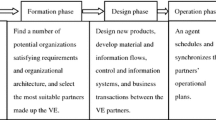
Abstract
How to select satisfactory partners is essential to virtual enterprise and has attracted lots of attention from practitioners and researchers. In many real situations, preference relation is an important structure in representing decision makers’ preference information during the partner selection process. As a special case of neutrosophic sets, interval neutrosophic set (INS) can be used to handle uncertain and inconsistent information in decision making. To show the application, this paper introduces the concept of interval neutrosophic preference relations (INPRs) using interval neutrosophic numbers to denote the true, indeterminacy and false judgments independently. Then, a multiplicative consistency concept for INPRs is proposed to guarantee the ranking accurately. After that, several multiplicative consistency-based nonlinear programming models to derive multiplicatively consistent INPRs and to determine missing values in incomplete INPRs are constructed, respectively. To broaden the application of INPRs, a consensus index based on the distance measure is defined. Meanwhile, an algorithm to group decision making based on INPRs is developed, which can be applied to address incomplete and inconsistent INPRs. Finally, the feasibility and practicability of the developed approach is manifested through an illustrative example, and comparison analysis is performed with several related previous methods about decision making with INSs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansari AQ, Biswas R, Aggarwal S (2011) Proposal for applicability of neutrosophic set theory in medical AI. Int J Comput Appl 27(5):5–11
Arora M, Biswas R, Pandey US (2011) Neutrosophic relational database decomposition. Int J Adv Comput Sci Appl 2(8):121–125
Atanassov KT (1986) Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 20(1):87–96
Atanassov KT, Gargov G (1989) Interval valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 31(3):343–349
Bausys R, Zavadskas EK (2017) Multicriteria decision making approach by VIKOR under interval neutrosophic set environment. Econ Comput Econ Cybern Stud Res 49(4):33–48
Chen JQ, Ye J, Du SG (2017) Vector similarity measures between refined simplified neutrosophic sets and their multiple attribute decision-making method. Symmetry 9(153):1–13
Chi PP, Liu PD (2013) An extended TOPSIS method for the multiple attribute decision making problems based on interval neutrosophic set. Neutrosophic Sets Syst 1:63–70
Dey PP, Pramanik S, Giri BC (2015) An extended grey relational analysis based interval neutrosophic multi attribute decision making for weaver selection. J N Theory 9:82–93
Dong JY, Wan SP (2016) Virtual enterprise partner selection integrating LINMAP and TOPSIS. J Oper Res Soc 67(10):1288–1308
Guo YH, Şengur A (2014) A novel image edge detection algorithm based on neutrosophic set. Comput Electr Eng 40(8):3–25
Guo YH, Cheng HD, Zhang Y (2009) A new neutrosophic approach to image denoising. N Math Nat Comput 5(3):653–662
Ip WH, Huang M, Yung KL, Wang DW (2003) Genetic algorithm solution for a risk-based partner selection problem in a virtual enterprise. Comput Oper Res 30(2):213–231
Li YY, Wang JQ, Wang TL (2018) A linguistic neutrosophic multi-criteria group decision-making approach with EDAS method. Arab J Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3487-5
Liang RX, Wang JQ, Zhang HY (2018) A multi-criteria decision-making method based on single-valued trapezoidal neutrosophic preference relations with complete weight information. Neural Comput Appl 30(11):3383–3398
Liu PD, Li HG (2017) Interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy power Bonferroni aggregation operators and their application to group decision making. Cogn Comput 9(4):494–512
Liu PD, Chu YC, Li YW, Chen YB (2014) Some generalized neutrosophic number Hamacher aggregation operators and their application to group decision making. Int J Fuzzy Syst 16(2):242–255
Luo SZ, Zhang HY, Wang JQ, Li L (2018) Group decision-making approach for evaluating the sustainability of constructed wetlands with probabilistic linguistic preference relations. J Oper Res Soc. https://doi.org/10.1080/01605682.2018.1510806
Meng FY, Chen XH, Tan CQ (2016) Cooperative fuzzy games with interval characteristic functions. Oper Res 16(1):1–24
