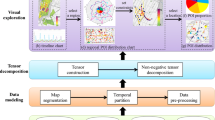
Abstract
A city contains a variety of different urban functions with referring to the purpose of land use to support the diverse needs of urban residents, such as residence, working and recreation. Exploring urban functional zones is a critical task, which provides valuable applications for business site selection, transportation management and urban planning. It is well known that location information and human mobility semantics both are significant factors for identifying urban functional zones, just considering one factor is not effective. However, most of existing techniques capture the transformation of functional zones and interpret the results based solely on location or mobility semantics, and lack the capacity to deal with the multifaceted features of urban data. To tackle these problems, in this paper, we propose an interactive visual analytics system for effectively exploring urban functional zones based on spatio-temporal OD data and Points of Interest data. We first adaptively partition the territory into region units based on adaptive blue noise sampling method, extract POI feature matrix (location information) as a prior knowledge, model multidimensional spatio-temporal OD data as a tensor for addressing multifaceted features and propose an augment tensor-based algorithm that enables users to simultaneously combine mobility semantics and inherent location information for identifying functional zones. In addition, we design a set of visual encodings to better understand and interpret the results in a visual and intuitive manner. This system has been demonstrated using two case studies with a real-world dataset of HangZhou city and domain-expert interviews.
Graphic Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrienko N, Adrienko G (2011) Spatial generalization and aggregation of massive movement data. IEEE Trans Visual Comput Graph 17(2):205–219
Blei DM, Ng AY, Jordan MI (2003) Latent Dirichlet allocation. J Mach Learn Res 3:993–1022
Bridson R (2007) Fast Poisson disk sampling in arbitrary dimensions, p 22
Cai L, Jun X, Liu J, Ma T, Pei T, Zhou C (2019) Sensing multiple semantics of urban space from crowdsourcing positioning data. Cities 93:31–42
Cao N, Lin C, Qiuhan Zhu Y-R, Lin XT, Wen X (2018) Voila: visual anomaly detection and monitoring with streaming spatiotemporal data. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 24(1):23–33
Carroll JD, Chang J-J (1970) Analysis of individual differences in multidimensional scaling via an N-way generalization of Eckart–Young decomposition. Psychometrika 35(3):283–319
Chen W, Huang Z, Feiran W, Zhu M, Guan H, Maciejewski R (2018) VAUD: a visual analysis approach for exploring spatio-temporal urban data. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 24(9):2636–2648
Cichocki A, Zdunek R, Phan AH, Amari SI (2009) Nonnegative matrix and tensor factorizations: applications to exploratory multi-way data analysis and blind source separation. Wiley, Hoboken
Deng JS, Wang K, Hong Y, Qi JG (2009) Spatio-temporal dynamics and evolution of land use change and landscape pattern in response to rapid urbanization. Landsc Urban Plan 92(3–4):187–198
Deng Z, Weng D, Chen J, Liu R, Wang Z, Bao J, Zheng Y, Wu Y (2020) Airvis: visual analytics of air pollution propagation. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 26:800–810
Di Lorenzo G, Sbodio M, Calabrese F, Berlingerio M, Pinelli F, Nair R (2016) Allaboard: visual exploration of cellphone mobility data to optimise public transport. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 22(2):1036–1050
Ferreira N, Poco J, Vo HT, Freire J, Silva CT (2013) Visual exploration of big spatio-temporal urban data: a study of New York city taxi trips. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 19(12):2149–2158
Gao S, Janowicz K, Couclelis H (2017) Extracting urban functional regions from points of interest and human activities on location-based social networks. Trans GIS 21:446–467
Harshman RA et al (1970) Foundations of the PARAFAC procedure: models and conditions for an ”explanatory” multimodal factor analysis, pp. 1–84
Hitchcock FL (1927) The expression of a tensor or a polyadic as a sum of products. J Math Phys 6:164–189
Jolliffe IT (1986) Principal component analysis. Springer-Verlag, New York
Karlsson C (2007) Clusters, functional regions and cluster policies. JIBS and CESIS Electronic Working Paper Series (84), 03
Kim Y-D, Choi S (2007) Nonnegative tucker decomposition. In: 2007 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1–8. IEEE
Klema V, Laub AJ (1980) The singular value decomposition: its computation and some applications. IEEE Trans Autom Control 25(2):164–176
Kruskal JB (1964) Multidimensional scaling by optimizing goodness of fit to a nonmetric hypothesis. Psychometrika 29(1):1–27
Lee DD, Seung HS (1999) Learning the parts of objects by non-negative matrix factorization. Nature 401(6755):788–791
Lee DD, Seung HS (2000) Algorithms for non-negative matrix factorization, pp 556–562
Levin J (1965) Three-mode factor analysis. Psychol Bull 64(6):442–452
