Abstract
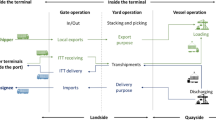
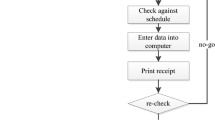
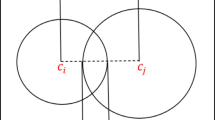
Railway container yard is an important node in container transportation system, plays a very important role in the global logistics integration, improve the railway container freight yard handling equipment operation scheduling level, speed up the internal connection efficiency, reasonable co-ordination of container truck railway container freight yard handling equipment resources configuration can significantly improve the overall efficiency of railway container freight yard, reduce comprehensive operation cost. Study on railway container freight yard yard crane scheduling problem, the problem is to train a known time and external conditions of each container truck into time a container under the proposed “dig box coefficient” concept for decision making for yard crane storing containers, container sequence of the target position, work process, according to the problem, established the mathematical model, the design of multi stage genetic algorithm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bortfeldt, Forster F (2012a) A tree search procedure for the container pre-marshalling problem. Eur J Oper Res 217(3):532–541
Boysen, Roodbergen KJ (2014) Scheduling of container storage and retrieval. Oper Res 57(2):456–467
Carlo, Vis J (2014) Storage yard operations in container terminals lite overview. Eur J Oper Res 235(2):412–430
Caserta, Schwarze S (2011) A new binary description of the blocks relocation problem and benefits in a look ahead heuristic. Lect Notes Comput Sci 5482(1):38–49
Chao, Hsu NY (2010) An optimization model for the container pre-marshalling problem. Comput Oper Res 34(11):3296–3314
Chen, Lu Z (2012) The storage location assignment problem for outbound containers in a maritime terminal. Int J Prod Econ 135(1):73–80
Forster, Bortfeldt A (2012b) A tree search procedure for the container relocation problem. Comput Oper Res 39(2):299–309
Hakan Akyuz, Lee CY (2014) A mathematical formulation and efficient heuristics for the dynamic container relocation problem. Nav Res Logist 61(2):101–108
Hong, Fliedner M (2017) A survey on container processing in railway yards. Transp Sci 47(3):313–330
Huang, Lin TH (2012) Heuristic algorithms for container pre-marshalling problems. Comput Ind Eng 62(1):14–21
Imai, Sasaki K (2016) Multi-objective simulations stowage and load planning for a container ship with container in yard stacks. Eur J Oper Res 172:374–390
Jang, Kim SW (2013) The optimization of mixed block stacking requiring locations. Int J Prod Econ 143(2):256–262
Jovanovic, Vop S (2014) A chain heuristic for the blocks relocation problem. Comput Ind Eng 75(1):79–86
Kang, Ryu K (2016) Deriving stacking strategies for export containers with uncertain weight information. J Intell Manuf 17(4):399–410
Kim, Bae JW (2016) Re-marshaling export containers in port container terminals. Comput Ind Eng 35(4):656–659
Kim, Hong GP (2016) A heuristic rule for relocation blocks. Comput Oper Res 33(4):940–954
Lee, Chao SL (2015) A neighborhood search heuristic for pre-marshalling export containers. Eur J Oper Res 196(3):469–476
Lee, Zhang YJ (2013) A heuristic for retrieving containers from a yard. Comput Oper Res 37(6):1140–1148
Lehnfeld, Knust (2014) Loading and unloading and premarshalling of stacks in storage areas survey and classification. Eur J Oper Res 239(2):297–312
Meisel, Wichmann M (2011) Container sequencing for quay cranes with internal reshuffles. OR Spectr 32:570–592
Ng, Mak K (2015) Yard crane scheduling in port container terminals. Appl Math Model 30:264–277
Petering, Hussein MI (2013) A new mixed integer program and extended look-ahead heuristic algorithm for the block relocation problem. Eur J Oper Res 231(1):121–131
Vis, Koster (2013) Transshipment of containers at a container terminal an overview. Eur J Oper Res 147(1):1–15
Zhu, Qin H (2012) Iterative deepening A algorithms for the container relocation problem. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng 9(4):711–724
Funding
The work described in this paper was supported by Grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 71501190 and 71771218).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lei, D., Zhang, P., Zhang, Y. et al. Research on optimization of multi stage yard crane scheduling based on genetic algorithm. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 11, 483–494 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-0918-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-0918-9