Abstract
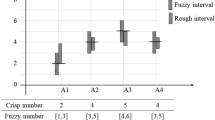
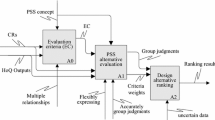
In the last 20 years, the Kansei engineering system (KES) has employed a variety of mathematical models to overcome design problems in consumer products. However, the increasing globalization of consumer markets has made the acquisition of market knowledge more competitive than ever; therefore, a strong focus has recently been placed on developing the means to capture consumer affective responses and obtain comprehensive data related to preferences in product exterior features. Rough set theory (RST) is a rule-based knowledge acquisition method capable of targeting imprecise, non-linear human perceptions. Surprisingly, little research has been conducted into the development of KES combined with RST. Therefore, this study used a systemic approach to perform a visual design of a toothbrush by combining the Kansei engineering and RST for exploring the relationship between form and color during a product evaluation. We also provide a point-by-point comparison of KES with RST to provide a reference for the merging of these two techniques. These findings will be of considerable interest to marketing researchers, artists, product designers, and color scientists as well as manufacturers and research centers.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akcay O, Sable P, Dalgin MH (2012) The importance of color in product choice among young Hispanic, Caucasian, and African-American groups in the USA. Int J Bus Soc Sci 3:1–6
Bloch PH (1995) Seeking the ideal form: product design and consumer response. J Mark 59:16–29
Choo S, Kim Y (2003) Effect of color on fashion fabric image. Color Res Appl 28:221–226
Coates D (2003) Watches tell more than time. Mc. Graw Hill, New York
Craven MW, Shavlik JW (1997) Using neural networks for data mining. Future Gener Comput Syst 13:211–229
Demirbilek O, Sener B (2003) Product design, semantics and emotional response. Ergonomics 46:1346–1360
Han SH, Yun MH, Kim KJ, Kwahk J (2000) Evaluation of product usability: development and validation of usability dimensions and design elements based on empirical models. Int J Ind Ergon 26:477–488
Hotta H, Hagiwara M (2006) A fuzzy rule based personal Kansei modeling system 2006. In: IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems Sheraton Vancouver Wall Centre Hotel Vancouver, BC, Canada
Hsiao SW, Huang HC (2002) A neural network based approach for product form design. Des Stud 23:67–84
Hsiao SW, Tsai HC (2005) Applying a hybrid approach based on fuzzy neural network and genetic algorithm to product form design. Int J Ind Ergon 35:411–428
Hsu SH, Chuang MC, Chang CC (2000) A semantic differential study of designers’ and users’ product form perception. Int J Ind Ergon 25:375–391
Inuiguchi M, Miyajima T (2007) Rough set based rule induction from two decision tables. Eur J Oper Res 181:1540–1553
Jindo T, Hirasago K, Nagamachi M (1995) Development of a design support system for office chairs using 3-D graphics. Int J Ind Ergon 15:49–62
Jiro K (1986) KJ method. Chuokoron-Sha, Tokyo
Jones JC (1992) Design methods. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York
Kim HS, Cho SB (2000) Application of interactive genetic algorithm to fashion design. Eng Appl Artif Intell 13:635–644
Kwahk J, Han SH (2002) A methodology for evaluating the usability of audiovisual consumer electronic products. Appl Ergon 33:419–431
Mak B, Munakata T (2002) Rule extraction from expert heuristics: a comparative study of rough sets with neural networks and ID3. Eur J Oper Res 136:212–229
Nagamachi M (1995) Kansei Engineering: a new ergonomic consumer-oriented technology for product development. Int J Ind Ergon 15:3–11
Nayatani Y, Komatsubara H (2005) Relationships among chromatic tone, perceived lightness, and degree of vividness. Color Res Appl 30:221–234
Øhrn A (1999) Discernibility and Rough Sets in Medicine: Tools and Applications. Norwegian University of Science and Technology
Park J, Han SH (2004) A fuzzy rule-based approach to modeling affective user satisfaction towards office chair design. Int J Ind Ergon 34:31–47
Pawar KS, Driva H (1999) Performance measurement for product design and development in a manufacturing environment. Int J Prod Econ 60–61:61–68
Pawlak Z, Skowron A (2007) Rudiments of rough sets. Inf Sci 177:3–27
Schütte S, Eklund J (2005) Design of rocker switches for work-vehicles—an application of Kansei Engineering. Appl Ergon 36:557–567
Shieh MD, Hsu FC (2013) Using FCM clustering for consumer segmentation in Kansei engineering system. Int J Digit Content Technol Appl 7:563–571
Shieh MD, Yang CC (2008) Classification model for product form design using fuzzy support vector machines. Comput Ind Eng 55:150–164
Shimizu Y, Jindo T (1995) A fuzzy logic analysis method for evaluating human sensitivities. Int J Ind Ergon 15:39–47
Singh S (2006) Impact of color on marketing. Manag Decis 44:783–789
Tanoue C, Ishizaka K, Nagamachi M (1997) Kansei Engineering: a study on perception of vehicle interior image. Int J Ind Ergon 19:115–128
Tsai JL, Knutson B, Fung HH (2006) Cultural variation in affect valuation. J Pers Soc Psychol 90:288–307
Tsuchiya T, Maeda T, Matsubara Y, Nagamachi M (1996) A fuzzy rule induction method using genetic algorithm. Int J Ind Ergon 18:135–145
Wallace DR (1991) A computer model of aesthetic industrial design. Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Yang CC (2011) Constructing a hybrid Kansei engineering system based on multiple affective responses: application to product form design. Comput Ind Eng 60:760–768
Yang SM, Nagamachi M, Lee SY (1999) Rule-based inference model for the Kansei Engineering System. Int J Ind Ergon 24:459–471
Yang BS, Lim DS, Tan ACC (2005) VIBEX: an expert system for vibration fault diagnosis of rotating machinery using decision tree and decision table. Expert Syst Appl 28:735–742
Yang CC, Shieh MD, Chen KH, Lin PJ (2011a) Product form feature selection for mobile phone design using LS-SVR and ARD. J Converg Inf Technol 6:138–150
Yang CC, Sun CC, Lin PJ, Tsai CC (2011b) A general framework for Kansei engineering system. Int J Digit Content Technol Appl 5:173–180
Yun MH, Han SH, Hong SW, Kim J (2003) Incorporating user satisfaction into the look-and-feel of mobile phone design. Ergonomics 46:1423–1440
Zhai LY, Khoo LP, Zhong ZW (2009) A dominance-based rough set approach to Kansei Engineering in product development. Expert Syst Appl 36:393–402
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shieh, MD., Yeh, YE. & Huang, CL. Eliciting design knowledge from affective responses using rough sets and Kansei engineering system. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 7, 107–120 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-015-0307-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-015-0307-6