Liu D, Weng D, Li Y, Jie Bao Yu, Zheng HQ, Yingcai W (2017) Smartadp: visual analytics of large-scale taxi trajectories for selecting billboard locations. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 23(1):1–10
Liu D, Panpan X, Ren L (2019a) TPFlow: progressive partition and multidimensional pattern extraction for large-scale spatio-temporal data analysis. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 25(1):1–11
Liu L, Zhang H, Liu J, Man J (2019b) Visual analysis of traffic data via spatio-temporal graphs and interactive topic modeling. J Vis 22(1):141–160
Lv P, Zhang Z, Li C, Guo Y, Zhou B, Mingliang X (2019) Crowd behavior evolution with emotional contagion in political rallies. IEEE Trans Comput Soc Syst 6(2):377–386
Mingliang X, Ge Z, Jiang X, Cui G, Lv P, Zhou B, Changsheng X (2019) Depth information guided crowd counting for complex crowd scenes. Pattern Recogn Lett 125:563–569
Salton G, Yang C (1973) On the specification of term values in automatic indexing. J Doc 29(4):351–372
Salton G, Yang CS, Yu CT (1975) A theory of term importance in automatic text analysis. J Am Soc Inf Sci 26(1):33–44
Seto KC, Fragkias M (2005) Quantifying spatiotemporal patterns of urban land-use change in four cities of china with time series landscape metrics. Landsc Ecol 20(7):871–888
Sun L, Axhausen KW (2016) Understanding urban mobility patterns with a probabilistic tensor factorization framework. Transp Res Part B-Methodol 91:511–524
Tucker LR (1963) Implications of factor analysis of three-way matrices for measurement of change. Probl Meas Change 15:122–137
Tucker LR (1966) Some mathematical notes on three-mode factor analysis. Psychometrika 31(3):279–311
Tucker LR et al (1964) The extension of factor analysis to three-dimensional matrices. In: Frederiksen N, Gulliksen H (eds) Contributions to mathematical psychology. Holt, Rinehart & Winston, New York, p 110119
Van Der Maaten L, Hinton GE (2008) Visualizing data using T-SNE. J Mach Learn Res 9:2579–2605
Vatsavai RR, Bright E, Varun C, Budhendra B, Cheriyadat A, Grasser J (2011) Machine learning approaches for high-resolution urban land cover classification: a comparative study. In: Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on computing for geospatial research & applications, p 11. ACM
Von Landesberger T, Brodkorb F, Roskosch P, Andrienko N, Andrienko G, Kerren A (2016) Mobilitygraphs: visual analysis of mass mobility dynamics via spatio-temporal graphs and clustering. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 22(1):11–20
Wang Y, Tung HY, Smola AJ, Anandkumar A (2015) Fast and guaranteed tensor decomposition via sketching, pp 991–999
Wang H, Mingliang X, Zhu F, Deng Z, Li Y, Zhou B (2018) Shadow traffic: a unified model for abnormal traffic behavior simulation. Comput Graph 70:235–241
Wu W, Zheng Y, Cao N, Zeng H, Ni B, Qu H, Ni LM (2017) MobiSeg: interactive region segmentation using heterogeneous mobility data. In: 2017 IEEE Pacific visualization symposium (PacificVis), pp 91–100. IEEE
Xu M, Wu Y, Ye Y, Farkas I, Jiang H, Deng Z (2015) Collective crowd formation transform with mutual information-based runtime feedback. Comput Graph Forum 34(1):60–73
Xu M, Li C, Lv P, Lin N, Hou R, Zhou B (2017) An efficient method of crowd aggregation computation in public areas. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 28(10):2814–2825
Yao Z, Fu Y, Liu B, Hu W, Xiong H (2018) Representing urban functions through zone embedding with human mobility patterns. In: IJCAI, pp 3919–3925
Yingcai W, Chen Z, Sun G, Xie X, Cao N, Liu S, Cui W (2018) StreamExplorer: a multi-stage system for visually exploring events in social streams. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 24(10):2758–2772
Yuan J, Zheng Y, Xie X (2012) Discovering regions of different functions in a city using human mobility and POIs, pp 186–194
Yuan NJ, Zheng Y, Xie X, Wang Y, Zheng K, Xiong H (2015) Discovering urban functional zones using latent activity trajectories. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 27(3):712–725
Zhou Z, Jiajun Yu, Guo Z, Liu Y (2018) Visual exploration of urban functions via spatio-temporal taxi OD data. J Vis Lang Comput 48:169–177
Zhu M, Chen W, Xia J, Ma Y, Zhang Y, Luo Y, Huang Z, Liu L (2019) Location2vec: a situation-aware representation for visual exploration of urban locations. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 20(10):3981–3990
Acknowledgements
The authors thank anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments. This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1909204) and the key fund of Hunan provincial education department (18A001). Wei Chen is Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (61772456, U1609217).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Zhang, H., Liu, J. et al. Visual exploration of urban functional zones based on augmented nonnegative tensor factorization. J Vis 24, 331–347 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-020-00713-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-020-00713-3