Meng FY, An QX, Tan CQ, Chen XH (2017a) An approach for group decision making with interval fuzzy preference relations based on additive consistency and consensus analysis. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 47(8):2069–2082
Meng FY, Tan CQ, Chen XH (2017b) Multiplicative consistency analysis for interval fuzzy preference relations: a comparative study. Omega 68:17–38
Meng FY, Tang J, An QX, Chen XH (2018a) Decision making with intuitionistic linguistic preference relations. Int Trans Oper Res. https://doi.org/10.1111/itor.12383
Meng FY, Tang J, Xu ZS (2018b) Exploiting the priority weights from interval linguistic fuzzy preference relations. Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-017-2878-y
Moore RE (1996) Interval analysis. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Orlovsky SA (1978) Decision-making with a fuzzy preference relation. Fuzzy Sets Syst 1(3):155–167
Peng JJ, Wang JQ, Wang J, Zhang HY, Chen XH (2015) Multi-valued neutrosophic sets and power aggregation operators with their applications in multi-criteria group decision-making problems. Int J Comput Intell Syst 8(2):345–363
Pramanik S, Mondal K (2015) Interval neutrosophic multi-attribute decision making based on grey relational analysis. Neutrosophic Sets Syst 9:13–22
Pramanik S, Biswas P, Giri BC (2017) Hybrid vector similarity measures and their applications to multi-attribute decision making under neutrosophic environment. Neural Comput Appl 28(5):1163–1176
Saaty TL (1980) The analytic hierarchy process. McGraw-Hall, New York
Şahin R (2017) Cross-entropy measure on interval neutrosophic sets and its applications in multicriteria decision making. Neural Comput Appl 28(5):1177–1187
Şahin R, Karabacak M (2014) A multi attribute decision making method based on inclusion measure for interval neutrosophic sets. Int J Adv Eng Sci Appl Math 2(2):13–15
Şahin R, Liu P (2016) Maximizing deviation method for neutrosophic multiple attribute decision making with incomplete weight information. Neural Comput Appl 27(7):2017–2029
Salama AA, Smarandache F, Kroumov V (2014) Neutrosophic crisp sets and neutrosophic crisp topological spaces. Neutrosophic Sets Syst 32:24–30
Smarandache F (1999) A unifying field in logics: neutrosophic logic. American Research Press, Rehoboth
Sun HX, Yang HX, Wu JZ, Yao OY (2015) Interval neutrosophic numbers choquet integral operator for multi-criteria decision making. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 28(6):2443–2455
Tang J, Meng FY (2018a) Decision making with multiplicative hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-3227-x
Tang J, Meng FY (2018b) Ranking objects from group decision making with interval-valued hesitant fuzzy preference relations in view of additive consistency and consensus. Knowl Based Syst. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2018.09.017
Tian ZP, Zhang HY, Wang JQ, Chen XH (2015) Multi-criteria decision-making method based on a cross-entropy with interval neutrosophic sets. Int J Syst Sci 47(15):3598–3608
Tian ZP, Nie RX, Wang JQ, Zhang HY (2018a) Signed distance-based ORESTE for multi-criteria group decision-making with multi-granular unbalanced hesitant fuzzy linguistic information. Expert Syst. https://doi.org/10.1111/exsy.12350
Tian ZP, Nie RX, Wang JQ, Zhang HY (2018b) A two-fold feedback mechanism to support consensus-reaching in social network group decision-making. Knowl Based Syst. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2018.09.030
Turksen I (1986) Interval valued fuzzy sets based on normal forms. Fuzzy Sets Syst 20(2):191–210
Wang YM, Chin KS (2008) A linear goal programming priority method for fuzzy analytic hierarchy process and its applications in new product screening. Int J Approx Reason 49(2):451–465
Wang HB, Smarandache F, Zhang YQ, Sunderraman R (2005) Interval neutrosophic sets and logic: theory and applications in computing. Hexis, Phoenix
Wang YM, Elhag TMS, Hua ZS (2006) A modified fuzzy logarithmic least squares method for fuzzy analytic hierarchy process. Fuzzy Sets Syst 157(23):3055–3071
Wang HB, Smarandache F, Zhang YQ, Sunderraman R (2010) Single valued neutrosophic sets. Multispace Multistruct 4:410–413
Wang N, Meng FY, Xu YW (2018) Deriving the priority weights from multiplicative consistent single-valued neutrosophic preference relations. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3493-2
