procedure for multiple criteria decision making problems. Eur J Oper Res. 1995;96(2):379–86.
Chen N, Xu ZS, Xia MM. Interval-valued hesitant preference relations and their applications to group decision making. Knowl Based Syst. 2013;37:528–40.
Chiclana F, Herrera F, Herrera-Viedma E. Integrating three representation models in fuzzy multipurpose decision making based on fuzzy preference relations. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1998;97(1):33–48.
Choquet G. Theory of capacities. Annales de l’institut Fourier. 1953;5:131–295.
Czubenko M, Kowalczuk Z, Ordys A. Autonomous driver based on an intelligent system of decision-making. Cogn Comput. 2015. doi:10.1007/s12559-015-9320-5.
Dong B, Wu JS, Jiao LC. Robust routing and channel allocation in multi-hop cognitive radio networks. Wirel Netw. 2015;21(1):127–37.
Doll BB, Shohamy D, Daw ND. Multiple memory systems as substrates for multiple decision systems. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2015;117(SI):4–13.
De Luca A, Termini S. A definition of nonprobabilistic entropy in the setting of fuzzy theory. Inform Control. 1972;20:301–12.
Fodor J, Marichal JL, Roubens M. Characterization of the ordered weighted averaging operators. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst. 1995;3(2):236–40.
Grabisch M. Fuzzy integral in multicriteria decision making. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1995;69(3):279–98.
Grabisch M. The application of fuzzy integrals in multicriteria decision making. Eur J Oper Res. 1996;89(3):445–56.
Grabisch M. k-order additive discrete fuzzy measures and their representation. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1997;92(2):167–89.
Chen SJ, Hwang CL. Fuzzy multiple attribute decision making methods. Berlin: Springer; 1992.
Herrera F, Herrera-Viedma E, Martínez L. A fusion approach for managing multi-granularity linguistic term sets in decision-making. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2000;114(1):43–58.
Herrera-Viedma E, Lopez-Herrera AG. A review on information accessing systems based on fuzzy linguistic modeling. Int J Comput Intell Syst. 2010;3(4):420–37.
Herrera F, Martínez L. A model based on linguistic 2-tuple for dealing with multigranular hierarchical linguistic contexts in multi-expert decision making. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern. 2001;31(2):227–34.
Herrera F, Martínez L. A 2-tuple fuzzy linguistic representation model for computing with words. IIEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst. 2000;8(6):746–52.
Herrera F, Herrera-Viedma E. Choice functions and mechanisms for linguistic preference relations. Eur J Oper Res. 2000;120(1):144–61.
Hei YQ, Li WT, Li M, Qiu Z, Fu WH. Optimization of multiuser MIMO cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks. Cogn Comput. 2014. doi:10.1007/s12559-014-9297-5.
Haikonen POA. Yes and no: match/mismatch function in cognitive robots. Cogn Comput. 2014;6(2):158–63.
Lorenzo V, Andrea P, Marco C. Scalable data dissemination in opportunistic networks through cognitive methods. Pervasive Mob Comput. 2015;16:115–35.
Liu PD, Jin F. Methods for aggregating intuitionistic uncertain linguistic variables and their application to group decision making. Inform Sci. 2012;205(1):58–71.
Liu PD. Some geometric aggregation operators based on interval intuitionistic uncertain linguistic variables and their application to group decision making. Appl Math Modell. 2013;37(4):2430–44.
Laurent PA. A neural mechanism for reward discounting: insights from modeling hippocampal–striatal interactions. Cogn Comput. 2013;5(1):152–60.
Merigó JM, Gil-Lafuente AM. The induced generalized OWA operator. Inform Sci. 2009;179(6):729–41.
Merigó JM, Casanovas M. Fuzzy generalized hybrid aggregation operators and its application in fuzzy decision making. Int J Fuzzy Syst. 2010;12(1):15–24.
Marichal JL. The influence of variables on pseudo-Boolean functions with applications to game theory and multicriteria decision making. Dis Appl Math. 2000;107(1–3):139–64.
Meng FY, Chen XH, Zhang Q. Multi-attribute decision analysis under a linguistic hesitant fuzzy environment. Inform Sci. 2014;267:287–305.
Meng FY, Chen XH. Correlation coefficients of hesitant fuzzy sets and their application based on fuzzy measures. Cogn Comput. 2015. doi:10.1007/s12559-014-9313-9.
Meng FY, Tang J. Interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy multi-criteria group decision making based on cross entropy and Choquet integral. Int J Intell Syst. 2013;28(12):1141–213.
Meng FY, Chen XH. A hesitant fuzzy linguistic multi-granularity decision making model based on distance measures. J Intell Fuzzy Syst. 2015. doi:10.3233/IFS-141435.
Meng FY, Chen XH. Entropy and similarity measure of Atanassov’s intuitionistic fuzzy sets and their application to pattern recognition based on fuzzy measures. Pattern Anal Appl. doi:10.1007/s10044-014-0378-6.
Meng FY, Chen XH. Interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy multi-criteria group decision making based on cross entropy and 2-additive measures. Soft Comput. 2014. doi:10.1007/s00500-014-1393-7.
Meng FY, Chen XH, Zhang Q. Some uncertain generalized Shapley aggregation operators for multi-attribute group decision making. J Intell Fuzzy Syst. doi:10.3233/IFS-131069.
Myriam C, Anne GD, Benoît L. A computational cognitive model of information search in textual materials. Cogn Comput. 2014;6(1):1–17.
