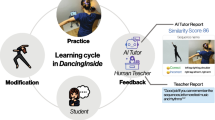
Abstract
In online cheer and dance education, teacher needs to evaluate students’ performance manually based on their uploaded training videos. However, conventional training evaluation models suffer from the problems of strong subjection, low efficiency, low accuracy, and fuzzy training paths. To address these problems, we closely collaborate with domain experts and characterize requirements to design a comprehensive visualization system DanceVis, which has the characteristics of objective evaluation, fine-grained analysis, high efficiency, high accuracy and clear training paths, so as to track the dynamic changes of groups and individuals from coarse-to-fine granularity, the global-to-local dimension, and the time dimension. In terms of dimensional analysis, we divide the overall cheerleading dance performance of one student into nine dimensions, and these scores are calculated to a visual quantitative score that can replace the expert score. Simultaneously, we track the individual performance change through the dimension scores of in-class and after-class. In terms of group analysis, a nonlinear dimensionality reduction and clustering method is proposed to classify trainees and further build group portraits which help propose training paths for each group. In terms of individual analysis, we use human pose estimation method to automatically analyze videos, which improves the analysis efficiency, and obtains individual global performance curves. We invite experts to conduct with DanceVis, and demonstrate the usability of the system through expert interviews. The results show that DanceVis can fully make up for the shortcomings of existing training evaluation models, and greatly improve the efficiency and accuracy of online cheer and dance training.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrienko G, Andrienko N, Budziak G, Dykes J, Fuchs G, von Landesberger T, Weber H (2017) Visual analysis of pressure in football. Data Min Knowl Discov 31(6):1793–1839
Cao Z, Hidalgo G, Simon T, Wei S-E, Sheikh Y (2019) Openpose: realtime multi-person 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 43(1):172–186
Cava R, Freitas CDS (2013) Glyphs in matrix representation of graphs for displaying soccer games results. In: The 1st workshop on sports data visualization, vol 13. IEEE, p 15
Chan C, Ginosar S, Zhou T, Efros AA (2019) Everybody dance now. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp 5933–5942
Chen Q, Chen Y, Liu D, Shi C, Wu Y, Qu H (2015) Peakvizor: visual analytics of peaks in video clickstreams from massive open online courses. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 22(10):2315–2330
Chen Q, Yue X, Plantaz X, Chen Y, Shi C, Pong T-C, Qu H (2018) Viseq: visual analytics of learning sequence in massive open online courses. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 26(3):1622–1636
Chen Y, Shen C, Wei X-S, Liu L, Yang J (2017) Adversarial posenet: a structure-aware convolutional network for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 1212–1221
Guo H, Zou S, Lai C, Zhang H (2021) Phycovis: a visual analytic tool of physical coordination for cheer and dance training. Comput Anim Virtual Worlds 32(1):e1975
He K, Gkioxari G, Dollár P, Girshick R (2017) Mask R-CNN. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 2961–2969
International Cheer Union official website. https://www.cheerunion.org/
Luo Y, Ren J, Wang Z, Sun W, Pan J, Liu J, Pang J, Lin L (2018) LSTM pose machines. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 5207–5215
Newell A, Huang Z, Deng J (2016) Associative embedding: end-to-end learning for joint detection and grouping. arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.05424
Newell A, Yang K, Deng J (2016) Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 483–499
Peng X, Tang Z, Yang F, Feris RS, Metaxas D (2018) Jointly optimize data augmentation and network training: adversarial data augmentation in human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2226–2234
Raaj Y, Idrees H, Hidalgo G, Sheikh Y (2019) Efficient online multi-person 2d pose tracking with recurrent spatio-temporal affinity fields. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 4620–4628
Ryoo M, Kim N, Park K (2018) Visual analysis of soccer players and a team. Multimedia Tools and Applications 77(12):15603–15623
Sacha D, Stein M, Schreck T, Keim DA, Deussen O et al (2014) Feature-driven visual analytics of soccer data. In: IEEE conference on visual analytics science and technology (VAST). IEEE, pp 13–22
Shi C, Fu S, Chen Q, Qu H (2015) Vismooc: visualizing video clickstream data from massive open online courses. In: IEEE Pacific visualization symposium (PacificVis). IEEE, pp 159–166
Stein M, Janetzko H, Lamprecht A, Seebacher D, Schreck T, Keim D, Grossniklaus M (2016) From game events to team tactics: visual analysis of dangerous situations in multi-match data. In: 1st International conference on technology and innovation in sports, health and wellbeing (TISHW). IEEE, pp 1–9
Sun K, Xiao B, Liu D, Wang J (2019) Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 5693–5703
Turchet P (2013) LE LANGAGE UNIVERSEL DU CORP
Vuillemot R, Perin C (2015) Investigating the direct manipulation of ranking tables for time navigation. In: CHI ’15-33rd Annual ACM conference on human factors in computing systems. ACM, Seoul, pp 2703–2706. Best paper honorable mention. https://doi.org/10.1145/2702123.2702237
Wei S-E, Ramakrishna V, Kanade T, Sheikh Y (2016) Convolutional pose machines. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 4724–4732
Wongsuphasawat K, Gotz D (2012) Exploring flow, factors, and outcomes of temporal event sequences with the outflow visualization. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 18(12):2659–2668
Wu Y, Xie X, Wang J, Deng D, Liang H, Zhang H, Cheng S, Chen W (2018) Forvizor: visualizing spatio-temporal team formations in soccer. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 25(1):65–75
Xiao B, Wu H, Wei Y (2018) Simple baselines for human pose estimation and tracking. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 466–481
Acknowledgements
This paper was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1909204).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, H., Zou, S., Xu, Y. et al. DanceVis: toward better understanding of online cheer and dance training. J Vis 25, 159–174 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-021-00783-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-021-00783-x