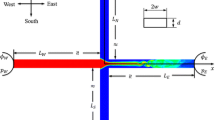
Abstract
An experimental study was conducted to assess the effectiveness of manipulating convective electrokinetic instability (EKI) waves to control/enhance fluid mixing inside three Y-shaped microchannels, which includes a conventional straight channel, a channel with micro-cavities, and a channel with micro-steps. Epi-fluoresence imaging technique was used to conduct qualitative flow visualization and quantitative scalar concentration field measurements inside the microchannels. The effects of the applied static and alternating electric fields on the evolution of the convective EKI waves and the resultant fluid mixing process were quantified in terms of scalar concentration distributions, shedding frequency of the EKI waves, fluid mixing efficiency and mixing augmentation factor. While the fluid mixing efficiency was found to increase monotonically with the increasing strength of the applied static electric fields for all the studied microchannels, the channel with micro-cavities was found to have the best overall mixing enhancement performance among the three studied microchannels. It was found that fluid mixing processes in the microchannels would be further enhanced by adding alternating electric perturbations to the applied static electric fields, regardless the frequency and magnitude of the alternating electric perturbations. The fluid mixing process would be most enhanced when the frequency of the alternating electric perturbations is close to the “natural frequency” of the EKI waves (i.e., the shedding frequency of the EKI waves with the applied static electric fields only).
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bryden MD, Brenner E (1996) Effect of laminar chaos on reaction and dispersion in eccentric annular flow. J Fluid Mech 325:219–237
Campbell CJ, Grzybowski BA (2004) Microfluidic mixers: from microfabricated to self-assembling devices. Phil Trans R Soc Lond A 362:1069–1086
Chen CH, Lin H, Lele SK, Santiago JG (2005) Convective and absolute electrokinetic instability with conductivity gradients. J Fluid Mech 524:263–303
Hu H, Jin Z, Dawoud A, Jankowiak R (2008) Fluid mixing control inside a Y-shaped microchannel by using electrokinetic instability. J Fluid Sci Technol 3–2:260–273
Huang MZ, Yang RJ, Tai CH, Tsai CH, Fu LM (2006) Application of electrokinetic instability flow for enhanced micromixing in cross-shaped microchannel. Biomed Microdevices 8:309–315
Inoue S, Spring K (1997) Video microscopy: the fundamentals. Plenum Press, New York
Jin Z, Someya S, Okamoto K, Hu H (2008) Mixing enhancement in a microfluidic device. J Vis 11–1:35–36
Johnson TJ, Ross D, Locascio LE (2002) Rapid microfluidic mixing. Anal Chem 74(1):45–51
Lee SM, Im DJ, Kang IS (2000) Circulating flows inside a drop under time-periodic nonuniform electric fields. Phys Fluids 12:1899–1910
Nguyan NT, Wu Z (2005) Micromixers—a review. J Micromech Microeng 15:r1–r16
Oddy MH, Santiago JG, Mikkelsen JC (2001) Electrokinetic instability micromixing. Anal Chem 73:5822–5832
Park J, Shin SM, Kang YH, Kang IS (2005) Application of electrokinetic instability for enhanced mixing in various micro-T-channel geometries. Phys Fluids 17:118101
Posner JD, Santiago JG (2006) Convective instability of electrokinetic flows in a cross-shaped microchannel. J Fluid Mech 555:1–42
Schrum KF, Lancaster JM, Johnston SE, Gilman SD (2000) Monitoring electroosmotic flow by periodic photobleaching of a dilute, neutral fluorophore. Anal Chem 72:4317–4321
Shin SM, Kang IS, Cho YK (2005) Mixing enhancement by using electrokinetic instability under time-periodic electric field. J Micromech Microeng 15:445–462
Tai CH, Yang RJ, Huang MZ, Liu CW, Tsai CH, Fu LM (2006) Micromixer utilizing electrokinetic instability-induced shedding effect. Electrophoresis 27:4982–4990
Acknowledgments
The support of National Science Foundation CAREER program under award number of CTS-0545918 is gratefully acknowledged. The authors would also like to thank Prof. Ryszard Jankowiak and Dr. Abdulilah Dawoud for their help in making the Y-shaped microchannels used in the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, Z., Hu, H. Mixing enhancement by utilizing electrokinetic instability in different Y-shaped microchannels. J Vis 13, 229–239 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-010-0034-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-010-0034-1