Negi DS. Fuzzy analysis and optimization. PhD Thesis, Department of Industrial Engineering, Kansas State University, 1989.
Park JH, Gwak MG, Kwun YC. Uncertain linguistic harmonic mean operators and their applications to multiple attribute group decision making. Computing. 2011;93(1):47–64.
Patryk A, Laurent A. Neural mechanism for reward discounting: insights from modeling hippocampal–striatal interactions. Cogn Comput. 2013;5(1):152–60.
Rodríguez LF, Ramos F. Development of computational models of emotions for autonomous agents: a review. Cogn Comput. 2014;6(3):351–75.
Ribeiro RA. Fuzzy multiple attribute decision making: a review and new preference elicitation techniques. Fuzzy Set Syst. 1996;78(2):155–81.
Rodríguez RM, Martínez L, Herrera F. Hesitant fuzzy linguistic terms sets for decision making. IIEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst. 2012;20(1):109–19.
Sugeno M. Theory of fuzzy integral and its application, Doctorial Dissertation, Tokyo Institute of Technology, 1974.
Shapley LS. A value for n-person game. In: Kuhn H, Tucker A, editors. Contributions to the theory of games. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 1953.
Savitha R, Suresh S, Kim HJ. A meta-cognitive learning algorithm for an extreme learning machine classifier. Cogn Comput. 2014;6(2):253–63.
Torfia F, Farahani RZ, Rezapour S. Fuzzy AHP to determine the relative weights of evaluation criteria and Fuzzy TOPSIS to rank the alternatives. Appl Soft Comput. 2010;10(2):520–8.
Torra V. Hesitant fuzzy sets. Int J Intell Syst. 2010;25(6):529–39.
Torra V, Narukawa Y. On hesitant fuzzy sets and decision. In: The 18th IEEE Int Con Fuzzy Syst. Jeju Island, Korea, 2009, pp. 1378–82.
Türkşen IB. Type 2 representation and reasoning for CW. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2002;127(1):17–36.
Tan CQ. A multi-criteria interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy group decision making with Choquet integral-based TOPSIS. Expert Syst Appl. 2011;38(4):3023–33.
Tan CQ, Chen XH. Induced intuitionistic fuzzy Choquet integral operator for multi-criteria decision making. Int J Intell Syst. 2011;26(7):659–86.
Tan CQ, Chen XH. Intuitionistic fuzzy Choquet integral operator for multi-criteria decision making. Expert Syst Appl. 2010;37(1):149–57.
Wang JQ, Li JJ. The multi-criteria group decision making method based on multi-granularity intuitionistic two semantics. Sci Tech Inform. 2009;33(1):8–9.
Wang XZ, Liu JS, Wei YQ. Concept of consistence and weights of the judgment matrix in the uncertainty type of AHP. Syst Eng Theory Pract. 1994;14(1):16–22.
Wang JH, Hao JY. A new version of 2-tuple fuzzy linguistic representation model for computing with words. IIEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst. 2006;14(3):435–45.
Wei GW. Uncertain linguistic hybrid geometric mean operator and its application to group decision making under uncertain linguistic environment. Int J Uncertain Fuzz. 2009;17(2):251–67.
Wu ZB, Chen YH. The maximizing deviation method for group multiple attribute decision making under linguistic environment. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2007;158(14):1608–17.
Xu ZS. Uncertain linguistic aggregation operators based approach to multiple attribute group decision making under uncertain linguistic environment. Inform Sci. 2004;168(1–4):171–84.
Xu ZS. An approach based on the uncertain LOWG and induced uncertain LOWG operators to group decision making with uncertain multiplicative linguistic preference relations. Decis Support Syst. 2006;41(2):488–99.
Xu ZS. Induced uncertain linguistic OWA operators applied to group decision making. Inform Fusion. 2006;7(2):231–8.
Xu ZS. An approach based on the uncertain LOWG and induced uncertain LOWG operators to group decision making with uncertain multiplicative linguistic preference relations. Decis Support Syst. 2006;41(2):488–99.
Xu ZS. Choquet integrals of weighted intuitionistic fuzzy information. Inform Sci. 2010;180(5):726–36.
Yang J, Gong LY, Tang YF, Yan J, He HB, Zhang LQ. An improved SVM-based cognitive diagnosis algorithm for operation states of distribution Grid. Cogn Comput. 2015. doi:10.1007/s12559-015-9323-2.
Zadeh LA. Outline of a new approach to the analysis of complex systems and decision processes interval-valued fuzzy sets. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern. 1973;3(1):28–44.
Zadeh LA. The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning—part I. Inform Sci. 1975;8(3):199–249.
Zadeh LA. Fuzzy logic = computing with words. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst. 1996;4(1):103–11.
Acknowledgments
The authors first want to thank the Editor-in-Chief Professor Amir Hussain, the associate Editor and five anonymous referees for their constructive and valuable comments, which have much improved the paper. This work was supported by the State Key Program of National Natural Science of China (No. 71431006), the Funds for Creative Research Groups of China (No. 71221061), the Projects of Major International Cooperation NSFC (No. 71210003), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 71201089, 71201110, 71271217 and 71271029), the National Science Foundation for Post-doctoral Scientists of China (2014M560655) and the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University of China (No. NCET-12-0541).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, F., Wang, C. & Chen, X. Linguistic Interval Hesitant Fuzzy Sets and Their Application in Decision Making. Cogn Comput 8, 52–68 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-015-9340-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-015-9340-1