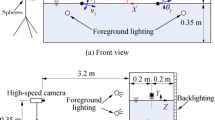
Abstract
In this paper, the hydrodynamic characteristics associated with oblique water entry of two tandem spheres were experimentally investigated using high-speed photography. The results indicated that in the cavity formed by the first sphere, a suction effect due to the pressure difference between inside and outside the cavity was developed, which consequently led the second sphere to accelerate when it was totally submerged in the cavity. In addition, the first sphere was accelerated with a sudden expansion of the cavity radius due to the energy transfer effect associated with the collision of the two spheres, with a ring joint geometry observed, and the cavity finally broke up into two sections. Since the second sphere moved inside the cavity with less drag, it finally reached the first sphere and a second collision event was observed.
Graphic abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abelson HI (1970) Pressure measurements in the water-entry cavity. J Fluid Mech 44:129–144
Chen C, Ma Q, Wei Y, Wang C (2018) Experimental study on the cavity dynamics in high-speed oblique water-entry. Fluid Dyn Res 50:45511
Epps BP, Truscott TT, Techet AH (2010) Evaluating derivatives of experimental data using smoothing splines. In: Mathematical methods in engineering international symposium, IPC, Coimbra, Portugal
Gilbarg D, Anderson RA (1948) Influence of atmospheric pressure on the phenomena accompanying the entry of spheres into water. J Appl Phys 19:127–139
Hurd R, Fanning T, Pan Z, Mabey C, Bodily K, Hacking K, Speirs N, Truscott T (2015) Matryoshka cavity. Phys Fluids 27:091104
Lu L, Wei Y, Wang C, Song W, Liu K (2019) Tests for cavities and motion characteristics in process of two cylinders in parallel water entry at low speed. J Vib Shock 38:42–49 (in Chinese)
Mansoor MM, Vakarelski IU, Marston JO, Truscott TT, Thoroddsen ST (2017) Stable–streamlined and helical cavities following the impact of Leidenfrost spheres. J Fluid Mech 823:716–754
May A (1952) Vertical entry of missiles into water. J Appl Phys 23:1362–1372
May A, Woodhull JC (1948) Drag coefficients of steel spheres entering water vertically. J Appl Phys 19:1109–1121
Miloh T (1991) On the oblique water-entry problem of a rigid sphere. J Eng Math 25:77–92
Shi HH, Takami T (2001) Some progress in the study of the water entry phenomenon. Exp Fluids 30:475–477
Truscott TT, Techet AH (2009) Water entry of spinning spheres. J Fluid Mech 625:135–165
Truscott TT, Epps BP, Techet AH (2012) Unsteady forces on spheres during free-surface water entry. J Fluid Mech 704:173–210
Truscott TT, Epps BP, Belden J (2014) Water entry of projectiles. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 46:355–378
Wang W, Wang Y (2010) Influence of parameters of twin cylinders on hydrodynamic during synchronous water entry. Chin J Hydrodyn 25:23–30 (in Chinese)
Wei Z, Hu C (2014) An experimental study on water entry of horizontal cylinders. J Mar Sci Technol Jpn 19:338–350
Wei Z, Hu C (2015) Experimental study on water entry of circular cylinders with inclined angles. J Mar Sci Technol Jpn 20:722–738
Yousefnezhad R, Zeraatgar H (2014) A parametric study on water-entry of a twin wedge by boundary element method. J Mar Sci Technol 19:314–326
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Project Number of 51609115 and 11702173, Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Project Number of 30918012201 and 30917012101, Key Laboratory Fund under Project Number of 614260403040317 and 614260403041803, and Open Fund of State Key Laboratory of Ocean Engineering under Project Number of 1818.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yun, H., Lyu, X. & Wei, Z. Experimental study on oblique water entry of two tandem spheres with collision effect. J Vis 23, 49–59 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-019-00602-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-019-00602-4