Xu ZS (2001) A practical method for priority of interval number complementary judgment matrix. Oper Res Manag Sci 10(1):16–19
Xu ZS (2004) Uncertain multiple attribute decision making: methods and applications. Tsinghua University Press, Beijing
Xu ZS (2005) On method for uncertain multiple attribute decision making problems with uncertain multiplicative preference information on alternatives. Fuzzy Optim Decis Mak 4(2):131–139
Xu ZS (2007a) Intuitionistic preference relations and their application in group decision making. Inf Sci 177(11):2363–2379
Xu ZS (2007b) Intuitionistic fuzzy aggregation operators. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 15(6):1179–1187
Xu ZS, Cai XQ (2009) Incomplete interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy preference relations. Int J Gen Syst 38(8):871–886
Xu ZS, Chen J (2007) On geometric aggregation over interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy information. Int conf Fuzzy Syst Knowl Dis 2:466–471
Xu ZS, Liao HC (2015) A survey of approaches to decision making with intuitionistic fuzzy preference relations. Knowl Based Syst 80(5):131–142
Xu ZS, Yager RR (2009) Intuitionistic and interval-valued intutionistic fuzzy preference relations and their measures of similarity for the evaluation of agreement within a group. Fuzzy Optim Decis Mak 8(2):123–139
Yao LH, Shen GQ, Wang M, Zhang GX (2008) An improved method for virtual enterprise partner selection. Inf Comput Autom 3:1177–1180
Ye F, Li YN (2009) Group multi-attribute decision model to partner selection in the formation of virtual enterprise under incomplete information. Expert Syst Appl 36(5):9350–9357
Ye F, Lin Q (2013) Partner selection in a virtual enterprise: a group multiattribute decision model with weighted possibilistic mean values. Math Probl Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/519629
Yuan RP, Meng FY, Tang J (2018) Linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy group decision making based on aggregation operators. Int J Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-018-0582-4
Yuen KKF, Lau HCW (2011) A fuzzy group analytical hierarchy process approach for software quality assurance management: Fuzzy logarithmic least squares method. Expert Syst Appl 38(8):10292–10302
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Zhang M, Zhang L, Cheng HD (2010) A neutrosophic approach to image segmentation based on watershed method. Signal Process 90(5):1510–1517
Zhang HY, Wang JQ, Chen XH (2014) Interval neutrosophic sets and their application in multicriteria decision making problems. Sci World J. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/645953
Zhang HY, Ji P, Wang JQ, Chen XH (2015) An improved weighted correlation coefficient based on integrated weight for interval neutrosophic sets and its application in multi-criteria decision-making. Int J Comput Intell Syst 8(6):1027–1043
Zhang HY, Wang JQ, Chen XH (2016) An outranking approach for multi-criteria decision-making problems with interval-valued neutrosophic sets. Neural Comput Appl 27(3):615–627
Zhang YN, Tang J, Meng FY (2018a) Programming model-based method for ranking objects from decision making with interval-valued hesitant fuzzy preference relations. Appl Intell. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-018-1292-1
Zhang XY, Wang XK, Yu SM, Wang JQ, Wang TL (2018b) Location selection of offshore wind power station by consensus decision framework using picture fuzzy modeling. J Clean Prod 202:980–992
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 71571192, 71601049, 71874112, and 71671188), the Innovation-Driven Project of Central South University (no. 2018CX039), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Central South University (no. 2018zzts094), the Major Project for National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 71790615), and the State Key Program of National Natural Science of China (no. 71431006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, F., Wang, N. & Xu, Y. Interval neutrosophic preference relations and their application in virtual enterprise partner selection. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 10, 5007–5036 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01178-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01178-5